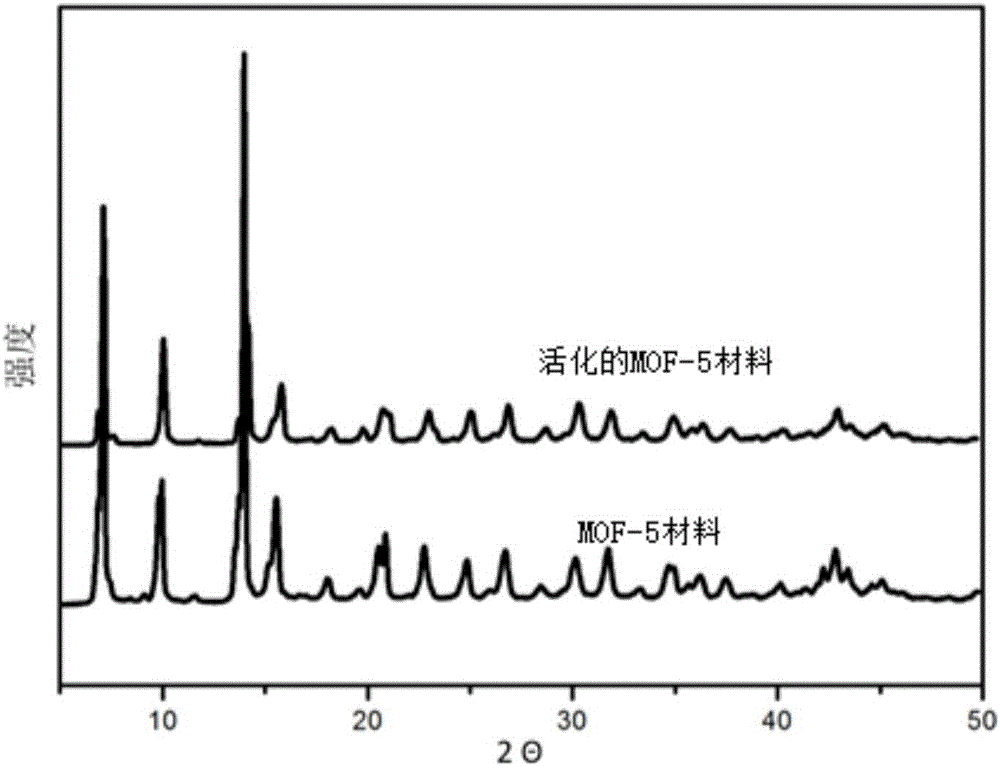
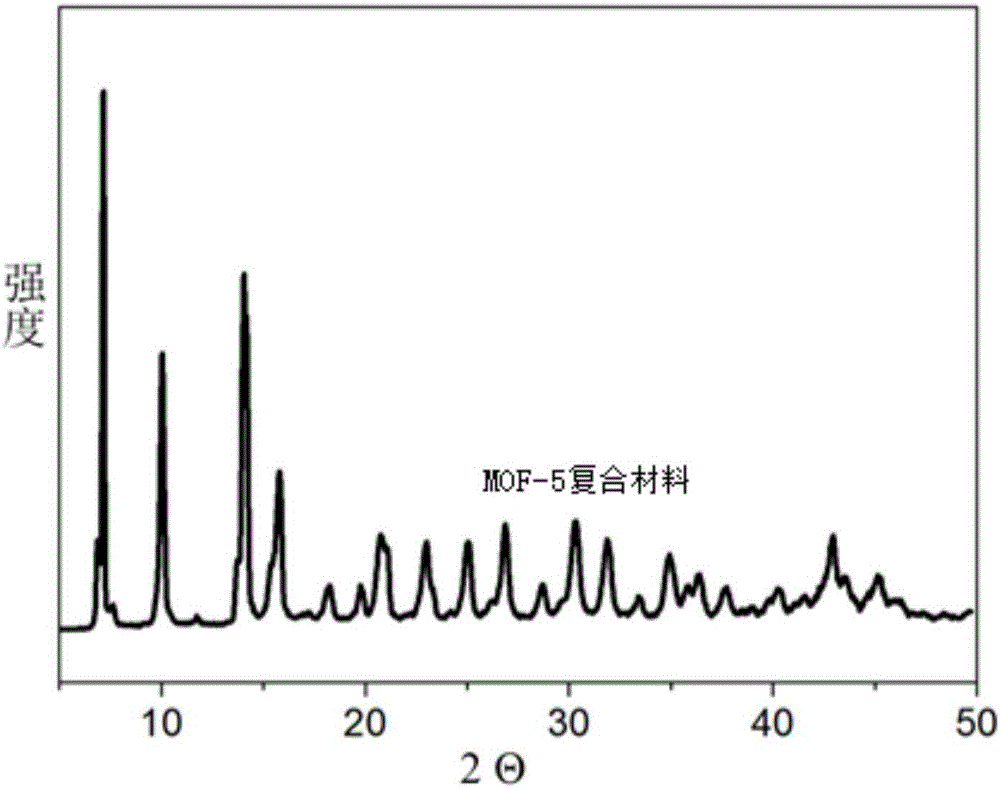
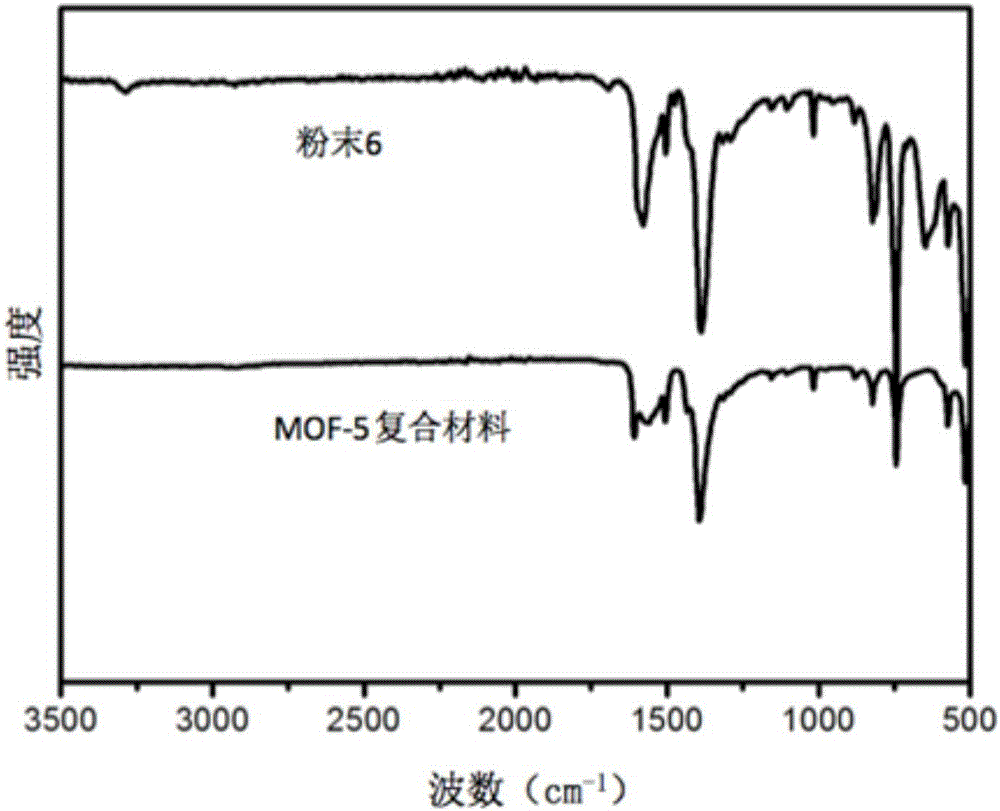
Method for improving CO2 adsorption of MOF (metal-organic framework) material
A metal-organic framework and carbon dioxide technology, applied in the field of inorganic-organic hybrid preparation, can solve the problems of reducing carbon dioxide adsorption capacity and selectivity, reducing carbon dioxide adsorption and selectivity, and skeleton structure collapse, so as to improve hydrophobicity and Effects of water stability, low raw material cost, and improved adsorption performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] A method for improving the carbon dioxide adsorption of metal-organic framework materials, the specific steps of the method are as follows:
[0065] (1) Synthesis of 1,2-bis(trimethylsilylethynyl)benzene
[0066] 0.2669g Pd (PPh 3 ) 4 and 0.0440g CuI, added to a 100mL three-neck flask, and repeated vacuuming and nitrogen filling three times. Place 15mL of triethylamine and 45mL of toluene in a conical flask to obtain a mixed solution, blow nitrogen gas, and inject the mixed solution into the three-necked flask, add 2.5400g of 1,2-diiodobenzene and 1.8905g of trimethyl Silica acetylene was added to the three-necked flask, and the reaction was stirred at 25 °C for 20 h to obtain a black product, which was filtered with suction to obtain a yellow solution, which was evaporated to dryness to obtain an oily yellow liquid; the yellow liquid was analyzed by wet column chromatography ( Petroleum ether as eluent) was separated, rotary evaporated to dryness, and light yellow o...
Embodiment 2
[0078] A method for improving the carbon dioxide adsorption of metal-organic framework materials, the specific steps of the method are as follows:
[0079] (1) Synthesis of 1,2-bis(trimethylsilylethynyl)benzene
[0080] Prepare 1,2-bis(trimethylsilylethynyl)benzene according to the method of step (1) of Example 1
[0081] The volumes of triethylamine and toluene used were 60 mL and 60 mL, respectively; 1,2-diiodobenzene, trimethylsilylacetylene, Pd(PPh 3 ) 4 The masses of , CuI were 2.5400g, 1.8905g, 0.3559g, 0.0587g respectively; the stirring temperature was 20°C, and the reaction time was 15h.
[0082] The structure of the light yellow oily liquid was characterized by NMR spectroscopy, and the corresponding data were as follows: 1 H NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ0.27(s, 18H), 7.24(q, 2H), 7.47(q, 2H), it can be seen that the light yellow oily liquid is 1,2-bis(trimethylsilylethynyl)benzene.
[0083] (2) Preparation of DEB
[0084] DEB was synthesized according to the method ...
Embodiment 3
[0093] A method for improving the carbon dioxide adsorption of metal-organic framework materials, the specific steps of the method are as follows:
[0094] (1) Synthesis of 1,2-bis(trimethylsilylethynyl)benzene
[0095] 1,2-Bis(trimethylsilylethynyl)benzene was prepared according to the method of step (1) of Example 1. The volumes of triethylamine and toluene used were 15 mL and 60 mL, respectively; 1,2-diiodobenzene, trimethylsilylacetylene, Pd(PPh 3 ) 4 , the masses of CuI were 2.5400g, 1.8905g, 0.5338g, 0.0880g respectively; the stirring temperature was 70°C and the time was 25h.
[0096] The structure of the light yellow oily liquid was characterized by NMR spectroscopy, and the corresponding data were as follows: 1 H NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ0.27(s, 18H), 7.24(q, 2H), 7.47(q, 2H), it can be seen that the light yellow oily liquid is 1,2-bis(trimethylsilylethynyl)benzene.
[0097] (2) Preparation of DEB
[0098] DEB was synthesized according to the method of step (2) o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com