Full resource utilization method of sweet potato starch processing wastewater
A technology for sweet potato starch and wastewater processing, applied in chemical instruments and methods, peptide preparation methods, peptide sources, etc., can solve the problems of a large amount of wastewater, lack of effective treatment and utilization, and high cost of sweet potato protein, reducing environmental protection loads, increasing Effect of sewage treatment load
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
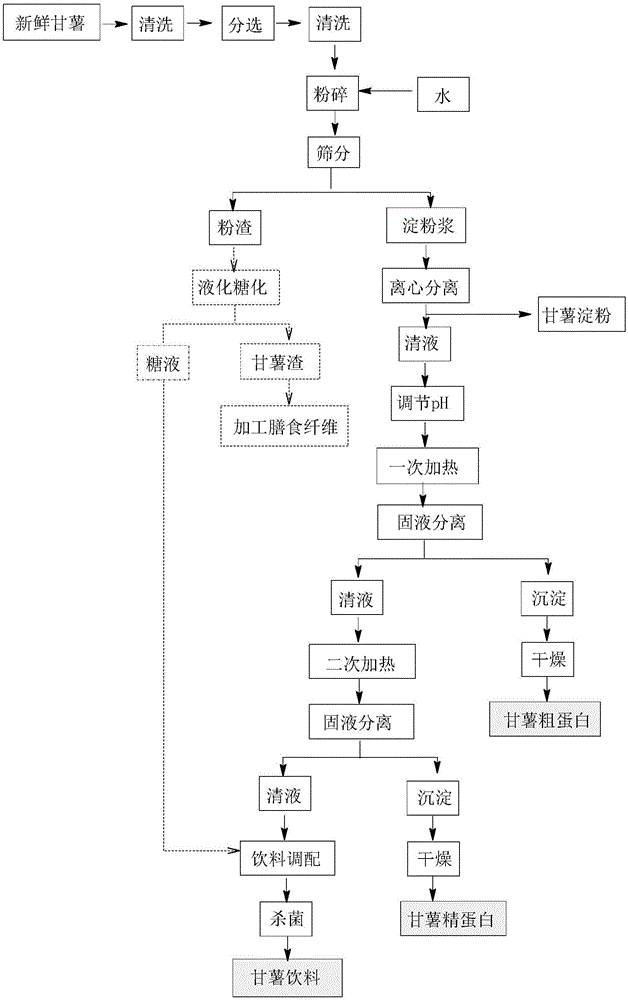
[0062] 1 sweet potato mashed
[0063] Select fresh and complete Jishu-21 sweet potatoes, after preliminary cleaning, then cut off the roots and further clean; weigh 2kg of fresh sweet potatoes that have been processed, cut them into small pieces of 1*1*1cm, add 4L of water, and use a beater Break up further, filter with 200 mesh filter cloth, wash the potato residue obtained by adding 2L of water once, filter with 200 mesh filter cloth, combine the two filtrates for starch separation, wash the potato residue with 2L of water, filter, and filtrate Can be used for the next sweet potato mash.
[0064] 2 Potato residue processing
[0065] Add water to the potato dregs after washing twice to adjust the appropriate concentration, then add an appropriate amount of medium-temperature amylase according to the amount of residual starch in the potato dregs, heat up to 88±2°C for 5 minutes, cool to 60±2°C, and adjust the pH to 4.4- 4.6. Add an appropriate amount of glucoamylase to keep ...
Embodiment 2
[0074] 1 sweet potato mashed
[0075] Select fresh and complete Jishu-21 sweet potatoes, preliminarily clean them, then cut off the roots, and clean them further; weigh 2 kg of fresh sweet potatoes that have been processed, cut them into small pieces, add 3.5 L of water, and further smash them with a beater. Filter with a 200-mesh filter cloth, wash the potato dregs with 1.5L water once, filter with a 200-mesh filter cloth, combine the two filtrates for starch separation, wash the potato dregs with 2.0L water, filter, and the filtrate can be used for the next step Once the sweet potatoes are mashed.
[0076] 2 Potato residue processing
[0077]Add water to the potato dregs after washing twice to adjust the appropriate concentration, then add an appropriate amount of medium-temperature amylase according to the amount of residual starch in the potato dregs, raise the temperature to 85±2°C, keep it warm for 10 minutes, cool down to 60±2°C, and adjust the pH to 4.4- 4.6. Add an ...
Embodiment 3
[0086] 1 sweet potato mashed
[0087] Select fresh and complete Jishu-21 sweet potatoes, after preliminary cleaning, then cut off the roots, further clean, peel off the outer skin, weigh 2kg, cut into small pieces, add 3L of water, further crush with a beater, and use a 200-mesh Filter through a filter cloth, wash the obtained potato residue with 2L of water once, filter with a 200-mesh filter cloth, and combine the two filtrates for starch separation. The potato dregs are washed with 2L of water, filtered, and the filtrate can be used for the next sweet potato beating.
[0088] 2 Potato residue processing
[0089] Add water to the potato dregs after washing twice to adjust the appropriate concentration, then add an appropriate amount of medium-temperature amylase according to the amount of residual starch in the potato dregs, raise the temperature to 88±2°C and keep it for liquefaction for 8 minutes, then cool down to 60±2°C, and adjust the pH to 4.4- 4.6. Add an appropriat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com