Method for preparing nanocellulose for efficiently adsorbing heavy metal ions from natural fallen leaves
A technology of nanocellulose and heavy metal adsorption, applied in the directions of alkali metal compounds, chemical instruments and methods, adsorption water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of low adsorption efficiency and low cost, and achieve the effect of cost saving
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
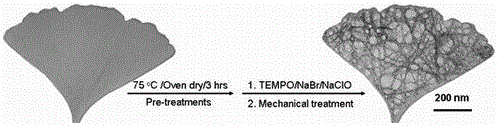
[0035] Example 1: Ginkgo fallen leaves were dried in an oven at 75 degrees Celsius for 3 hours, and ground into powder. Mix 5.0 grams of ginkgo leaf powder, 0.25 grams of TEMPO, and 1.25 grams of sodium bromide in 300 milliliters of water. Add 75 ml (10-15%) sodium hypochlorite aqueous solution, and adjust the pH value of the system to greater than 10 with sodium hydroxide aqueous solution (1M). After stirring at room temperature for 24 hours, the reaction was quenched with a small amount of ethanol. The resulting suspension was centrifuged and washed several times until neutral. The ginkgo leaf nanofiber suspension can be obtained by ultrasonic crushing with a cell pulverizer, and its concentration is determined by a weighing method. The preparation process is as figure 1 shown.
example 2
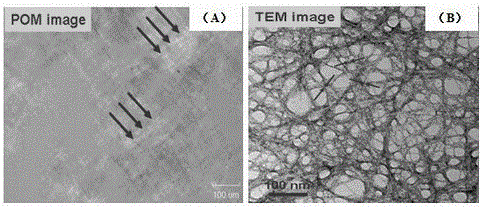
[0036] Example 2: Observe the above suspension (0.2 wt%) under a polarizing microscope, as shown in figure 2 As shown in (A), it can be seen that the ginkgo leaf nanocellulose is aggregated together and has a certain orientation. Because of its surface carboxylate (1.9 mmol per gram), it can be stained with uranyl acetate solution and observed by TEM ( figure 2 (B)). It can be seen from the figure that the diameter of ginkgo biloba nanocellulose is about 3 to 4 nanometers, and the length is about hundreds of nanometers to micrometers.
example 3
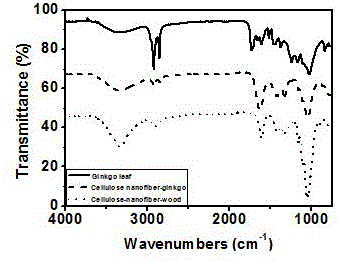
[0037] Example three: Ginkgo biloba, ginkgo biloba nanocellulose and wood nanocellulose are tested using ATR technology, such as image 3As shown, it can be seen that the main vibration peak of the infrared spectrum of ginkgo leaf nanofiber is very similar to that of wood nanocellulose, but it is quite different from the raw material of ginkgo leaf, indicating that the main component of ginkgo leaf nanocellulose is cellulose. The oxidation process removes most of the other components, and at 1621cm -1 The characteristic vibration peak of carboxylate is produced.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com