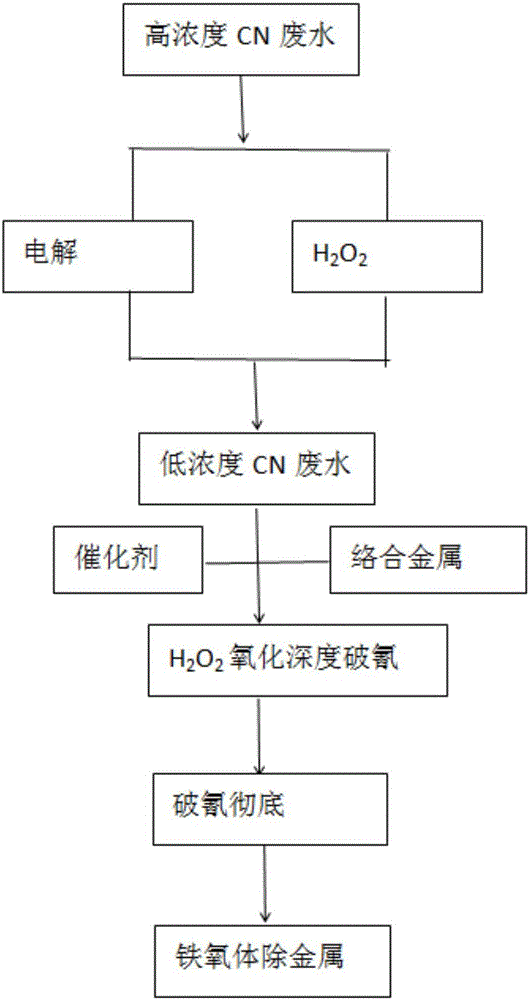
Method for removing heavy metal by carrying out cyanide breaking on high-concentration cyanide wastewater
A cyanide, high-concentration technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, metallurgical wastewater treatment, water pollutants, etc., can solve the problems of HCN safety hazards, limited microbial load capacity, and polluting the operating environment to avoid subsequent reprocessing, The effect of low reagent cost and improved electrolysis efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Take 500mL of cyanide wastewater from an electroplating factory. The main parameters of the raw water are: total cyanide: 15g / L, Fe content 35.2ppm, Zn content 2.5ppm, Ni content 5.6ppm, Cu content 10ppm.
[0031] Cyanogen removal and metal removal are mainly carried out through the following steps:
[0032] 1. Electrolysis: put 500mL of wastewater into the electrolytic cell, and use NaOH / H 2 SO 4 The pH value was adjusted to 10, and the cathode stainless steel plate and the anode titanium mesh plate were used, and the current was adjusted to 1.0A for constant current electrolysis.
[0033] 2. During the electrolysis process, a small amount of hydrogen peroxide was added several times, and the total volume of the hydrogen peroxide added was 32.64 mL.
[0034] 3. When the cyanide electrolysis reaches 100ppm, stop the electrolysis, the pH value of the solution is 10 at this time, open the heating tube, and when the temperature rises to 60°C, add 5g of EDTA disodium salt...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Take 800mL of cyanide wastewater from an electroplating plant. The main parameters of the raw water are: total cyanide: 16g / L, Fe content 27.5ppm, Cu content 12ppm, Ni content 6.3ppm, Pb content 2.4ppm.
[0040] Cyanogen removal and metal removal are mainly carried out through the following steps:
[0041] 1. Electrolysis: put 500mL of wastewater into the electrolytic cell, and use NaOH / H 2 SO 4 The pH value was adjusted to 11, the cathode stainless steel plate and the anode titanium mesh plate were used, and the current was adjusted to 10A for constant current electrolysis.
[0042] 2. During the electrolysis process, hydrogen peroxide was added in small amounts and several times, and the total volume of the hydrogen peroxide added was 66 mL.
[0043] 3. When the cyanide electrolysis reaches 80ppm, stop the electrolysis, the pH value of the solution is 11 at this time, open the heating tube, and when the temperature rises to 70°C, add 18g of EDTA disodium salt and 0.64...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com