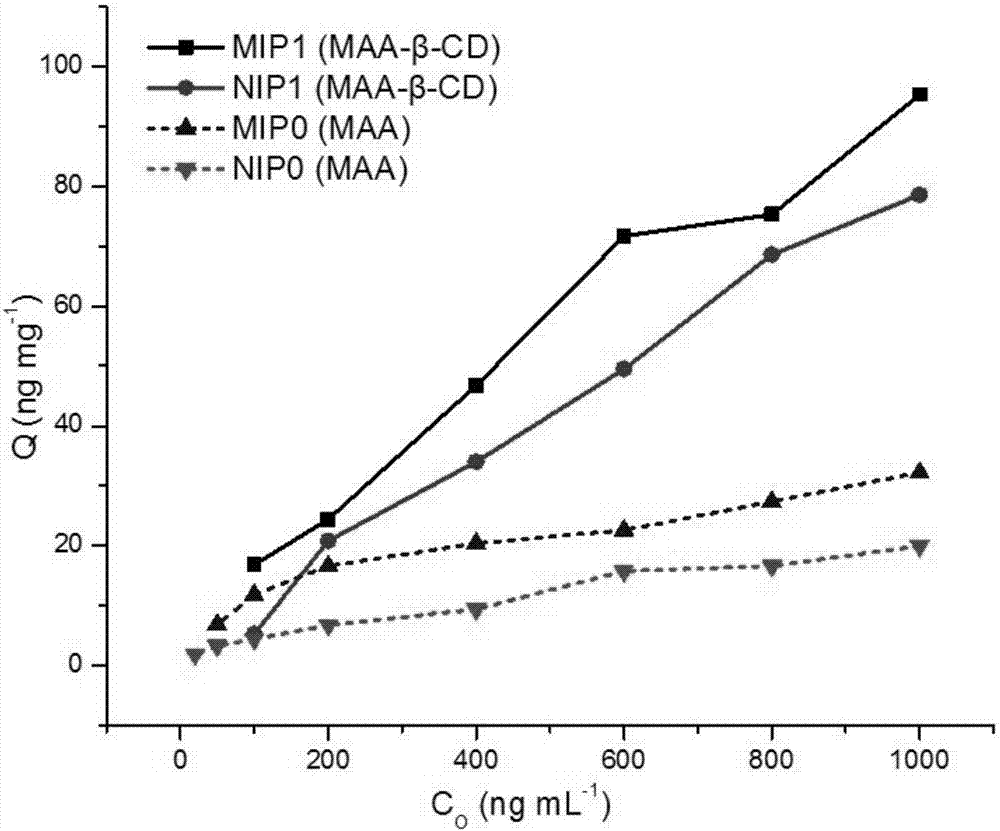
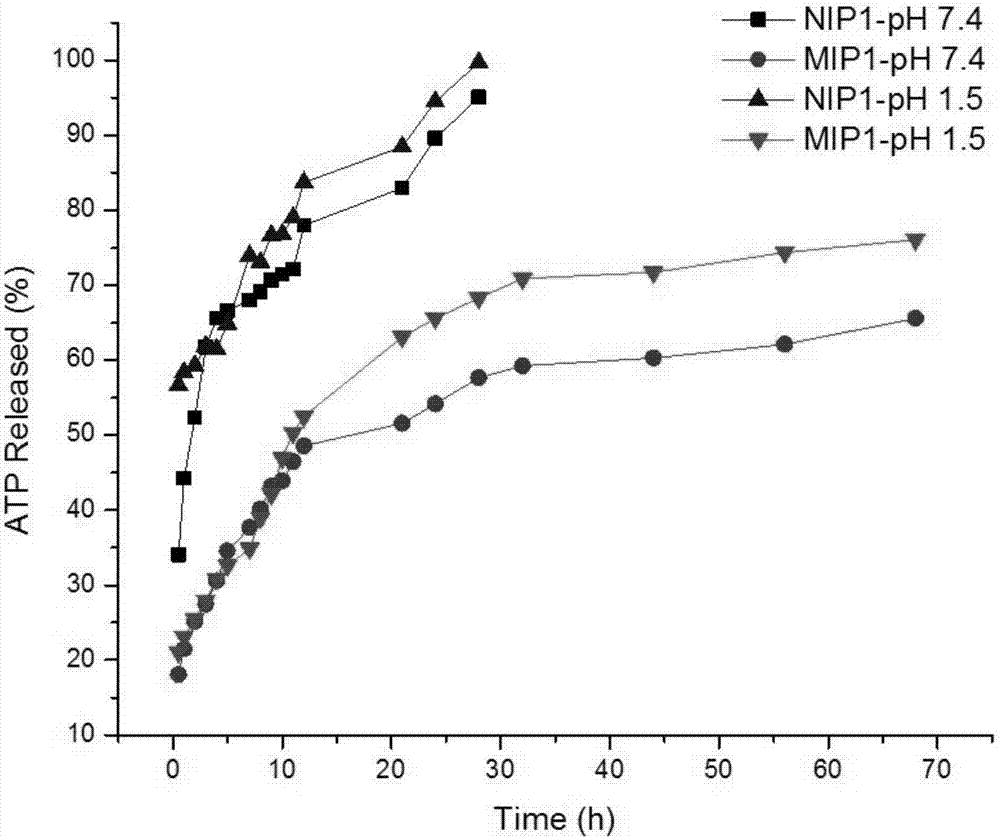
A Molecularly Imprinted Polymer with Controlled and Sustained Release Function
A technology of molecular imprinting and polymer, applied in the direction of active ingredients of heterocyclic compounds, medical preparations of non-active ingredients, pharmaceutical formulations, etc. People's satisfaction and other issues, to achieve the effect of drug sustained release
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0031] Preferably, the molecularly imprinted polymer as described above, the preparation method of the β-cyclodextrin modified methacrylic acid comprises:
[0032] 1), dissolving methacrylic acid and toluene diisocyanate in an aprotic polar solvent, and polymerizing under the catalysis of dibutyltin dilaurate;
[0033] 2) The aprotic polar solvent is added to the product obtained in step 1), and β-cyclodextrin is added for reaction, and the reaction product is obtained after washing, recrystallization and drying.
[0034] Preferably, in the above molecularly imprinted polymer, the molar ratio of methacrylic acid, toluene diisocyanate and β-cyclodextrin is (0.4-0.6):(0.8-1.2):(0.4-0.6).
[0035] More preferably, the toluene diisocyanate (TDI) is toluene-2,4-diisocyanate.
[0036] Methacrylic acid (MAA) and TDI were polymerized to form the backbone of molecularly imprinted polymer functional monomers.
[0037] Preferably, for the molecularly imprinted polymer as described abov...
Embodiment 1
[0052] (1) Synthesis of functionalized functional monomers:
[0053] Synthesized according to the stoichiometric ratio of 0.4M MAA:1.2M TDI:0.4Mβ-CD. Mix toluene-2,4-diisocyanate (TDI, 2.284mL, 0.4M), methacrylic acid (MAA, 1.018mL, 1.2M) and dissolve in 20mL dimethylacetamide (DMAC), stir, add 0.1% ( 0.02mL) of dibutyltin dilaurate (DBTDL) as catalyst. Nitrogen was blown for 10 min, and magnetic stirring was performed at room temperature for 1 h. The MAA-TDI system was analyzed by UV to confirm the reaction. Then β-cyclodextrin (β-CD, 0.4M, 454 mg) was added, supplemented with 5 mL of dimethylacetamide. Nitrogen blowing, stirring for 2h (TLC tracking reaction, developer: petroleum ether / ethyl acetate, 2 / 1 ~ 3 / 1, v / v). The obtained product MAA-β-CD was washed three times with ultrapure water, and recrystallized with methanol to obtain a white solid, which was vacuum-dried to constant weight.
[0054] (2) Preparation of atropine molecularly imprinted polymer by thermally i...
Embodiment 2
[0057] (1) Synthesis of functionalized functional monomers:
[0058] Synthesized according to the stoichiometric ratio of 0.6M MAA:0.8M TDI:0.6Mβ-CD. Mix toluene-2,4-diisocyanate (TDI, 3.426mL, 0.6M), methacrylic acid (MAA, 0.678mL, 0.8M) and dissolve in 20mL dimethylacetamide (DMAC), stir, add 0.1% ( 0.02mL) of dibutyltin dilaurate (DBTDL) as catalyst. Nitrogen was blown for 10 min, and magnetic stirring was performed at room temperature for 1 h. The MAA-TDI system was analyzed by UV to confirm the reaction. Then β-cyclodextrin (β-CD, 0.6M, 680 mg) was added, supplemented with 5 mL of dimethylacetamide. Nitrogen blowing, stirring for 2h (TLC tracking reaction, developer: petroleum ether / ethyl acetate, 2 / 1 ~ 3 / 1, v / v). The obtained product MAA-β-CD was washed 4 times with ultrapure water, and then recrystallized with methanol to obtain a white solid, which was dried in vacuo until constant weight.
[0059] (2) Preparation of atropine molecularly imprinted polymer by therm...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com