Fe3O4-graphite composite nanometer material and preparation method thereof and application of Fe3O4-graphite composite nanometer material in lithium ion battery
A technology of composite nanomaterials and ferroferric oxide, which is applied in the direction of battery electrodes, nanotechnology, nanotechnology, etc., can solve the problems of potential safety hazards, long preparation routes, industrial mass production and preparation, etc., to achieve enhanced conductivity and good circulation Performance, the effect of improving the magnification performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Weigh 7.0g potassium ferrate, 3.0g graphite, 250g zirconium balls (grinding medium), add them to a ball mill tank, stir evenly by hand, and then use a planetary ball mill at 500rpm to ball mill for 60 hours. The product is filtered, washed with water, and kept at a constant temperature. Drying in a drying box at 60° C. for 12 hours, and finally grinding into powder to obtain ferroferric oxide / graphite composite nano-material.
[0040] Mix and grind 0.200g ferroferric oxide / graphite composite nanomaterials, 0.025g PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride) and 0.025g carbon black, and then add 1ml NMP (N-methylpyrrolidone) and continue grinding for 0.5h to obtain the slurry The material was uniformly coated on the copper foil, dried for 12 hours to form an electrode, and the lithium sheet was used as the counter electrode to assemble a CR2016 button battery for electrochemical performance testing.
Embodiment 2
[0042] Weigh 8.0g potassium ferrate, 2.0g graphite, 250g zirconium balls (grinding medium), add them to a ball milling tank, stir evenly by hand, and then use a planetary ball mill to ball mill at 400 rpm for 48 hours. The product is filtered, washed with water, and kept at a constant temperature. Drying in a drying box at 60° C. for 12 hours, and finally grinding into powder to obtain ferroferric oxide / graphite composite nano-material.
[0043] Mix and grind 0.200g ferroferric oxide / graphite composite nanomaterials, 0.025g PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride) and 0.025g carbon black, and then add 1ml NMP (N-methylpyrrolidone) and continue grinding for 0.5h. The slurry was uniformly coated on the copper foil and dried for 12 hours to form an electrode. The lithium sheet was used as the counter electrode to assemble a CR2016 button cell, and the electrochemical performance test was performed.
Embodiment 3
[0045] Weigh 8.5g potassium ferrate, 1.5g graphite, 250g zirconium balls (grinding medium), add them to a ball mill tank, stir by hand, and then use a planetary ball mill to ball mill at 400 rpm for 48 hours. The product is filtered, washed with water, and kept at a constant temperature. Drying in a drying box at 60° C. for 12 hours, and finally grinding into powder to obtain ferroferric oxide / graphite composite nano-material.
[0046] Mix and grind 0.200g ferroferric oxide / graphite composite nanomaterials, 0.025g PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride) and 0.025g carbon black, and then add 1ml NMP (N-methylpyrrolidone) and continue grinding for 0.5h. The slurry was uniformly coated on the copper foil and dried for 12 hours to form an electrode. The lithium sheet was used as the counter electrode to assemble a CR2016 button cell, and the electrochemical performance test was performed.
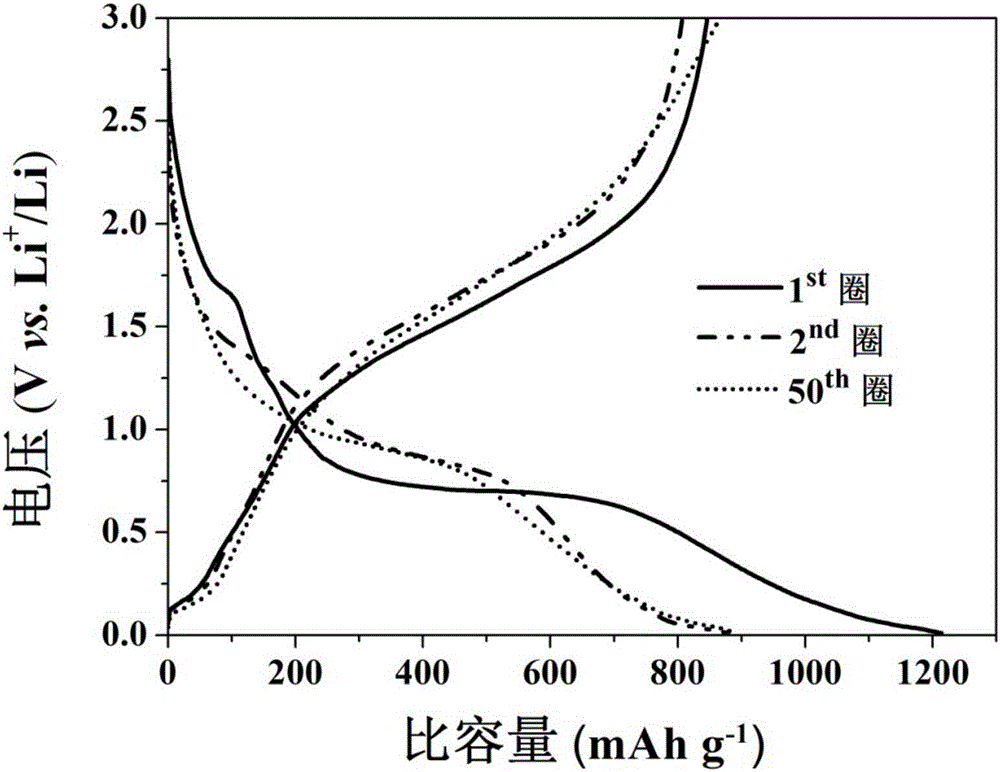
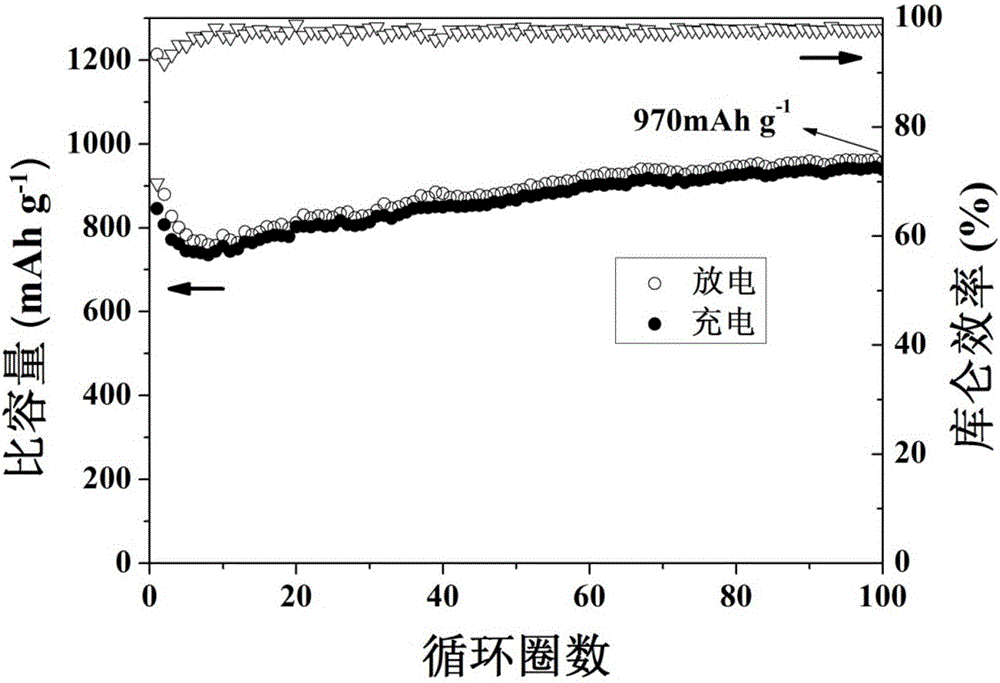
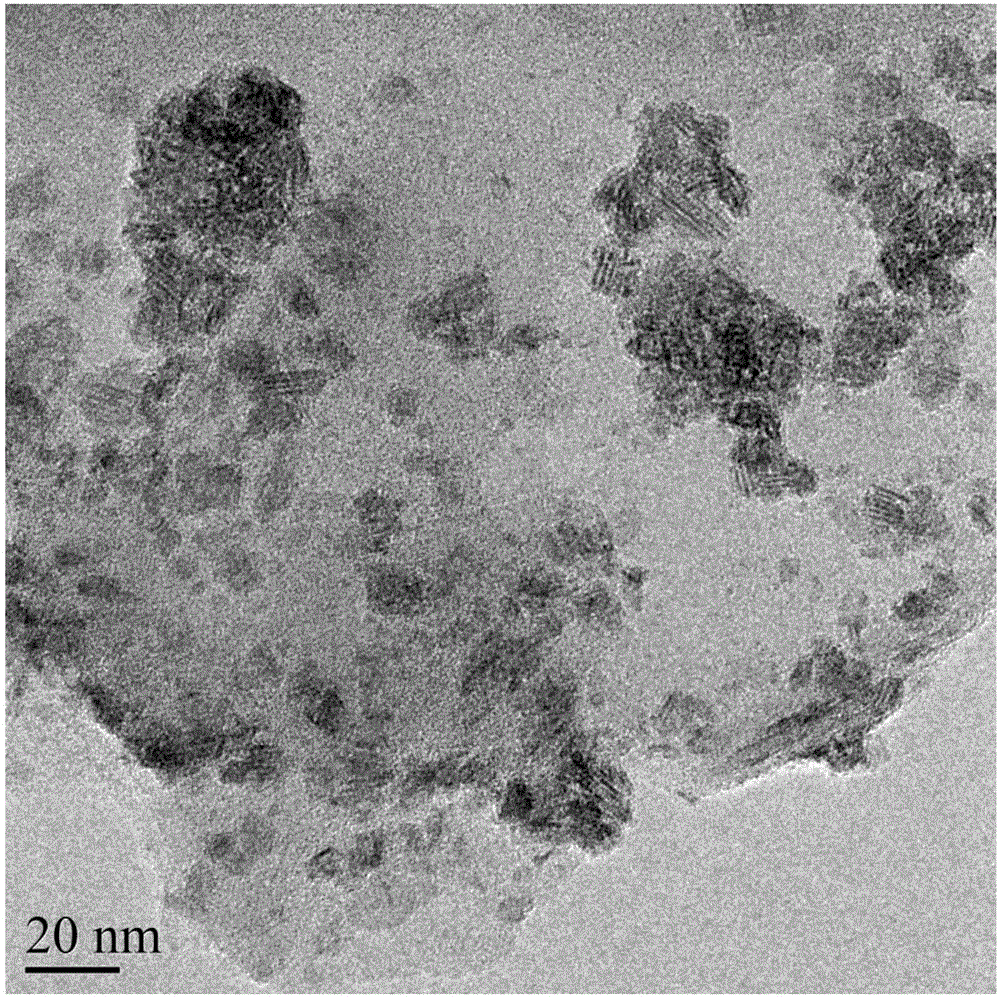
[0047] The ferroferric oxide / graphite composite nano material obtained in this embodiment has a current d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com