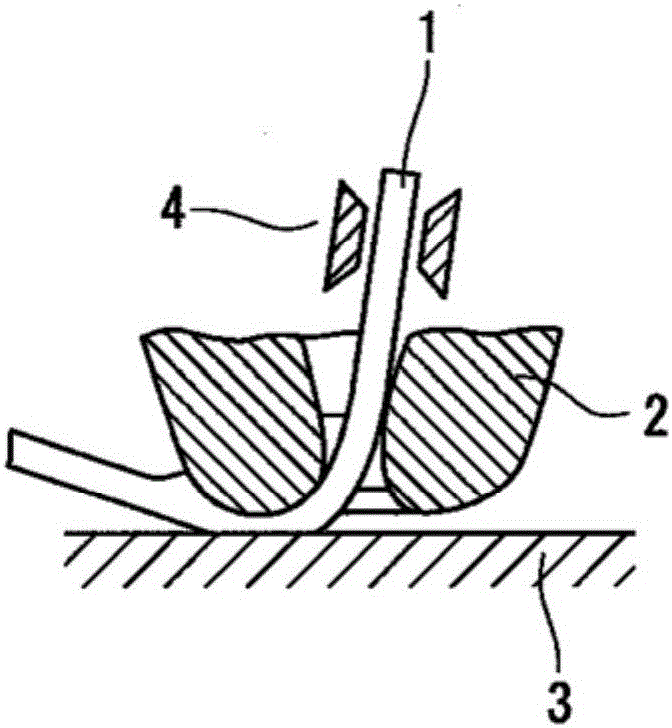
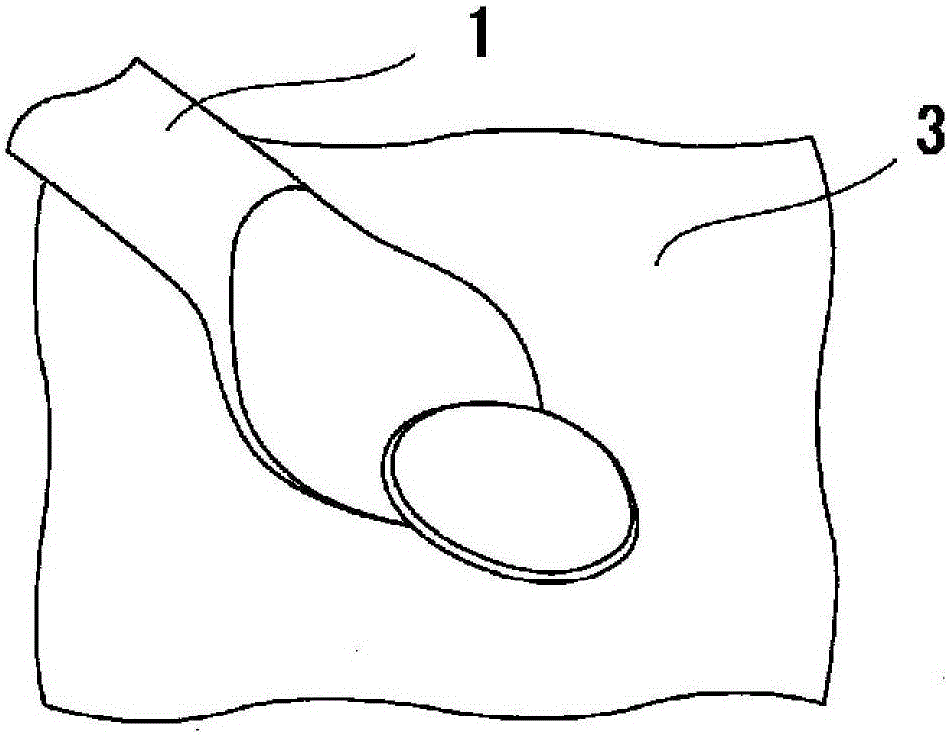
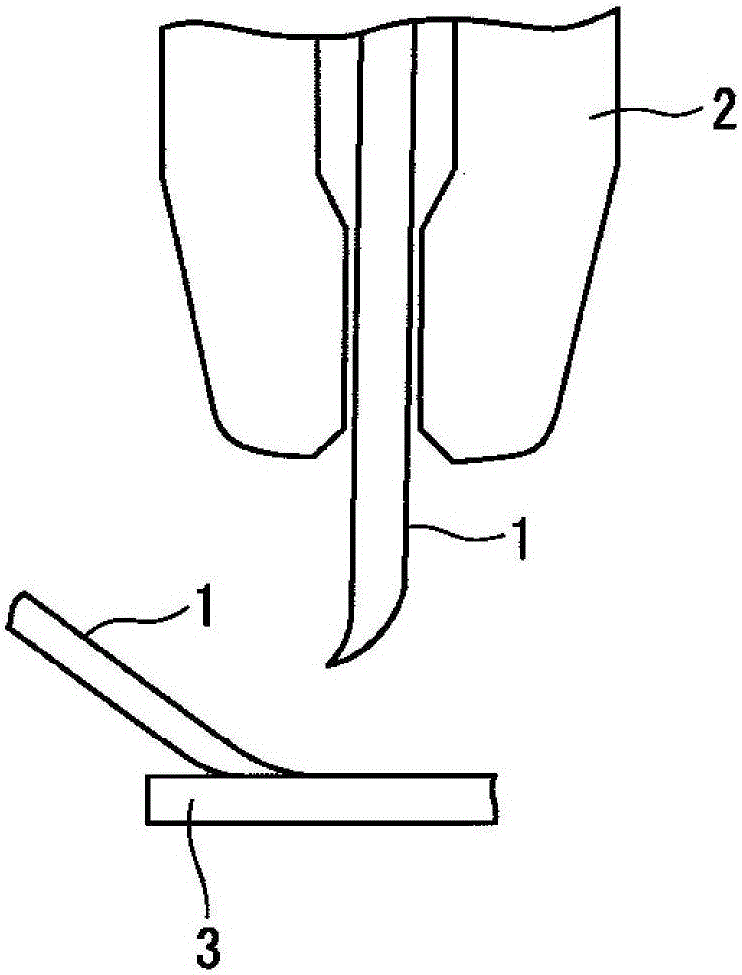
Copper alloy bonding wire
A technology of copper alloy and bonding wire, applied in the direction of semiconductor/solid-state device components, semiconductor devices, electrical components, etc., to achieve stable position, shorten the time of bonding steps, and stabilize the shape
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0062] The core material is copper (Cu) with a purity of 99.9998 mass % (5N), phosphorus (P), nickel (Ni), palladium (Pd), platinum (Pt), gold (Au) and silver (Ag) as an added element. As the base metal element, an element generally contained in high-purity copper is selected. That is, bismuth (Bi), selenium (Se), tellurium (Te), zinc (Zn), iron (Fe), nickel (Ni), and tin (Sn) are appropriately selected. Embodiments in which these metals are blended within a given range are referred to as Example 1 to Example 5, respectively.
[0063] Next, this was dissolved and continuously casted, and then the first wire drawing was performed within the range of 95 to 99.99% or less of the cross-sectional reduction rate to obtain a thick wire (diameter 1.0 mm) before coating the drawn material. Next, intermediate heat treatment (treatment at 300-600° C. for 0.5-3 hours) was performed (Example 4, Example 5) or no intermediate heat treatment was performed (Example 1-Example 3). Afterwa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com