Brown pigment-producing Gluconobacter sp. and application of same to liquid-state fermented vinegar
A technology of Gluconobacter and vinegar, which is applied to a brown pigment-producing Gluconobacter and its application in liquid fermented vinegar, can solve the problem of not conforming to consumer consumption habits, dull color, and liquid fermented food. Problems such as single vinegar flavor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
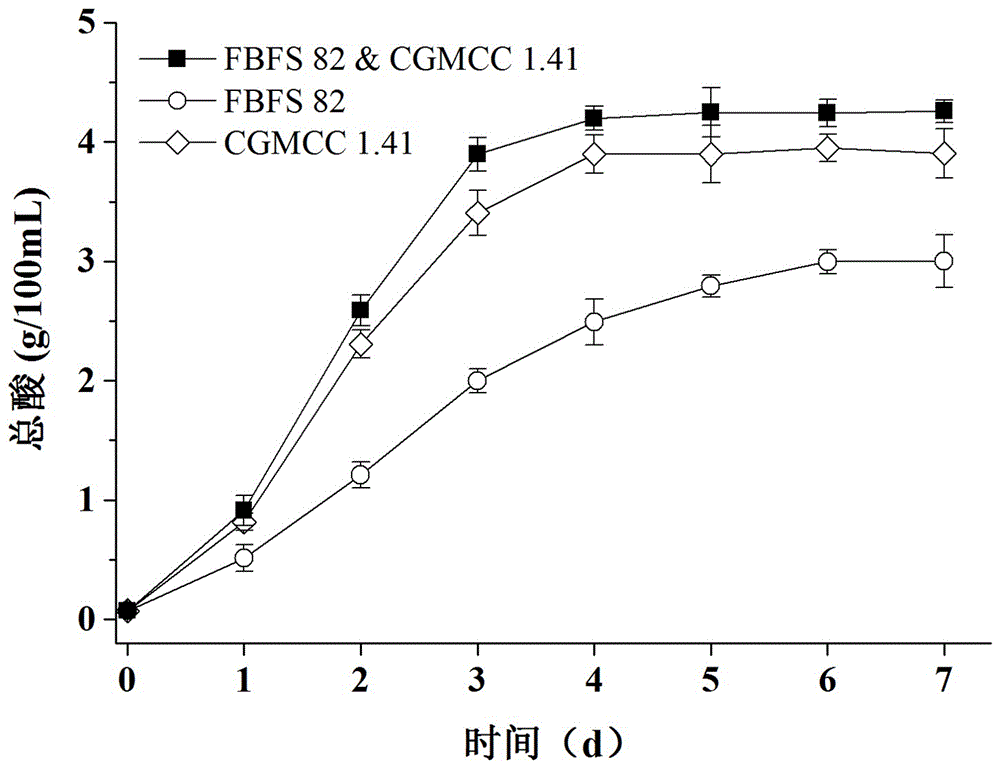
[0020] Example 1 Detection of total acid content in the fermentation process of vinegar: According to the method described in the manual, the total acid content of the fermented liquid was measured by acid-base titration at different fermentation times in the fermented process, and it was found that the acidity in the fermented liquid increased with time. Carry on, rise first and then stay flat. When Acetobacter pasteurii CGMCC 1.41 is fermented alone, the total acidity reaches 4%; when Gluconobacter FBFS 82 is fermented alone, the total acidity reaches 3%; when the two strains are fermented together, the total acidity reaches 4.3% ( figure 2 ).
[0021] The method for detecting the total acid content in the fermentation broth in the above example includes the following steps: take an appropriate amount of fermentation broth (1-5 mL) and dilute it to 20 mL with double distilled water, use 1% phenolphthalein as an indicator, and use 0.1 mol / L hydrogen The sodium oxide standar...
Embodiment 2
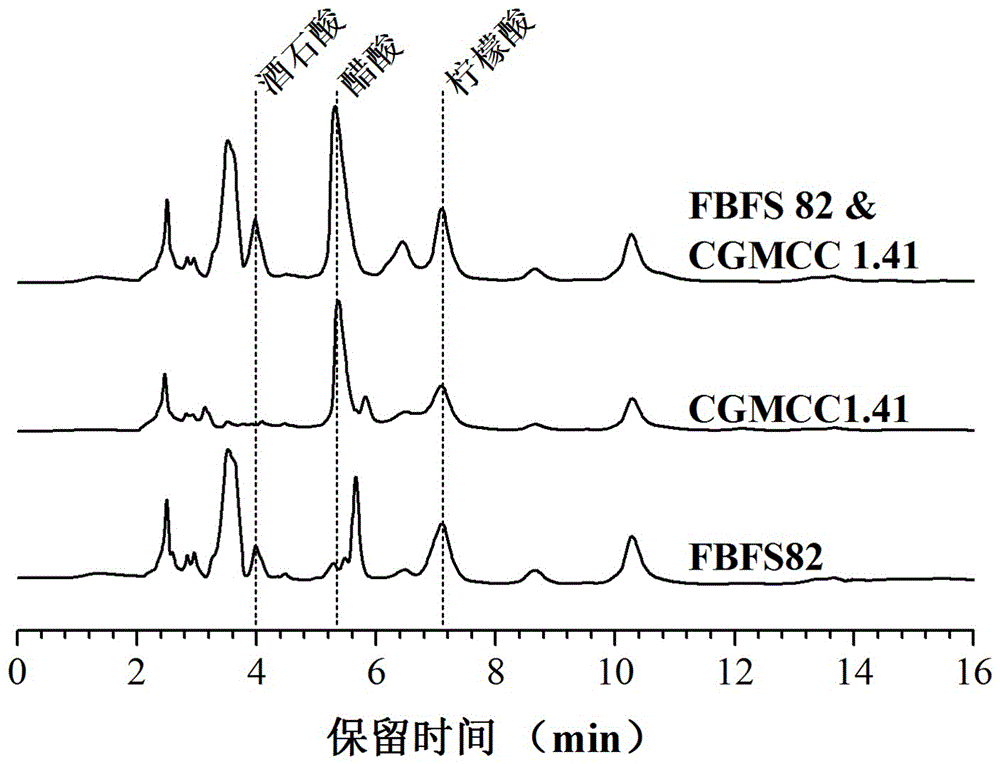
[0025] The composition of organic acid in the vinegar of embodiment 2: get vinegar by fermenting according to the method described in the manual, detect the content of organic acid in the vinegar by high-performance liquid chromatography, find that Acetobacter pasteurii CGMCC 1.41 can produce acetic acid and a small amount of citric acid Tartaric acid is produced, while Gluconobacter FBFS 82 can produce citric acid and a small amount of tartaric acid and almost no acetic acid, so the two are complementary to a certain extent, so that the vinegar after mixed fermentation contains acetic acid, tartaric acid and citric acid at the same time, and the acetic acid The contents of tartaric acid and tartaric acid were higher than those of the two strains when they were fermented alone, so that the content of organic acids in mixed fermented vinegar was more and the types were more abundant ( image 3 ).
[0026] The high-performance liquid chromatography method for detecting the conte...
Embodiment 3
[0028] Example 3 Identification of Flavor Components in Vinegar: Ferment vinegar according to the method described in the manual, detect the types of flavor components in vinegar by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, and find that the mixed-fermented vinegar contains esters, aldehydes Flavor components such as alcohols, alcohols, acids, etc., and produced flavor components that did not exist in the four original strains (FBFS82 and CGMCC 1.41), such as ethyl phenylacetate with honey aroma, and nononium with rose, citrus, etc. Aldehydes (Table 1).
[0029] The gas chromatography-mass spectrometry method for detecting flavor components in vinegar in the above example includes the following steps: the flavor components in vinegar are first extracted by solid-phase microextraction, and then detected by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry.
[0030] The above method of solid-phase microextraction is as follows: accurately measure 8 mL of vinegar and place it in a 15 mL sample bo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com