Lactobacillus curvatus for producing bacteriocin, and application thereof
A technology of Lactobacillus campylobacter and bacteriocin, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of poor solubility and low stability, and achieve the effect of obvious bacteriostatic effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Example 1: Screening and identification of bacteriocin-producing lactic acid bacteria
[0024] Preparation of MRS medium: 10g of peptone, 10g of beef extract, 5g of yeast extract, 20g of glucose, 5g of anhydrous sodium acetate, 2g of diammonium hydrogen citrate, 2.62g of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, 0.58g of magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, Water manganese sulfate 0.19g, Tween-801mL, add distilled water to 1L, pH 6.2-6.4.
[0025] Preparation of TSBYE medium: 30g of Tryptone soya broth (TSB), 6g of yeast extract, and distilled water to 1L, pH 7.2-7.4.
[0026] Preparation of solid medium: add 1.5% to 2.0% agar to the liquid medium.
[0027] (1) Isolation and purification of lactic acid bacteria
[0028] The used pickle materials of the present invention are all self-made, and its preparation method is: vegetables (cabbage, beans, white radish) are washed clean, mix with salt, capsicum, spices, put into the pickle tank and seal, place in a cool and dry place, 20 It ...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2: Thermotolerance of Lactobacillus flexus SK1 bacteriocin
[0035] Bacteriocin activity was determined by the Oxford cup serial two-fold dilution method, and the indicator bacterium was Listeria monocytogenes. One activity unit (AU) is defined as the minimum amount of bacteriocin that can make the indicator bacteria produce a clear transparent circle. The bacteriocin activity of the solution (AU / mL) = 2 n ×(1000 / x). n represents the maximum number of serial two-fold dilutions of the bacteriocin solution that caused the indicator bacteria to produce an inhibition zone; x represents the volume (μL) of the bacteriocin solution added to each well. The diluent used for the determination of viability was 20 mM citrate buffer, pH 6.0.
[0036] Preparation of SK1 bacteriocin samples: Inoculate Lactobacillus flexus SK1 into 5mL MRS liquid medium, culture at 30°C for 24h, transfer to 50mL MRS liquid medium with 3% inoculum size, culture at 30°C for 24h, ferment the fe...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Embodiment 3: acid and alkali resistance of Lactobacillus flexus SK1 bacteriocin
[0041] The determination method of bacteriocin activity is the same as in Example 2, and the preparation method of SK1 bacteriocin sample is basically the same as in Example 2, but cultured at 20° C. for 48 hours after transfer.
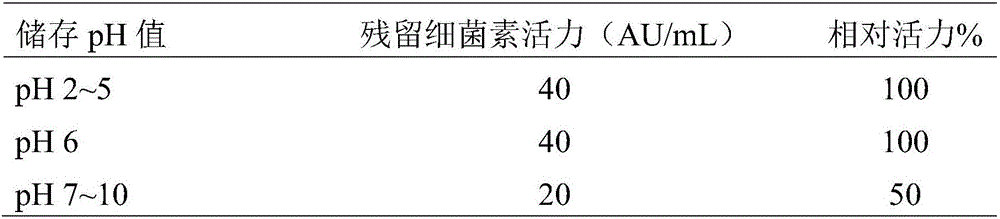
[0042] Determination of acid and alkali resistance of SK1 bacteriocin samples: Adjust the SK1 bacteriocin samples to different pH values (pH 2-10) with 5M NaOH or 4M HCl, store them at 25°C for 2 hours, then return them to pH 6.0, and finally pass The residual activity was determined by the Oxford cup method. The results are shown in Table 2. The SK1 bacteriocin sample has relatively good acid resistance. It can retain all the activity when stored at pH 2-6 for 2 hours, and has a certain alkali resistance. It can still retain half of the activity when stored at pH 7-10 for 2 hours.
[0043] Table 2 The acid and alkali resistance of Lactobacillus flexus SK1 b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com