Method for increasing grain number per ear and reducing plant height by use of rice SNB genes
A technology of grain number per ear and rice is applied in the application field of rice SNB gene in increasing grain number per ear and reducing plant height, which can solve the problems that cannot be directly used for rice breeding, and the number of branches and spikelets is reduced, so as to increase the number of grains per ear in rice. Count, the effect of reducing plant height
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Embodiment 1: the cloning of rice SNB gene
[0046] The present invention adopts the cDNA obtained by reverse transcription of the RNA of rice leaves as a template, and utilizes the specific primers of the SNB gene (LOC_Os07g13170, whose nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1), to isolate and clone the SNB gene by PCR. For the protein coding region, the specific operations are as follows:
[0047] (1) Extract RNA from rice leaves
[0048] Extract the RNA of rice variety Zhonghua 11 (Institute of Crop Science, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences) plant tillering stage leaves, the reagents used for RNA extraction are purchased using the Trizol extraction kit produced by Invitrogen Company (the specific operation steps are provided according to the instructions provided by the kit) operate).
[0049] (2) Reverse transcription to synthesize the first strand of cDNA
[0050] The steps are as follows: 1) Take 2 μg of extracted total RNA, add 1 μl of DNaseI, 1 μl...
Embodiment 2
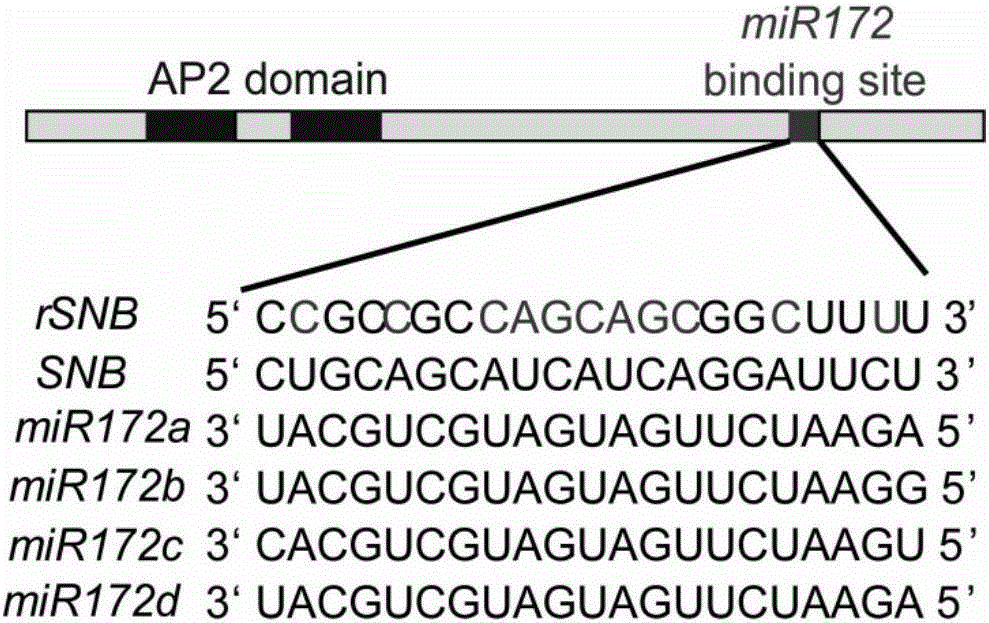
[0057] Example 2: Mutation of microRNA172 binding site in SNB
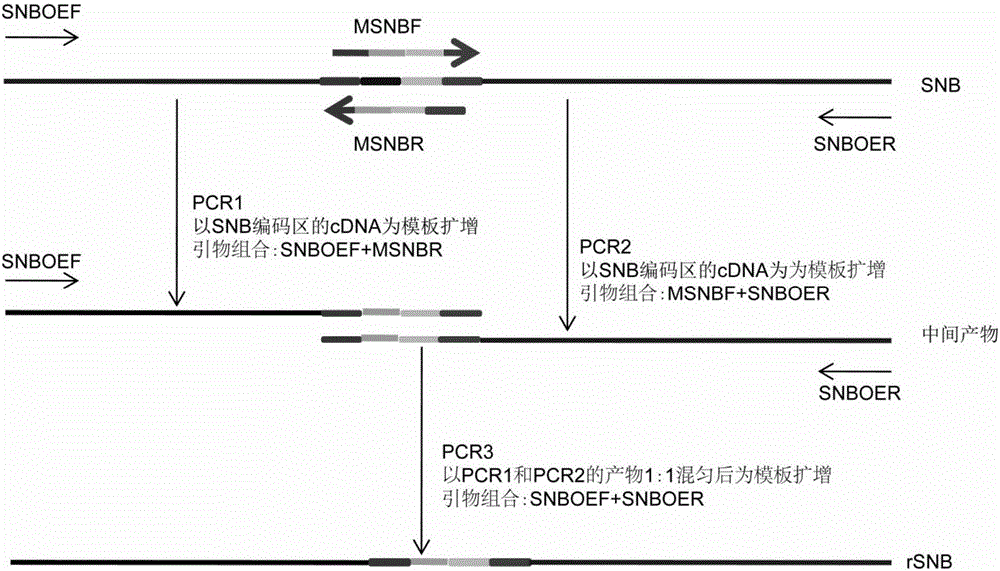
[0058] Because SNB is regulated by microRNA172 (such as figure 1 shown), therefore in order to overexpress SNB, the present invention uses overlap extension PCR to mutate the binding site of microRNA172 in the SNB gene (overlap extension PCR method with reference to Sam Brook, "Molecular Cloning Experiment Guide" third edition, Science Press, 2002; the basic process is as follows figure 2shown). The sequence of the binding site of microRNA172 in SNB is TGCAGCATCATCAGGATTCT, the present invention mutates the binding site to CGCCGCCAGCAGCGGCTTTT, and the mutated SNB gene is named rSNB gene. The rSNB gene will no longer be regulated by microRNA172, but the mutation is synonymous and therefore does not change the sequence of the protein encoded by SNB.
[0059] To achieve the above goals, the following primers were designed:
[0060] MSNBF (forward primer): 5'-CCTAC CGCCGCCAGCAGCAGCGGCTTTT CTACGGGCACCGTCGCC-3' ...
Embodiment 3
[0063] Example 3: construction of an overexpression vector for the protein coding region of the rSNB gene with mutations in the microRNA172 recognition site
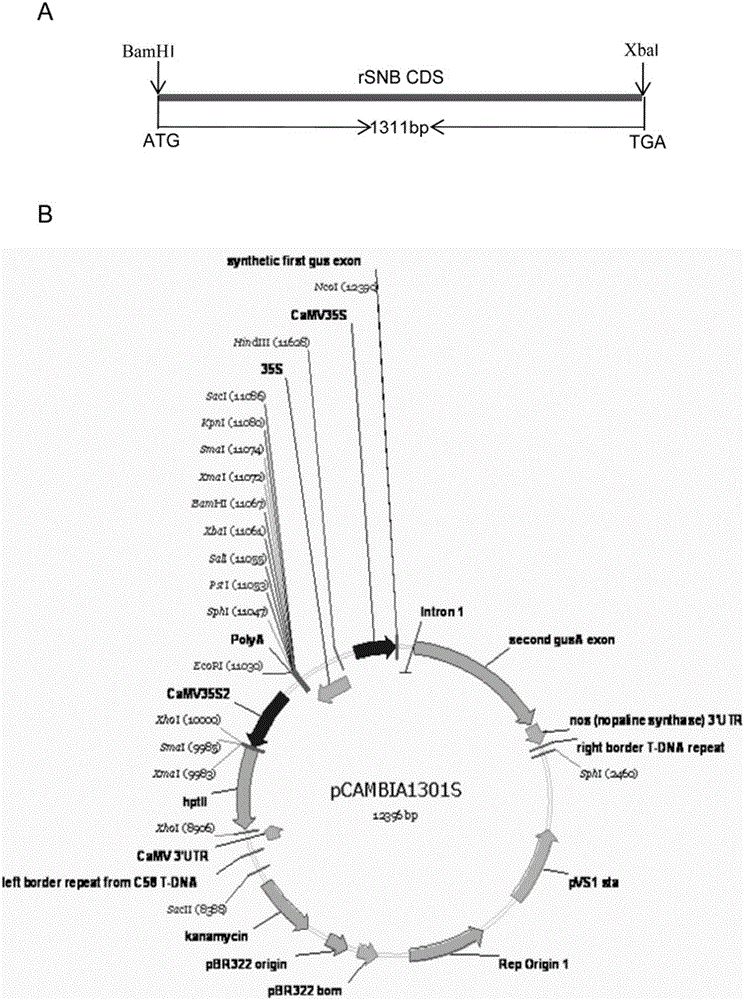
[0064] Double-digest plasmid TA-rSNB with BamHI and XbaI (the BamHI and XbaI were purchased from Bao Biological Engineering Dalian Co., Ltd., and the specific usage and dosage refer to the instructions of the corresponding products of the company. The plasmid TA-rSNB comes from Example 2, as shown in image 3 Shown in A figure in the middle), reclaim the DNA fragment of 1323bp that comprises rSNB, then with the vector plasmid pCAMBIA1301S [this vector is publicly reported through BamHI and XbaI double digestion: Zhou et al., Over-expression of aspartate aminotransferase genes in rice resulted in altered nitrogen metabolism and increased amino acid content in seeds. Theor Appl Genet, 2009, 118:1381-1390; its basic skeleton originated from CAMBIA laboratory in Australia (http: / / www.cambia.org / daisy / cambia / materials / overvi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com