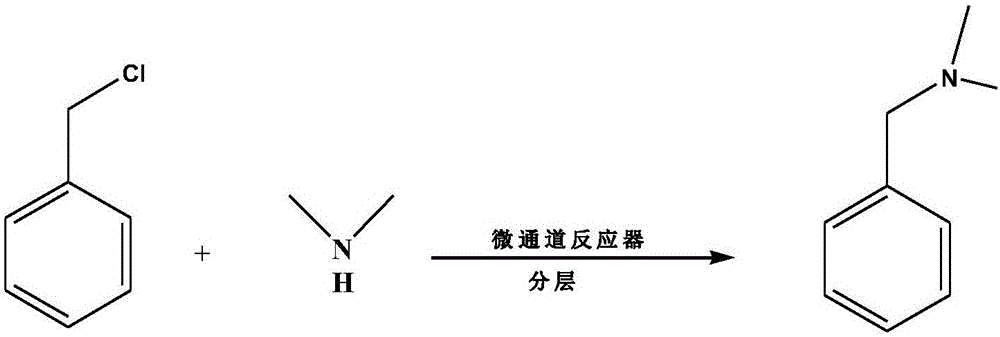
Preparation method of N,N-dimethyl benzylamine
A technology of dimethylbenzylamine and dimethylamine aqueous solution, applied in the N field, can solve the problems of generation of by-products, difficult separation and purification, large production energy consumption, etc., and achieves large wastewater treatment capacity, high yield and low pollution Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018]
[0019] (1) Get 1.7mol benzyl chloride to obtain solution A;
[0020] (2) Take 1mol dimethylamine and dissolve it in an appropriate amount of water to obtain a 30wt% aqueous solution of dimethylamine to obtain solution B. Since dimethylamine is a toxic gas, dissolving it in water can facilitate the reaction and prevent gas from escaping and causing pollution;
[0021] (3) After heating the glass reaction module of the Corning microchannel G1 glass reactor to 70°C, use two feed pumps to add solution A and solution B to the microchannel reactor at the same time to mix and react. The ratio of the feed rate of the pump to control the molar ratio of benzyl chloride and dimethylamine is 1:1.7;
[0022] (4) Since the volume in the glass reaction module of the reactor is a known fixed value, the total feed rate of the two feed pumps can be adjusted to control the reaction residence time to be 30 seconds;
[0023] (5) Collect the oil-water mixture that produces, cool immedi...
Embodiment 2
[0026] (1) Get 2.0mol benzyl chloride to obtain solution A;
[0027] (2) Dissolve 0.88mol dimethylamine in an appropriate amount of water to obtain a 20wt% dimethylamine aqueous solution to obtain solution B. Since dimethylamine is a toxic gas, dissolving it in water can facilitate the reaction and prevent gas from escaping and causing pollution;
[0028] (3) After heating the glass reaction module of the Corning microchannel G1 glass reactor to 90°C, use two feed pumps to add solution A and solution B to the microchannel reactor at the same time to mix and react. The ratio of pump feeding speed controls the feeding molar ratio of benzyl chloride and dimethylamine to be 1:2.2;
[0029] (4) Since the volume in the glass reaction module of the reactor is a known fixed value, the total feed rate of the two feed pumps can be adjusted to control the reaction residence time to be 40 seconds;
[0030] (5) Collect the oil-water mixture that produces, cool immediately, leave standstil...
Embodiment 3
[0033] (1) Get 1.0mol benzyl chloride to obtain solution A;
[0034] (2) Dissolve 0.4mol dimethylamine in an appropriate amount of water to obtain a 25wt% dimethylamine aqueous solution to obtain solution B. Since dimethylamine is a toxic gas, dissolving it in water can facilitate the reaction while preventing gas from escaping and causing pollution;
[0035] (3) After heating the glass reaction module of the Corning microchannel G1 glass reactor to 60°C, use two feed pumps to add solution A and solution B to the microchannel reactor at the same time to mix and react. The ratio of pump feeding speed controls the feeding molar ratio of benzyl chloride and dimethylamine to be 1:1.6;
[0036] (4) Since the volume in the glass reaction module of the reactor is a known fixed value, the total feed rate of the two feed pumps can be adjusted to control the reaction residence time to be 25 seconds;
[0037] (5) Collect the oil-water mixture that produces, cool immediately, leave stand...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com