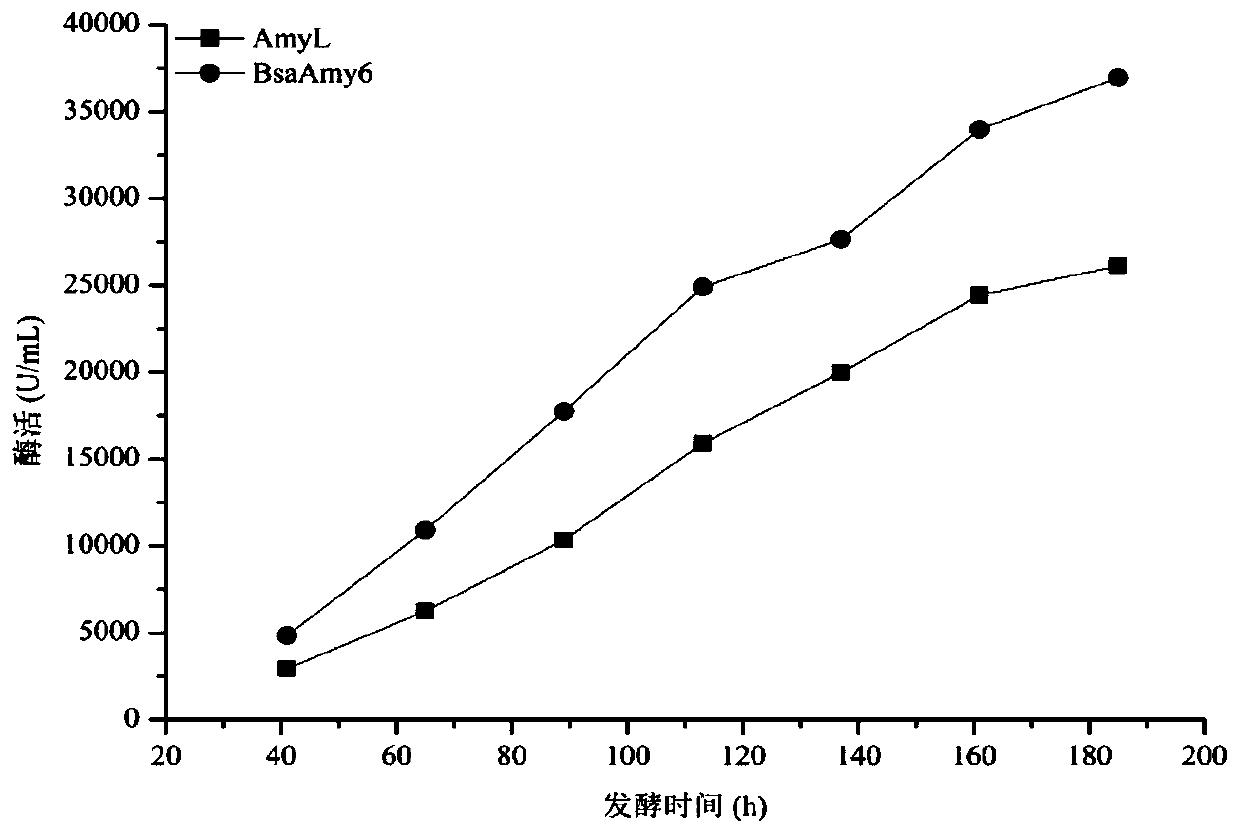
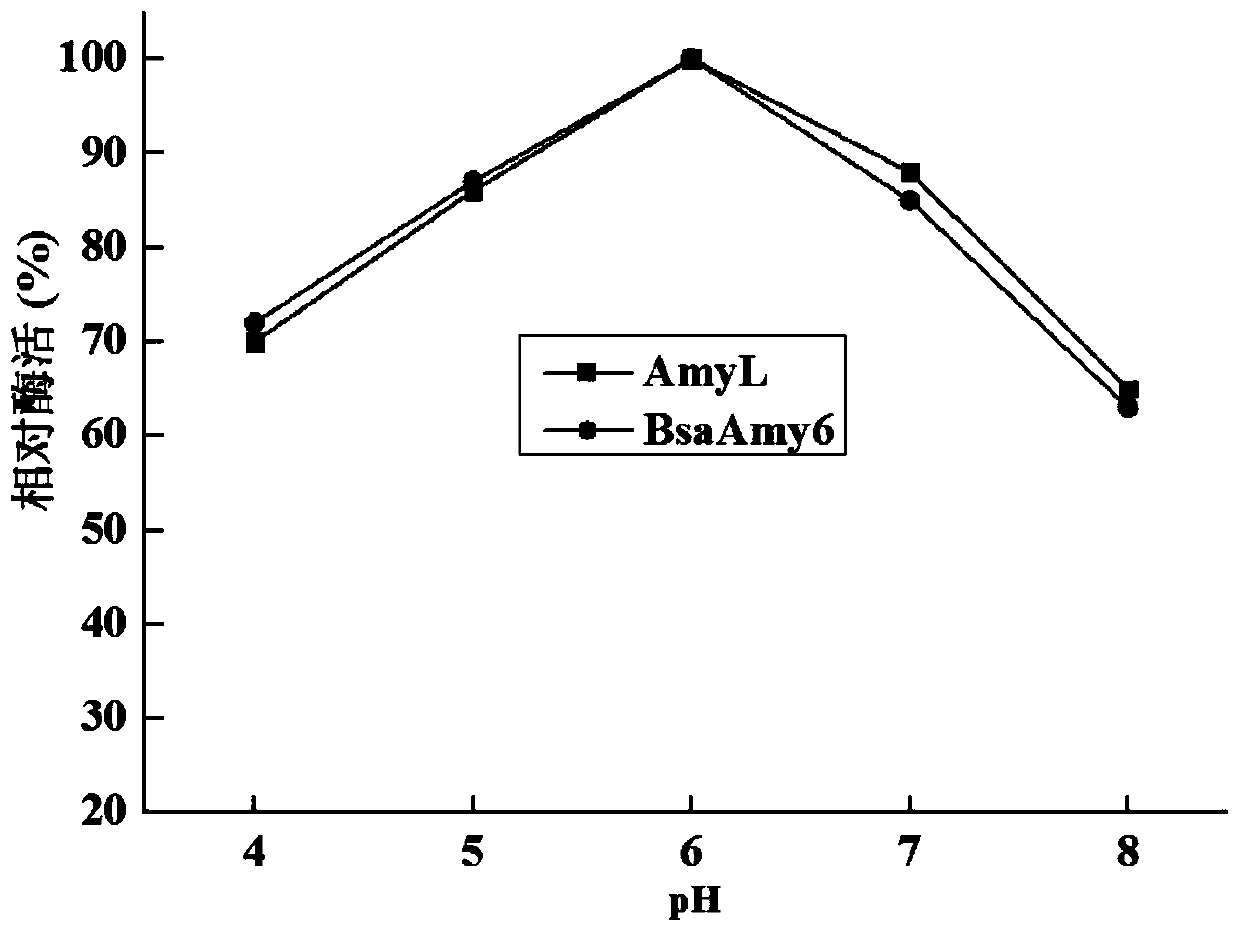
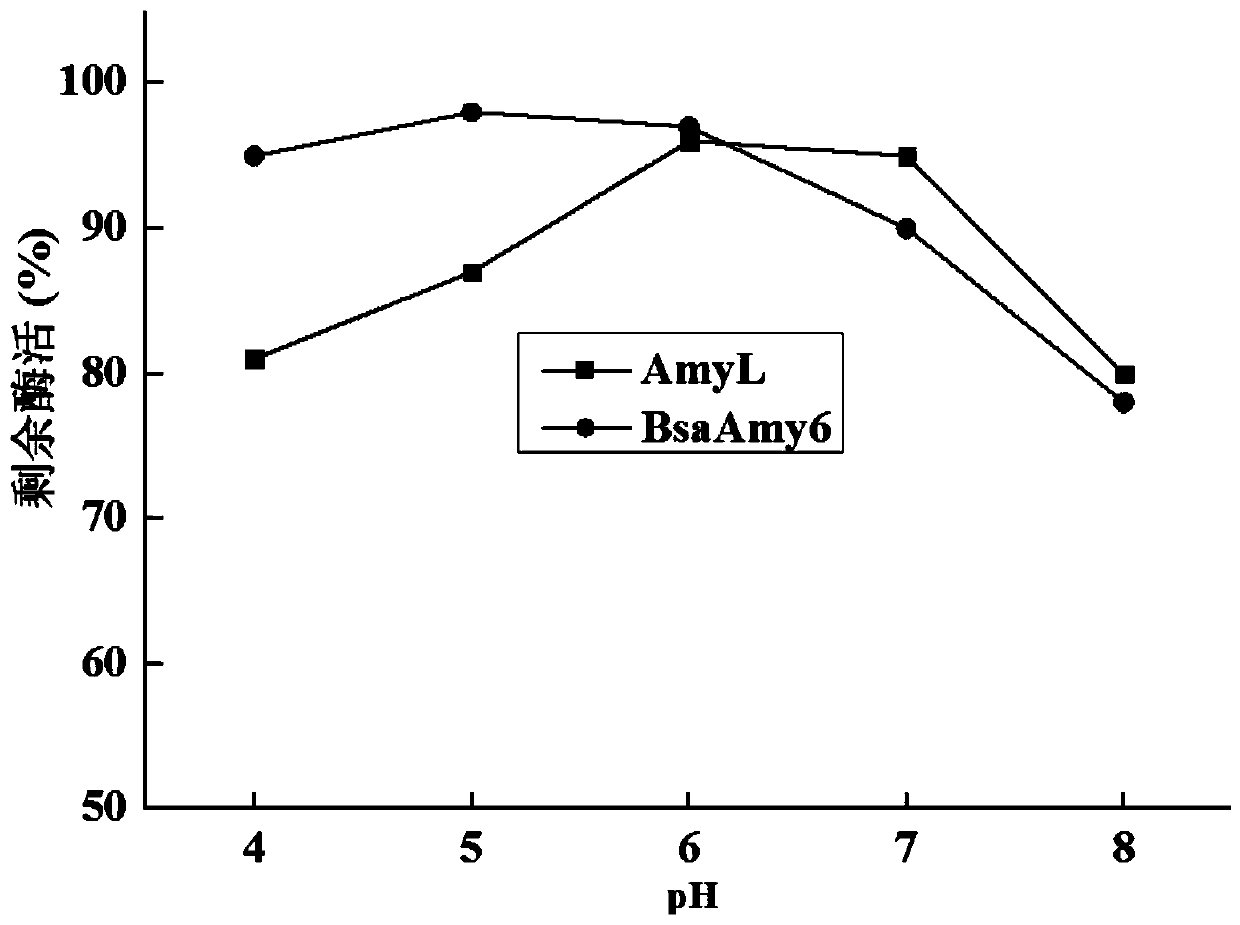
Activity-improved α-amylase amyl mutant and its coding gene and application
An amylase and mutant technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of high fermentation cost and low production activity, achieve huge application potential and reduce the cost of fermentation production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Example 1. Synthesis and cloning of the α-amylase AmyL gene of Bacillus salsus
[0042] The published amino acid sequence of Bacillus salsus α-amylase AmyL (Genebank: SDP85898) was synthesized according to the codon optimization of Pichia pastoris.
[0043] Design PCR primers containing EcoRI and NotI restriction enzyme sites at the 5' end and 3' end of the synthesized gene respectively, and the primer sequences are as follows:
[0044] 5' end primer amyl-F1: 5'-GTAGAATTC ATGAGACAGGTTAGAATTGCTTTTG-3'
[0045] 3' primer amyl-R1: 5'-ACTGCGGCCGCTTATTTTTGTACATAAACTGAAACT-3'
[0046] Using the synthetic gene as a template, PCR amplification was carried out with the above primers, and the amplified fragment was cloned into the vector pGAPzαA to obtain the recombinant vector pGAPzαA-AMYL.
Embodiment 2
[0047] Embodiment 2, gene error-prone PCR random mutation
[0048]Using the above pGAPzαA-AMYL as a template, carry out error-prone PCR random mutation amplification. The specific amplification method is:
[0049] The first round of amplification: use the vector promoter primers amyl-F1 and amyl-R1 as primers for PCR amplification, and the reaction system is as follows:
[0050]
[0051] The reaction procedure is as follows:
[0052]
[0053] The first-round PCR product was recovered, and 1uL was diluted 50-100 times to be used as a template for the second-round PCR. The second round of error-prone PCR also uses specific primers amyl-F1 and amyl-R1 for PCR reaction.
[0054] The product of the second round was double digested with EcoRI and NotI, and connected to the pGAPzαA vector. The ligation product was transformed into Pichia pastoris X33, and the mutant strains were screened on YPDZ agarose plate.
Embodiment 3
[0055] Embodiment 3, high-throughput screening high enzyme activity mutant strain
[0056] Pick mutant single colonies from the error-prone PCR plate in Example 2, pick the recombinant transformants one by one to a 24-well plate with a toothpick, add 1mL medium containing YPD to each well, culture at 30°C, 220rpm for about 48 hours, and take it by centrifugation. clear. 200 μL of the above supernatants were taken out to a 96-well plate for α-amylase activity assay. The detection of α-amylase activity was carried out with reference to the national standard "GB / T 24401-2009" of the People's Republic of China. Genomic DNA was extracted one by one from 8 positive mutant clones with improved enzyme activity, and the target gene was amplified by PCR to determine the mutation site.
[0057] The sequencing results determined the amino acid mutation site, the mutation site of clone 1 was +18N replaced by +18D; the mutation site of clone 2 was +39S replaced by +39N; the mutation site ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com