Method and system for processing high-calcium and high-phosphorus vanadium slag
A high-calcium, high-phosphorus vanadium slag, phosphorus-vanadium technology, applied in the field of metallurgy, can solve the problems of high CaO content, unsuitable and unusable, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
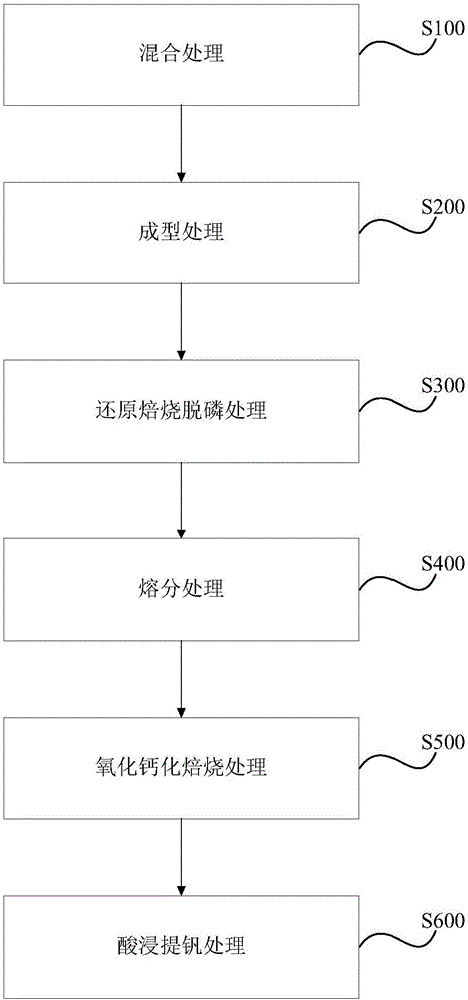
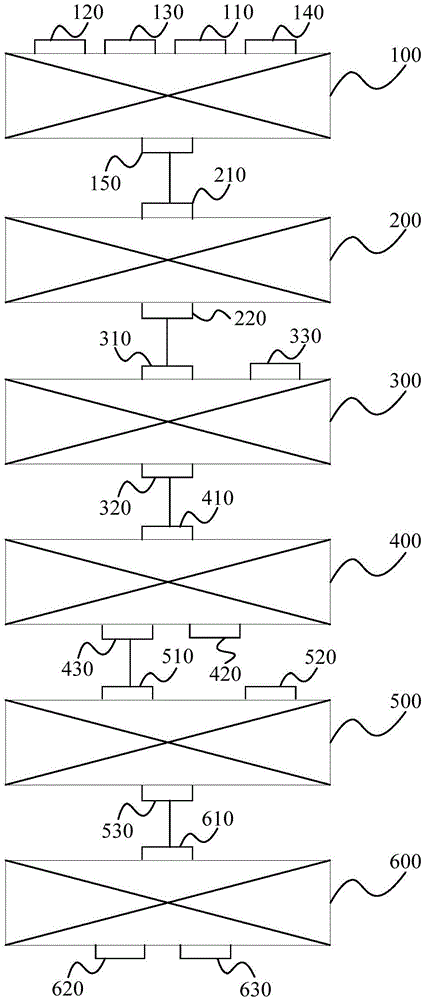
[0116] The high-calcium and high-phosphorus vanadium slag (CaO content is 3% by weight, P 2 o 5 Content is 0.2% by weight, V 2 o 5 Fe content is 20% by weight, Fe content is 35% by weight), silica, reduced coal and bentonite are mixed at a mass ratio of 100:5:15:2 to obtain a mixed material, and the mixed material is molded on a high-pressure double-roller ball press to obtain a mixed ball group. The mixed pellets are reduced and roasted in the tunnel kiln at 1200°C. Phosphorus mainly enters the flue gas in the form of phosphorus vapor. After the reaction, dephosphorized metallized pellets are obtained. The metallization rate of the dephosphorized metallized pellets is 80. %. The dephosphorized metallized pellets are melted on an electric furnace at a temperature of 1500°C to obtain molten iron and low-phosphorus vanadium slag. The molten iron can be sent to steelmaking, and the P in low-phosphorus vanadium slag 2 o 5 The Fe content is 0.09% by weight, and the Fe content...
Embodiment 2
[0118] The high-calcium and high-phosphorus vanadium slag (CaO content is 25% by weight, P 2 o 5 Content is 1% by weight, V 2 o 5 content is 5% by weight, Fe content is 20% by weight), silica, reduced coal and starch solution are mixed at a mass ratio of 100:15:8:3 to obtain a mixed material. The mixed material is molded on a high-pressure double-roller briquetting machine to obtain a mixed pellet. The mixed pellets are reduced and roasted in the tunnel kiln at 1400°C. Phosphorus mainly enters the flue gas in the form of phosphorus vapor. After the reaction, dephosphorized metallized pellets are obtained. The metallization rate of the dephosphorized metallized pellets is 75. %. The dephosphorized metallized pellets are melted on an electric furnace at a temperature of 1550°C to obtain molten iron and low-phosphorus vanadium slag. The molten iron can be sent to steelmaking, and the P in low-phosphorus vanadium slag 2 o 5 The Fe content is 0.05% by weight, and the Fe conte...
Embodiment 3
[0120] The high-calcium and high-phosphorus vanadium slag (CaO content is 15% by weight, P 2 o 5 Content is 0.6% by weight, V 2 o 5 content is 7% by weight, Fe content is 30% by weight), silica, reduced coal and water glass are mixed according to the mass ratio of 100:10:10:4 to obtain a mixed material. The mixed material is molded on a high-pressure double-roller briquetting machine to obtain a mixed pellet. The mixed pellets are reduced and roasted in the tunnel kiln at 1300°C, phosphorus enters the flue gas mainly in the form of phosphorus vapor, and dephosphorized metallized pellets are obtained after the reaction. The metallization rate of the dephosphorized metallized pellets is 82 %. The dephosphorized metallized pellets are melted on an electric furnace at a temperature of 1600°C to obtain molten iron and low-phosphorus vanadium slag. The molten iron can be sent to steelmaking, and P in low-phosphorus vanadium slag 2 o 5 The Fe content is 0.04% by weight, and the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com