Cadmium arsenide film-based passively mode-locked fiber laser
A fiber laser, passive mode-locking technology, applied in the field of laser technology and nonlinear optics, can solve the problems of inability to precisely control insertion loss of optical parameters, insignificant saturable absorption effect, narrow saturable absorption spectral range, etc., and achieve high stability The effect of stability, high repetition rate, high peak power
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
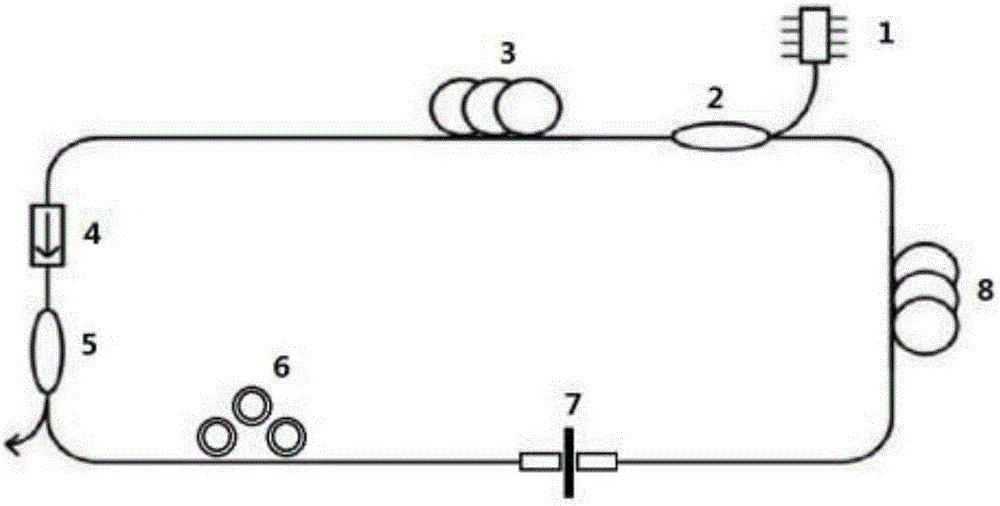
[0028]A passive mode-locked fiber laser structure based on cadmium arsenide thin film figure 1 shown. A pump source 1 with a central wavelength of 1550nm couples the pump light into a 2.5m rare-earth-doped gain fiber 3 through a 1550nm / 2000nm wavelength division multiplexer 2; the other end of the gain fiber 3 is connected to a 2μm polarization-independent isolator 4; The other end of the isolator 4 is connected to a 2 μm fiber coupler 5 with a beam splitting ratio of 30:70 and a 1X2 structure. The fiber coupler 5 has two output ports, the 30% end is used as the pulse laser output end, and the 70% end is connected to the polarization control 6; the polarization controller 6 is connected to the cadmium arsenide saturable absorber 7, and the cadmium arsenide saturable absorber 7 is connected to the ordinary single-mode fiber 8; the other end of the single-mode fiber 8 is connected to a 1550nm / 2000nm wavelength division multiplexer The 2000nm end; the polarization controller 6, ...
Embodiment 2
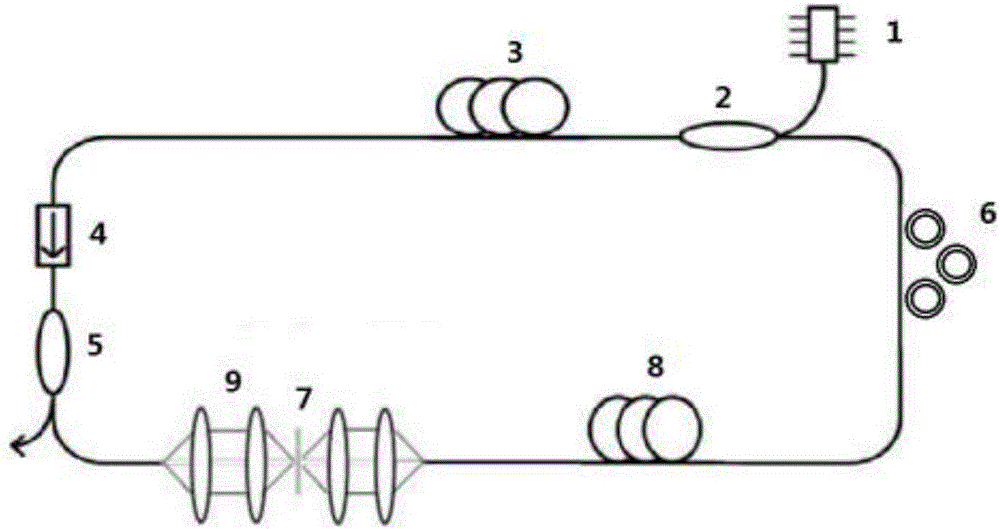
[0030] A passive mode-locked fiber laser structure based on cadmium arsenide thin film figure 2 shown. Central wavelength 1550nm pump source 1 is connected to the pump input end of 1550nm / 2000nm wavelength division multiplexer 2, and the pump light is injected into 2.5m rare earth-doped thulium-doped gain fiber 3; the gain fiber (3) is sequentially connected to 2μm A polarization-independent isolator (4) and a 2 μm fiber coupler 5 with a beam splitting ratio of 30:70 and a 1X2 structure; the fiber coupler 5 has two output ports, the 30% end is used as the pulse laser output end, and the 70% end couples the beam To the collimation-focusing system 9, and place the cadmium arsenide thin film saturable absorber 7 at the spot after focusing; in order to adjust the intracavity dispersion, connect the single-mode fiber 8; the other end of the single-mode fiber 8 is connected to the polarization controller 6, and the other end of the polarization controller 6 is connected to the 200...
Embodiment 3
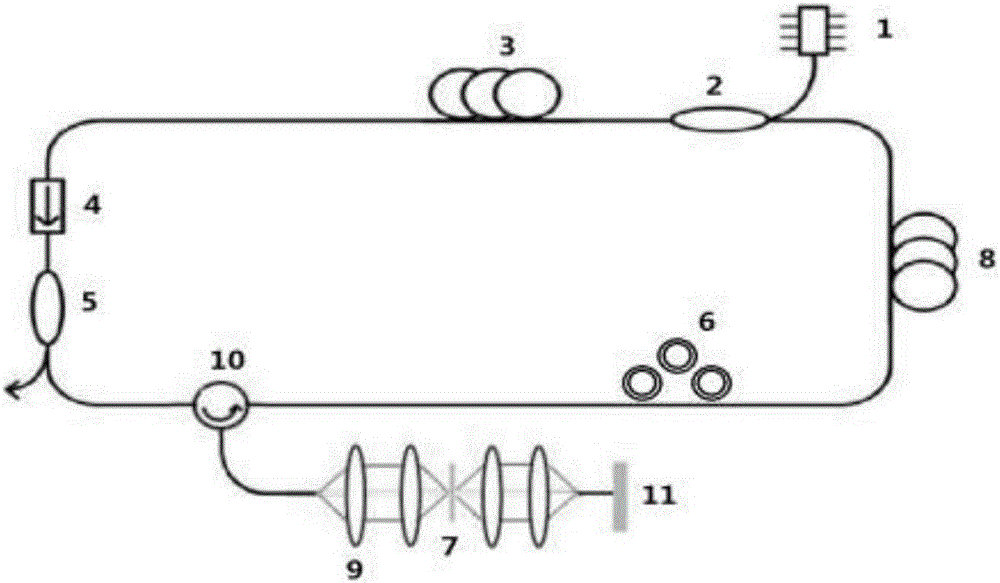
[0032] A passive mode-locked fiber laser structure based on cadmium arsenide thin film image 3 shown. The central wavelength of 1550nm pump source 1 is connected to the pump input port of 1550nm / 2000nm wavelength division multiplexer 2, and the pump light is injected into the 2.5m rare earth-doped thulium-doped gain fiber 3; A 2 μm fiber coupler 5 with a beam splitting ratio of 30:70 and a 1X2 structure of 2 μm fiber coupler 5, the fiber coupler 5 has two ports, the 30% end is used as the pulse laser output end, and the 70% end is connected to the No. 1 port of the 2 μm circulator 10 ; The second port of the circulator 10 couples the laser light into the collimation-focusing system 9, and places the cadmium arsenide thin film saturable absorber 7 at the focused spot; in order to form a reflective structure, another in the optical path A broadband total reflection golden mirror 11 is placed at one end; the No. 3 port of the circulator 10 is connected with the polarization con...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com