Molecular marker for indicating and identifying character of orange pulp of melon, and primer and application thereof
A molecular marker and molecular marker-assisted technology, which is applied to the determination/inspection of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve the problem of less use of CAPS molecular markers, so as to speed up the breeding work efficiency and shorten the breeding time. The effect of increasing the number of years and improving breeding efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Example 1: Development of Molecular Markers and Primers
[0033] In this example, the orange melon line MR-1 and the green melon line X191 were selected as experimental materials to develop CAPS molecular markers. The MR-1 and X191 melon lines were sequenced by high-throughput sequencing technology, and the sequence of the coding region of the CmOr gene of the melon was obtained through the GenBank website. By comparing the sequence with the sequencing material, the SNP mutation in the coding region of the CmOr gene of the melon was obtained. Interval, within this interval, the base segment with SNP mutation site in the sequencing data is mined, the enzyme digestion information of the SNP site is analyzed, and the sequence with CAPS mutation is obtained, that is, the CAPS molecular marker HF.
[0034] The melon CmOr gene sequence is located between chromosome 9 5207122-5214439. The nucleotide sequence of the molecular marker HF is shown in SEQ ID NO.1, wherein the 640t...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Embodiment 2: extraction of genomic DNA and PCR reaction
[0040] The leaves of MR-1 and X191 melon populations were collected, and the genomic DNA was extracted by the improved CTAB method.
[0041] The obtained CAPS primers and genomic DNA were used for PCR reaction, and the PCR reaction system was shown in Table 2 (20 μL):
[0042] Table 2 PCR reaction system
[0043]
[0044] Amplification was carried out by touchdown PCR (TD-PCR), the program was: 94°C pre-denaturation for 7 min, 94°C denaturation for 1 min, 60°C annealing for 30 s, 0.5°C reduction per cycle, 72°C extension for 90 s, 30 cycles; 94 Denaturation at ℃ for 30s, annealing at 45℃ for 30s, extension at 72℃ for 30s, 10 cycles; extension at 72℃ for 10min, storage at 4℃.
Embodiment 3
[0045] Example 3: Enzyme digestion verification of PCR products
[0046] Carry out the enzyme digestion reaction according to the Hinf I restriction endonuclease operation guide, and perform enzyme digestion verification on the obtained PCR product. The enzyme digestion system is shown in Table 3: (15.3 μL)
[0047] Table 3 enzyme digestion reaction system
[0048]
[0049]
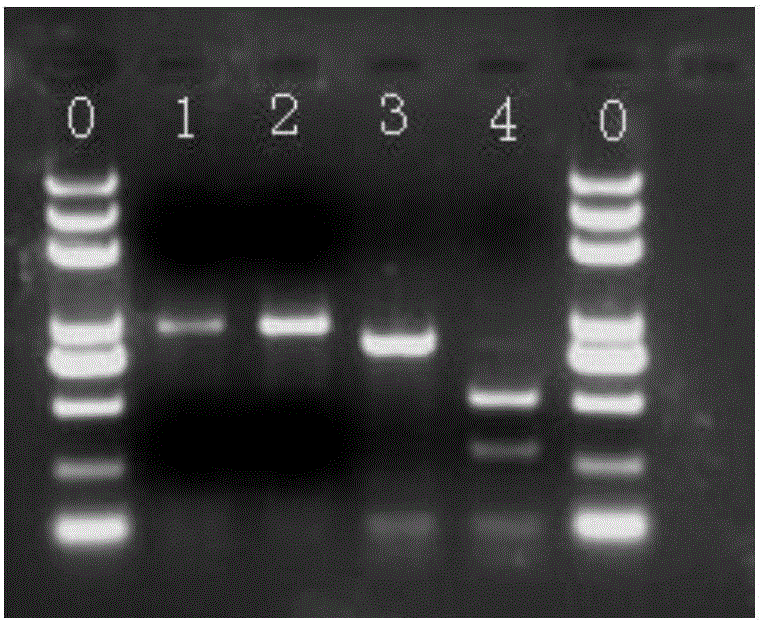
[0050] Enzyme digestion in 37°C water bath for 3-4 hours, and the digested products were detected by 1% agarose electrophoresis, and the detection results were as follows: figure 1 shown. X191 (green) was not cleaved by restriction endonucleases due to the absence of enzyme cleavage sites, and was still 946bp. Due to the presence of enzyme cleavage sites in MR-1 (orange), it was cleaved by HinfⅠ and obtained 640bp and 306bp fragment. The result is as figure 1 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com