Method for treating nitrobenzene exhaust gas by coupling bacterium biological filter bed
A biological filter bed, nitrobenzene technology, applied in gas treatment, separation methods, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of long start-up period of fungal filter bed, easy to contaminate bacteria, low metabolism rate, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
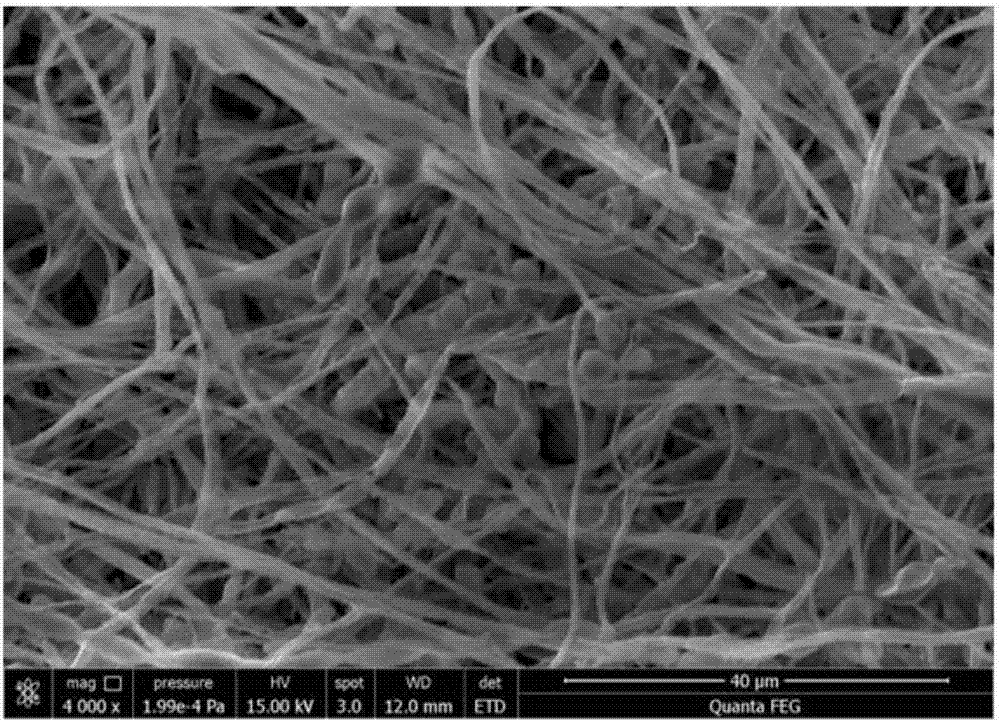
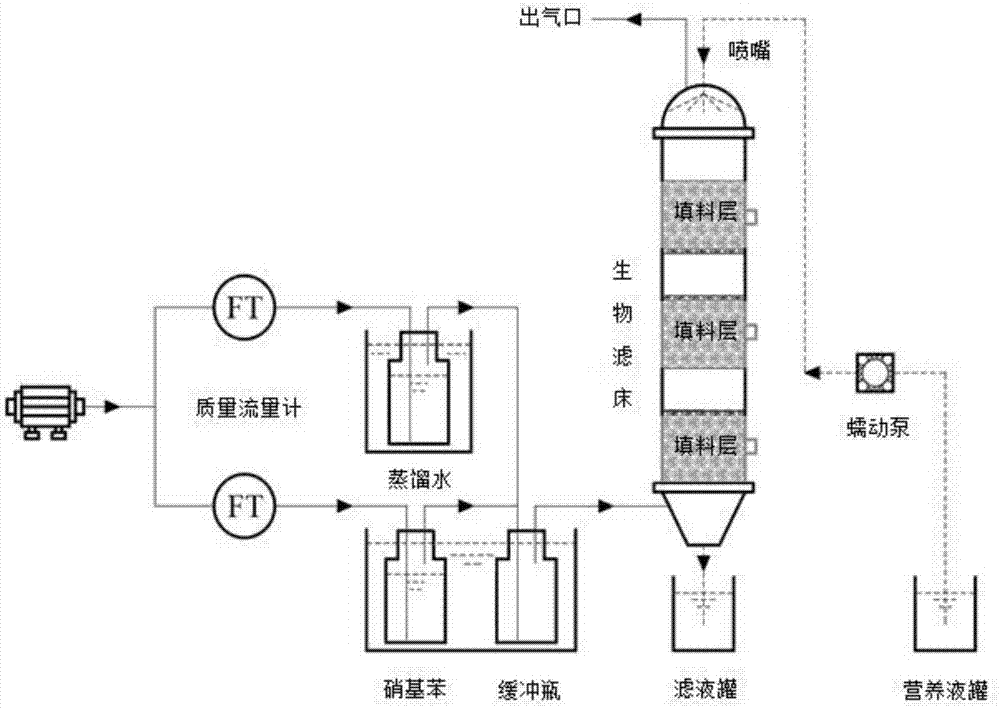
[0029] The polyurethane foam blocks with a side length of 4-6mm are used as fillers to construct the packed tower, which not only has a large surface area, but also does not cause compaction after the filler is filmed; the polyurethane foam blocks are filled into the packed tower by random stacking , the porosity of the polyurethane foam block filler is 95%, the pore diameter is 0.8mm, and the bulk density is 0.015g cm -3 , surface area is 1.7cm 2 cm -3 , water holding capacity of 55g-H 2 O g -1 ; The temperature of the packing layer is controlled at 20-25°C.
[0030] Prepared nutrient solution: Contains 0.5g K per liter 2 HPO 4 , 0.1g MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 4.5g KH 2 PO 4 , 2g NH 4 Cl and 2mL vitamin and trace mineral solution, the pH value of the nutrient solution was adjusted to 5.0.
[0031]Take the sludge from the secondary settling tank of the sewage treatment plant of the nitrobenzene production enterprise as the inoculation strain, and use the gas-liquid circulatio...
Embodiment 2
[0040] All the other operations are the same as in Example 1. After the biofilter bed is successfully coated, adjust the pH value of the nutrient solution to 5.0, when the nitrobenzene intake concentration is 400mg m -3 , the intake velocity is 107.6m h -1 , the residence time is 20s, the removal rate is 96%, and the removal capacity can reach 69.1g m -3 h -1 .
Embodiment 3
[0042] All the other operations are the same as in Example 1. After the biofilter bed is successfully coated, adjust the pH value of the nutrient solution to 5.0, when the nitrobenzene intake concentration is 350mg m -3 , the intake velocity is 107.6m h -1 , the residence time is 20s, the removal rate is 96.6%, and the removal capacity can reach 60.9g m -3 h -1 .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Side length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com