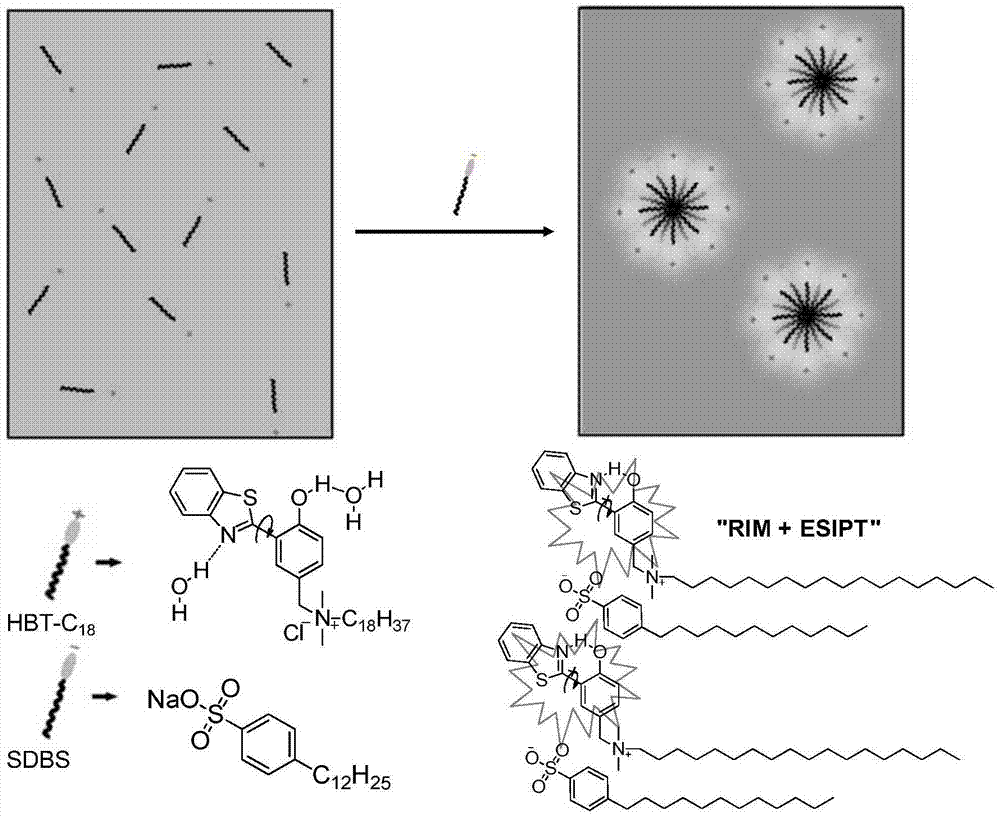
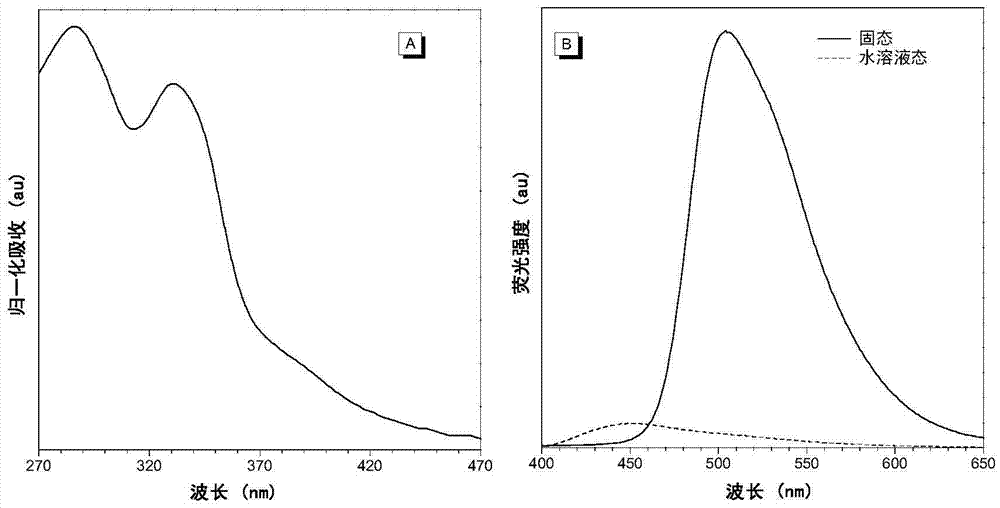
Fluorescent probe with aggregation-induced emission property, and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of surfactant and alkyl, which is applied in the field of surfactant detection, can solve the problems of fluorescence self-quenching, lower detection signal-to-noise ratio, etc., and achieve the effect of low toxicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] According to the following synthetic route, the following compounds are specifically synthesized:
[0066]
[0067] (1) Synthesis of N-(3-formyl-4-hydroxybenzyl)-N,N-dimethyloctadecyl-1-ammonium chloride (compound 3)
[0068] A mixture of 5-(chloromethyl)-2-hydroxysalicylaldehyde (340 mg, 2 mmol) and N,N-dimethyloctadec-1-amine (594 mg, 2 mmol) was stirred under reflux for 5 hours. After the reaction was complete, the precipitate was filtered and washed with diethyl ether (10 mL×2), and dried under vacuum to give the white solid product Compound 3 with a yield of 90% (841 mg).
[0069] 1 H NMR (CDCl 3 ,500MHz):δ11.26(br s,1H),8.16(d,J=3.5Hz,1H),7.80(d,J=8.5Hz,1H),7.09(d,J=8.5Hz,1H), 5.21(d, J=8.5Hz, 2H), 3.47(t, J=8.5Hz, 2H), 3.27(s, 6H), 1.26–1.25(m, 32H), 0.88(t, J=7.0Hz, 3H ); 13 C NMR(d 6 -DMSO,125MHz):190.0,162.3,140.1,132.9,122.5,118.8,118.0,65.3,63.1,48.7,31.3,29.0,29.0,28.9,28.76,28.66,28.5,25.8,22.1,21.7,13.9; ESI):m / z[M-Cl] + The computed value is C...
Embodiment 2
[0075] Embodiment 2: the detection of anionic surfactant
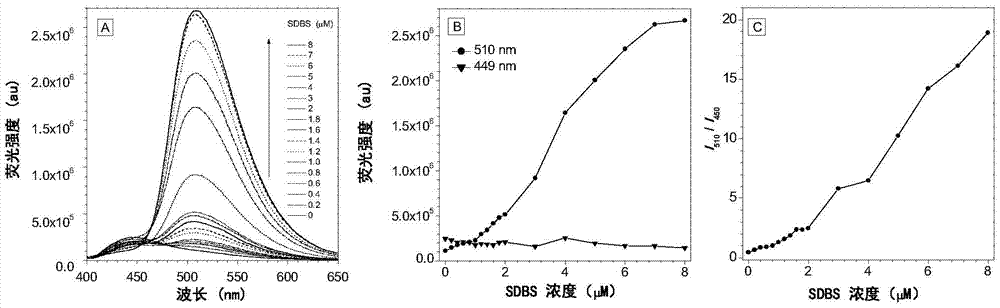
[0076] 15 μL of the HBT-C prepared in Example 1 18 The DMSO (1.0mM) mother solution was added to 2.985mL pure water containing different contents of anionic surfactant sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate (SDBS), vortexed for 10s, and the fluorescence was measured with a fluorescence spectrometer (excitation wavelength 334nm).
[0077] image 3 (A) is HBT-C with the increase of SDBS concentration 18 (5μM) in H 2 Fluorescence emission spectrum in O / DMSO (99:1, v / v) solution; (B) is HBT-C with the increase of SDBS concentration 18 Fluorescence emission intensity changes at 510nm and 450nm; (C) is as the increase of SDBS concentration, HBT-C 18 The ratio of the fluorescence emission intensity at 510nm and 450nm (I 510 / I 450 )Variety. lambda ex =334nm.
[0078] Figure 4 for HBT-C 18 (5μM) in H 2 Fluorescence quantum yield as a function of SDBS concentration in O / DMSO (99:1, v / v). As can be seen from the figure, HB...
Embodiment 3
[0085] Detection of different surfactants and ions
[0086] 15 μL of the HBT-C prepared in Example 1 18 Add 2.985mL of DMSO (1.0mM) mother solution containing different surfactants and ions (sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate (SDBS), sodium dodecylsulfate (SDS), Triton X-100, cetyl bromide Alkyltrimethylammonium (CTAB) and simple ions (such as: Na + ,K + ,Mg 2+ , Ca 2+ ,Zn 2+ NO 3 – , HCO 3 – , HCO 3 2– ,PO 4 3– , SO 4 2– )) in pure water, vortexed for 10 s, and measured fluorescence with a spectrofluorometer (excitation wavelength 334 nm). The result is as Figure 8 shown.
[0087] Figure 8 In the presence of different surfactants and ions, HBT-C 18 The ratio of the fluorescence emission intensity at 510nm and 450nm (I 510 / I 450 )Variety. The probe is highly sensitive to anionic surfactants with sulfonic acid groups, including: sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate (SDBS), sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), and neutral Surfactant Triton X-100 and cationic surfactant ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com