Special cast steel used for preparing large hot-work die under high temperature and heavy load conditions and preparation method of special cast steel
A hot forging die, a special technology, applied in the field of cast steel manufacturing, can solve the problems that the strength, plasticity and toughness cannot meet the requirements, and achieve the effects of avoiding serious failure, increasing service life and reducing scrap rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
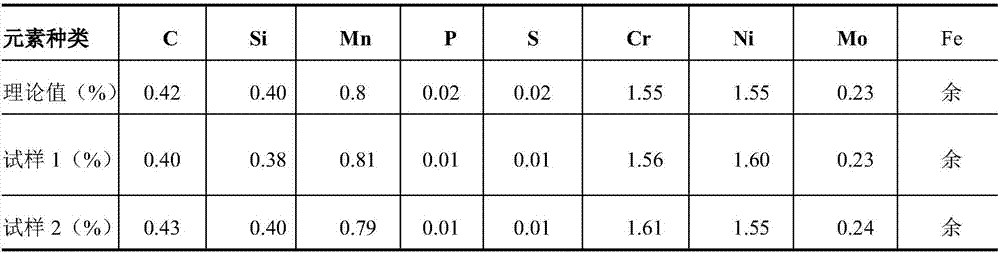
[0024] 1) Steelmaking and refining: In converter steelmaking, carbon and phosphorus in molten iron are removed to obtain molten steel; then the molten steel is refined in a refining furnace; the chemical composition of special cast steel is measured by mass percentage, and in the refining process Control the content of carbon element in molten steel to 0.42%, the content of silicon element to 0.4%, the content of manganese element to 0.8%, the content of phosphorus element to 0.02%, the content of sulfur element to 0.02%, the content of chromium element to 1.55%, nickel The element content is 1.55%, the molybdenum element content is 0.23%, and the balance is iron;
[0025] 2) Casting: Continuous casting of the molten steel obtained in step 1) to obtain a mold base billet;
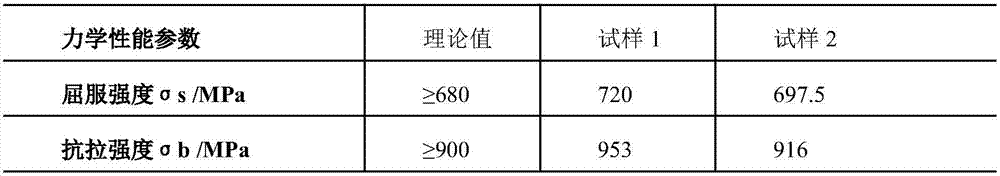
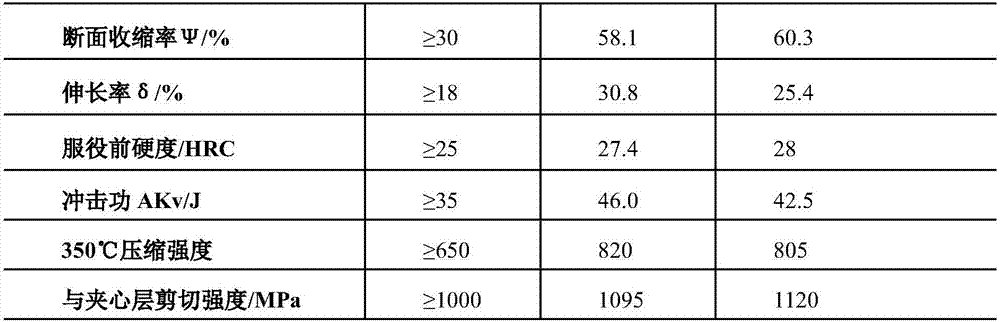
[0026] 3) Water quenching and oil-cooling the mold base billet in step 3), the quenching temperature is 890°C, and then tempering the oil-cooled mold base billet, controlling the tempering temperature to 62...
Embodiment 2
[0036] 1) Steelmaking and refining: In converter steelmaking, carbon and phosphorus in molten iron are removed to obtain molten steel; then the molten steel is refined in a refining furnace; the chemical composition of special cast steel is measured by mass percentage, and in the refining process Control the content of carbon element in molten steel to 0.35%, silicon element content to 0.2%, manganese element content to 0.60%, phosphorus element content to 0.02%, sulfur element content to 0.02%, chromium element content to 1.4%, nickel element content to 1.4%, molybdenum element content Content 0.15%, the balance is iron;
[0037] 2) Casting: Continuous casting of the molten steel obtained in step 1) to obtain a mold base billet;
[0038] 3) Water quenching and oil-cooling the mold base billet in step 3), the quenching temperature is 860°C, and then tempering the oil-cooled mold base billet, controlling the tempering temperature to 600°C;
[0039] 4) Removing the sticky sand,...
Embodiment 3
[0048] 1) Steelmaking and refining: In converter steelmaking, carbon and phosphorus in molten iron are removed to obtain molten steel; then the molten steel is refined in a refining furnace; the chemical composition of special cast steel is measured by mass percentage, and in the refining process Control the content of carbon element in molten steel to 0.5%, the content of silicon element to 0.6%, the content of manganese element to 1.0%, the content of phosphorus element to 0.02%, the content of sulfur element to 0.02%, the content of chromium element to 1.7%, nickel The element content is 1.7%, the molybdenum element content is 0.3%; the balance is iron;
[0049] 2) Casting: Continuous casting of the molten steel obtained in step 1) to obtain a mold base billet;
[0050] 3) Water quenching and oil cooling the mold base billet in step 3), the quenching temperature is 920°C, and then tempering the oil-cooled mold base billet, controlling the tempering temperature to 650°C;
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com