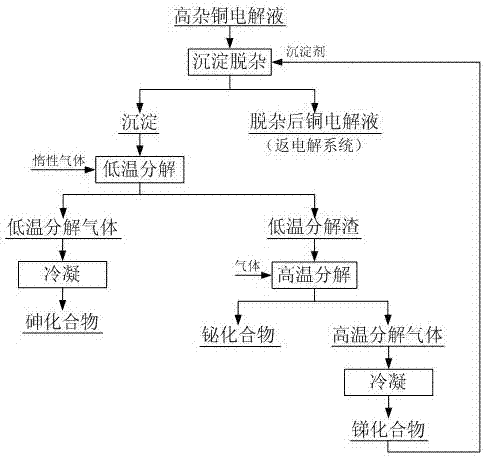
Method for carrying out precipitate impurity removal on copper electrolyte
A copper electrolyte and impurity removal technology, applied in the field of electrolyte purification, can solve the problems of long process flow, side effects of electrolyte, low impurity removal efficiency, etc., and achieve the effects of short process flow, simple operation and high removal rate.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] to 1 m 3 Add 15 kg of antimony trioxide to the copper electrolyte, react at a temperature of 85 °C for 1.0 hour, and filter to obtain a copper electrolyte of 0.99 m 3 and 24.46 kg of precipitation containing arsenic, antimony and bismuth, the removal rates of arsenic, antimony and bismuth in the copper electrolyte were 68.89%, 64.22% and 92.75%, respectively, and the precipitation reaction had a great influence on the copper and acid content in the copper electrolyte. The results of precipitation and impurity removal are as follows.
[0019] element
[0020] The precipitate containing arsenic, antimony and bismuth was decomposed under the protection of argon gas with a volume percentage of 99.99% at a temperature of 800 °C for 3 hours to obtain 17.58 kg of low-temperature decomposition slag and low-temperature decomposition gas. The low-temperature decomposition gas was condensed to obtain purity 98.59% As 2 o 3 6.88 kg; the low-temperature decomposition s...
Embodiment 2
[0022] to 1 m 3 Add 20 kg of antimony pentoxide to the copper electrolyte, react at a temperature of 65 °C for 1.5 hours, and filter to obtain a copper electrolyte of 0.99 m 3 and 33.21 kg of precipitation containing arsenic, antimony and bismuth, the removal rates of arsenic, antimony and bismuth in the copper electrolyte were 72.15%, 87.04% and 93.14%, respectively, and the precipitation reaction had a great influence on the copper and acid content in the copper electrolyte. The results of precipitation and impurity removal are as follows.
[0023] element
[0024] The precipitate containing arsenic, antimony and bismuth was decomposed at 700 °C for 2.5 h under the protection of argon gas with a volume percentage of 99.99%, and 23.26 kg of low-temperature decomposition slag and low-temperature decomposition gas were obtained. The low-temperature decomposition gas was condensed to obtain purity 99.04% As 2 o 3 9.95 kg; the low-temperature decomposition slag was ...
Embodiment 3
[0026] to 1 m 3 Add 32 kg of antimony pentoxide and 8 kg of antimony trioxide to the copper electrolyte, react at a temperature of 75 °C for 1.0 hour, and filter to obtain a copper electrolyte of 0.98 m 3 and 60.19 kg of precipitation containing arsenic, antimony and bismuth, the removal rates of arsenic, antimony and bismuth in the copper electrolyte were 71.65%, 79.53% and 94.18%, respectively, and the precipitation reaction had a great influence on the copper and acid content in the copper electrolyte. The results of precipitation and impurity removal are as follows.
[0027] element
[0028] The precipitate containing arsenic, antimony and bismuth was decomposed under the protection of argon gas with a volume percentage of 99.99% at a temperature of 550 °C for 3.0 h to obtain 42.90 kg of low-temperature decomposition slag and low-temperature decomposition gas. The low-temperature decomposition gas was condensed to obtain purity 99.48% As 2 o 3 17.29 kg; the l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com