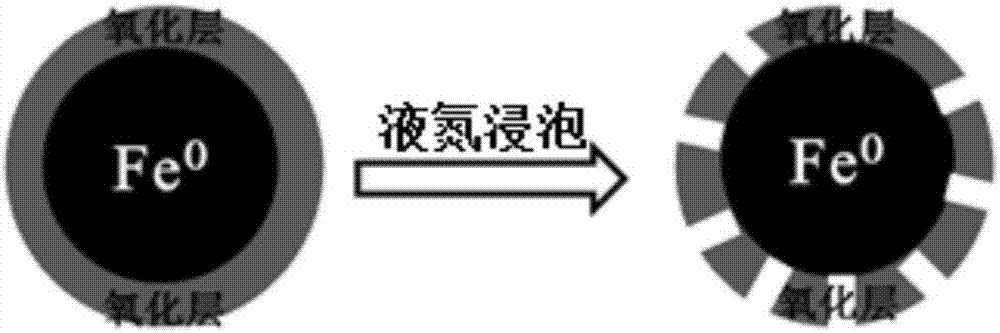
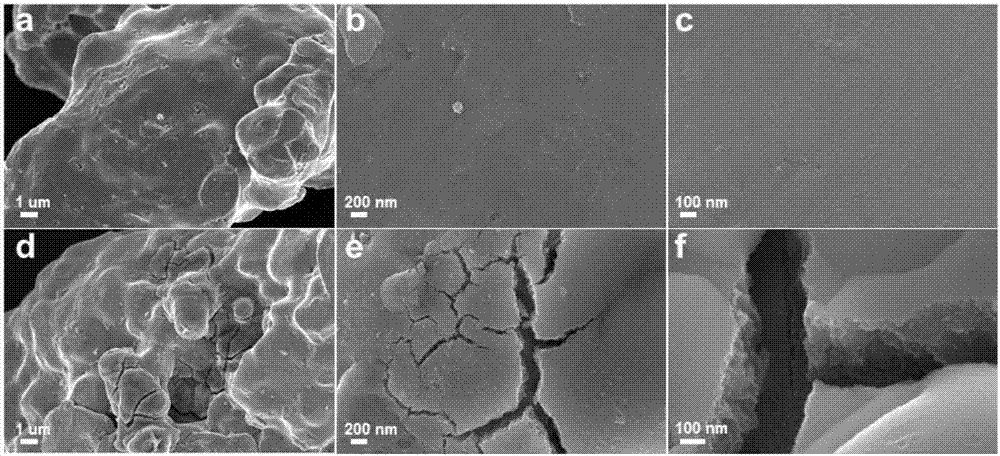
Method for treating commercial iron powder by liquid oxygen at low temperature for enhancing pollutant reductive removal ability
A technology for low temperature treatment and pollutants, applied in the field of environmental chemistry, can solve the problems of low pollutant removal activity and poor reducing ability, and achieve the effects of easy acquisition, simple method and easy preparation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
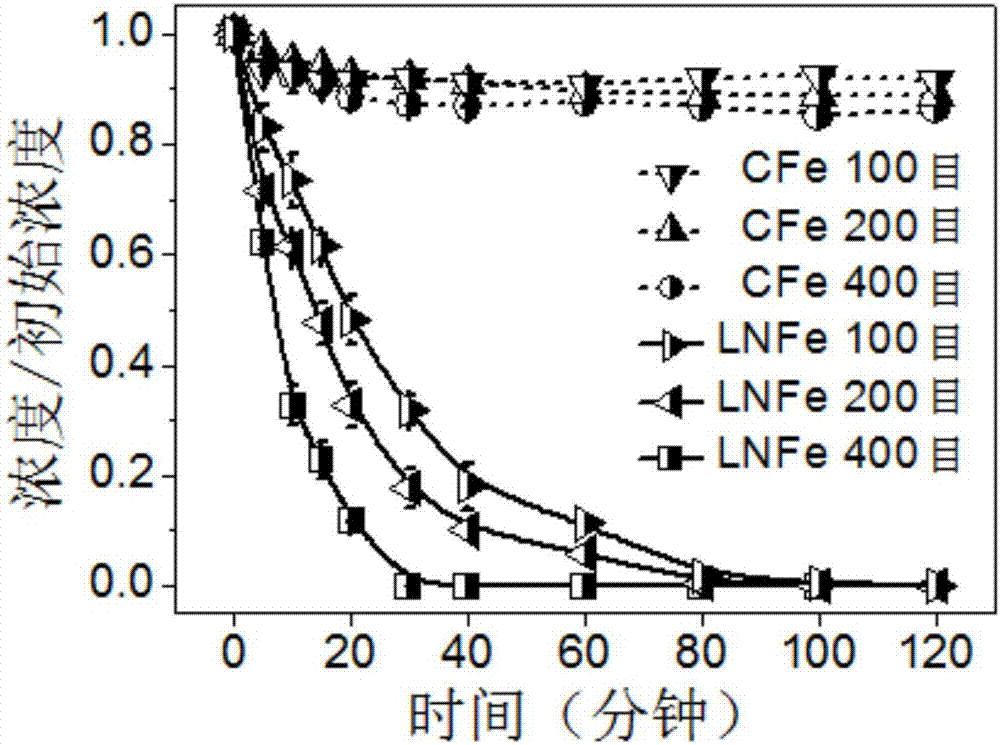
[0028] Example 1 Effect diagram of treating hexavalent chromium in polluted water by low-temperature treatment of iron powder with different particle sizes in liquid nitrogen
[0029] Pour 1g of commercial iron powder with a particle size of 100 mesh, 200 mesh, and 400 mesh into a Dewar bottle containing 1.0L liquid nitrogen. The iron powder has been sinking at the bottom of the Dewar bottle under the action of gravity. Nitrogen is poured into a liquid nitrogen bottle for recycling. After the residual liquid nitrogen is volatilized, the iron powder is poured out and dried at 50 degrees under the protection of nitrogen, which is the commercial iron powder (LNFe) treated with liquid nitrogen. Use 20mL of potassium dichromate aqueous solution with a hexavalent chromium concentration of 2mg / L to simulate chromium wastewater, add 0.1g of commercial iron powder (LNFe) treated at low temperature with liquid nitrogen, put it into a shaker with a rotation speed of 200rpm / min, take regul...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Example 2 Effect diagram of liquid nitrogen low temperature treatment of 200 mesh iron powder to treat bromate in water
[0031] Put 2g of commercial iron powder with a particle size of 200 mesh into a Dewar bottle containing 1.0L liquid nitrogen and soak for 20min, then pour out the iron powder and dry it under the protection of nitrogen. Use 20 mL of 2 mg / L bromate aqueous solution to simulate bromate-containing wastewater, add 0.5 g of commercial iron powder (LNFe) treated at low temperature with liquid nitrogen, and put it into a shaker with a rotation speed of 200 rpm / min. Sampling at regular intervals, measuring its concentration with anion chromatography, and using commercial iron powder (CFe) as a control test at the same time, the results are shown in Figure 4 . After 180 minutes of reaction, the bromate removal rate of commercial iron powder LNFe treated at low temperature with liquid nitrogen reached 100%, while the removal rate of commercial iron powder (C...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Example 3 Low-temperature treatment of 100-mesh iron powder with liquid nitrogen to treat uranyl ions in nuclear industry wastewater
[0033] Put 5 g of commercial iron powder with a particle size of 100 mesh into a Dewar bottle containing 1.0 L of liquid nitrogen and soak for 60 minutes, then pour out the iron powder and dry it under the protection of nitrogen. Use 20mL of uranyl aqueous solution of 20mg / L to simulate nuclear industry wastewater, add 0.2g of commercial iron powder (LNFe) treated at low temperature with liquid nitrogen, put it into a shaker with a rotation speed of 200rpm / min, take samples regularly and measure the concentration of uranyl, the results are shown in Figure 5 . After 50 minutes of reaction, the removal rate of commercial iron powder LNFe treated with liquid nitrogen at low temperature reached 100%, while the removal rate of commercial iron powder (CFe) was 35%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com