Gene mutation detection method and fluorescence-labeled oligonucleotide used in same
An oligonucleotide and fluorescent labeling technology, applied in the field of oligonucleotides, can solve the problems of impossible to correctly distinguish signals and difficult on-site application, and achieve the effect of high sensitivity and high precision
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
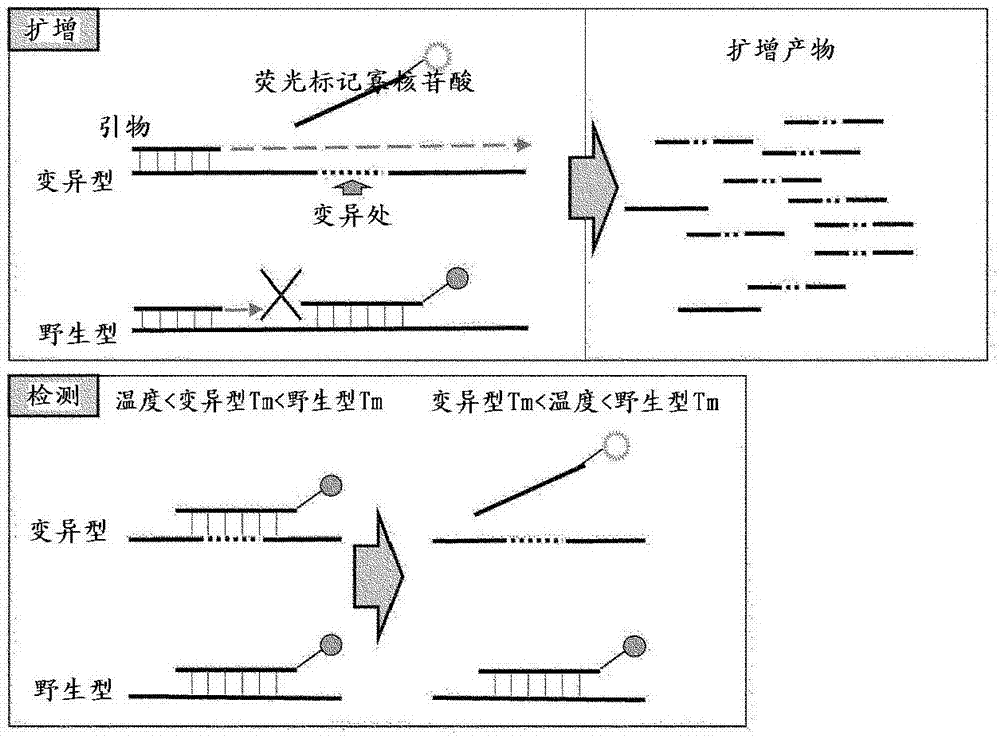
[0041] Next, the present invention will be described in further detail with reference to preferred embodiments. In the present invention, DNA, RNA, cDNA, mRNA, rRNA, NTPs, dNTPs, fluorescently labeled oligonucleotides, hybridization, hybridization, intercalator, primer, annealing, extension reaction, thermal denaturation reaction, nucleic acid melting curve, PCR, Terms such as RT-PCR, PCR method using PNA, devices for nucleic acid detection (gene detection), SNP (SNP: single nucleotide polymorphism), etc. are commonly used in molecular biology, genetic engineering, etc. The terms have the same meaning.
[0042] In the present invention, "wild-type gene" refers to a gene that has no variation in the nucleotide sequence and contains genetic information that functions normally. Herein, the genetic information refers not only to the transcriptional region encoding information such as rRNA, mRNA, etc., but also includes regulatory regions of expressed genes such as promoters.
[...
Embodiment 1
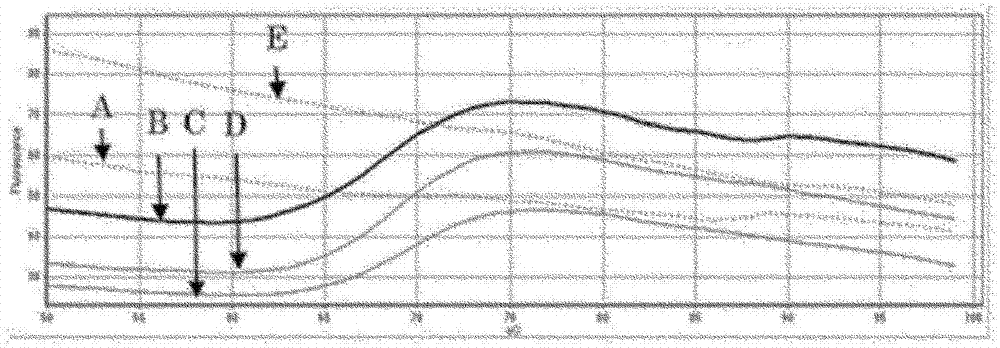
[0070] [Example 1] High-sensitivity detection of JAK2 gene variation (model system with PCR product as target)
[0071] As a template for the PCR reaction, the PCR product (363 bp) of a part of the human JAK2 gene sequence is a wild-type gene: the ratio of the mutant gene is 0:100, 90:10, 99:1, 99.5:0.5, 99.9:0.1, The method of 100:0 was set to a total of 10,000 copies / μl and prepared. Each reaction solution contained: 1 μl of template DNA (10000 copies), KOD+DNA polymerase (Toyobo Co., Ltd.) as a DNA polymerase, 4 kinds of dNTPs (0.2 mM each), forward primer (SEQ ID NO: 1. Final concentration 1.0 μM), reverse primer (SEQ ID NO: 2, final concentration 0.2 μM), magnesium sulfate solution (final concentration 1 mM), specified amount of KOD+ polymerase, and the 3' end with carboxy rhodan Ming 6G (CR6G) labeled quencher probe (SEQ ID NO: 3, final concentration 0.05 μM). Furthermore, the quencher probe functions as a clamp primer and a fluorescently-labeled oligonucleotide for de...
Embodiment 2
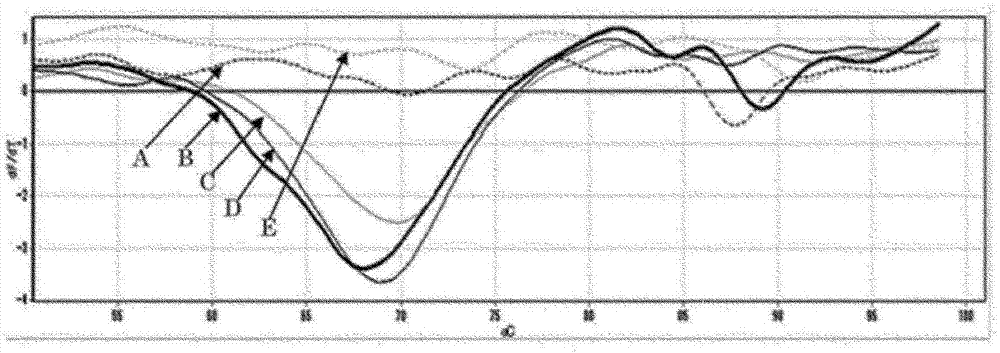
[0085] [Example 2] High-sensitivity detection of JAK2 gene variation (real sample)
[0086] Genomic DNA was extracted from the blood of a myeloproliferative neoplasm patient and used as a template DNA for PCR. In addition, DNA extraction was performed using QIAamp DNA Mini Kit (Qiagen). Each reaction solution is: PPD mix (Toyobo Co.), forward primer (SEQ ID NO: 1, final concentration 1.2 μM) dissolved in PPD mix, reverse primer (SEQ ID NO: 4, final concentration 0.2 μM) ) and the quenching probe (SEQ ID NO:5, final concentration 0.12 μM) whose 3' end was labeled with carboxyrhodamine 6G (CR6G) mixed solution 2.4 μl, KOD mix (Toyobo Co., Ltd.) 3.6 μl, containing A solution of 30 ng of genomic DNA and 6 μl of sterilized water were prepared to make a total of 12 μl. In addition, the quencher probe functions as a clamp primer and a fluorescently-labeled oligonucleotide for detection of a target nucleic acid in the same manner as in [Example 1].
[0087] In the following sequenc...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com