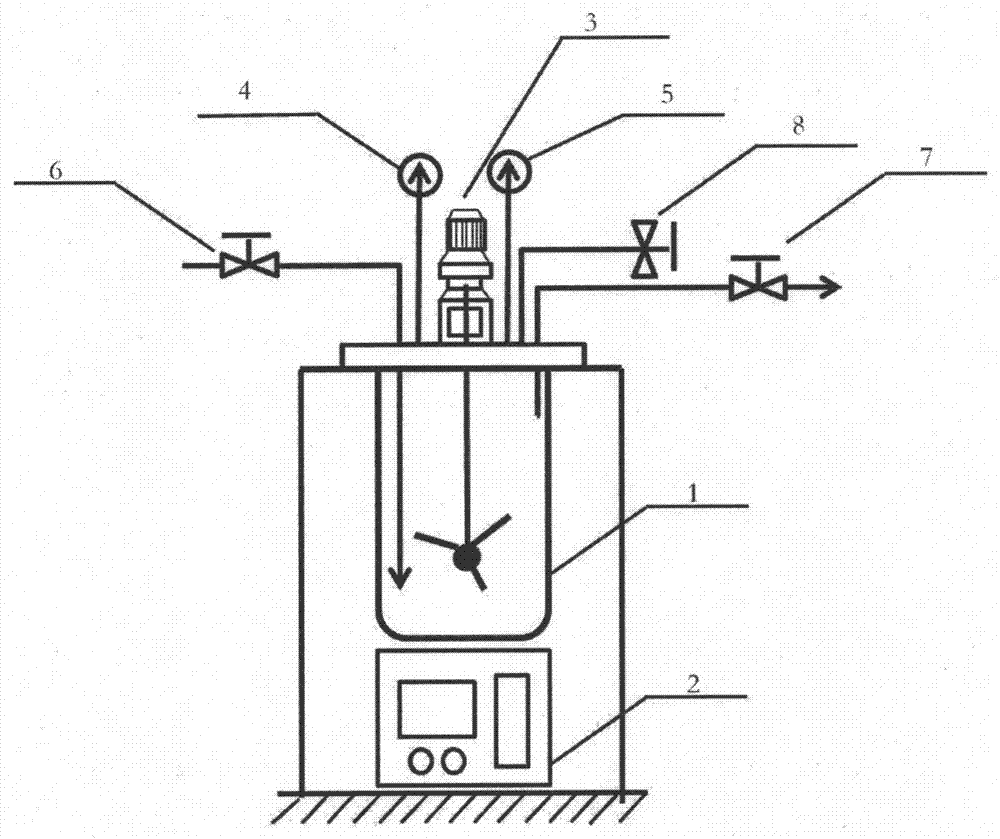
Method for improving dry weight reduction and dehydration performance of organic waste
A technology for organic waste and dehydration performance, applied in chemical instruments and methods, dehydration/drying/thickened sludge treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problem of high cost, uneven heating of waste sludge, no reduction In order to achieve the effect of low energy consumption, improve the effect of dry weight loss and dehydration performance, and promote the dissolution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] (1) First configure 1000g pretreatment agent: 0.5% oxalic acid, 15% acetic acid, 10% citric acid and 74.5% water by mass percentage, promptly weigh 5g oxalic acid, 150g acetic acid, 100g citric acid and 745g water respectively, and mix the four Together, stir properly, set aside.
[0032] (2) then take by weighing 300g of organic waste with a water content of 40% and pour it into a high-pressure reactor, then add a dosage of 4g / g pretreatment agent for dry organic waste in the reactor, namely take 720g of pretreatment agent Pour it into a high-pressure reactor and keep stirring at a speed of 80r / min for 30 minutes to fully mix the organic waste and the pretreatment agent evenly.
[0033] (3) After stirring evenly, close the reactor, prepare to turn on the power supply and start the pre-heating reaction, and at the same time ensure that the stirring motor continues to stir at a speed of 80r / min during the reaction process. When the temperature of the material in the rea...
Embodiment 2
[0037] (1) First configure 10g of pretreatment agent: 15% propionic acid, 40% lactic acid, 10% oxalic acid, 11% acetic acid and 24% water by mass percentage, that is, weigh 1.5g propionic acid, 4g lactic acid, 1g oxalic acid, 1.1 1 g of acetic acid and 2.4 g of water, the five are mixed together, stirred properly, and set aside.
[0038] (2) then take by weighing 200g of organic waste with a water content of 99% and pour it into a high-pressure reactor, then add a dosage of 0.1g / g pretreatment agent for dry organic waste in the reactor, namely take 0.2g pretreatment Pour the treatment agent into the high-pressure reactor and keep stirring at a speed of 200r / min for 5 minutes to fully mix the organic waste and the pretreatment agent evenly.
[0039](3) After stirring evenly, close the reactor, prepare to turn on the power supply and start the pre-heating reaction, and at the same time ensure that the material is continuously stirred at a speed of 200r / min during the reaction pr...
Embodiment 3
[0043] (1) First configure 10g pretreatment agent: 15% lactic acid, 55% citric acid and 30% water by mass percentage, that is, weigh 1.5g lactic acid, 5.5g citric acid, and 3g water respectively, and mix the three together. Stir well and set aside.
[0044] (2) then take by weighing 50g of organic waste with a water content of 84% and pour it into a high-pressure reactor, then add a dosage of 0.5g / g pretreatment agent for dry organic waste in the reactor, namely take 4g of pretreatment Pour the agent into the high-pressure reactor, and keep stirring at a speed of 150r / min for 20 minutes to fully mix the organic waste and the pretreatment agent evenly.
[0045] (3) After stirring evenly, close the reactor and prepare to turn on the power to start the pre-heating reaction, while ensuring that the stirring motor continues to stir at a speed of 150r / min during the reaction process. When the temperature of the material in the reactor rises to 110°C, start counting down for 60 minu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com