Method for treating tailings after extracting metal from electroplating sludge
A treatment method and electroplating sludge technology are applied in the field of treatment of tailings after metal extraction in electroplating sludge, which can solve problems such as incomplete leaching, and achieve the effects of easy control of conditions, reduction of process flow, and widening of application scope.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
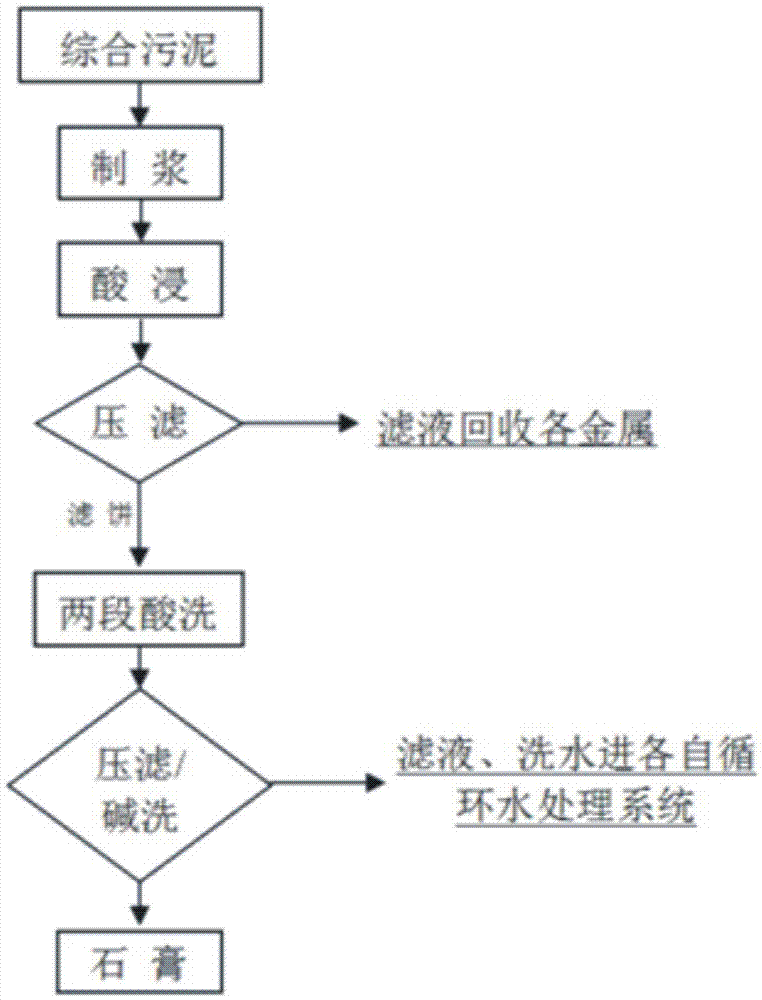
[0025] A treatment method for tailings after metal extraction in electroplating sludge: (the process flow chart is as follows figure 1 shown)
[0026] (1) Slurry: Pulverize the comprehensive electroplating sludge raw material containing copper, nickel, zinc, chromium, and cadmium. The main metal components of the raw material are shown in Table 1, and mixed with water at a mass ratio of 1:4 to obtain a mixed slurry. The solid ratio is 1~5:1;
[0027] (2) Acid leaching: fully stir the pulped sludge, and add 98% sulfuric acid until the pH value of the slurry is ≤0.5 and remains stable within 30 minutes;
[0028] (3) Pressure filtration: The sludge after acid leaching is subjected to solid-liquid separation, and the filter cake is washed with a dilute sulfuric acid solution with a pH value of 0.5 until the washing water is colorless, and the filtrate is collected;
[0029] (4) Two-stage pickling: Slurry the press-filtered filter cake and water at a mass ratio of 1:2, and adjust...
Embodiment 2
[0037] A method for treating tailings after metal extraction from electroplating sludge
[0038] The operation steps are the same as in the examples, except that the main metal components of the material are shown in Table 3, and the specific composition ratios in the finally obtained gypsum are shown in Table 4.
[0039] Table 3 List of main metal components of raw materials
[0040] .
[0041] Table 4 Composition list of gypsum products
[0042] .
[0043] Note: The determination of crystal water shall be carried out according to GB / T 5484, and the determination of sulfur trioxide shall be carried out according to GB / T 5484. According to the calculation method of 6.2 grade in GB / T5483-2008, the grade of gypsum (calcium sulfate dihydrate) is 85.34%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com