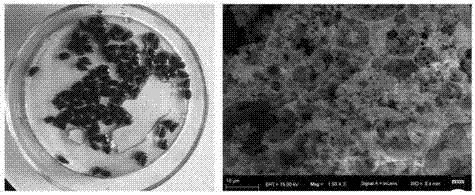
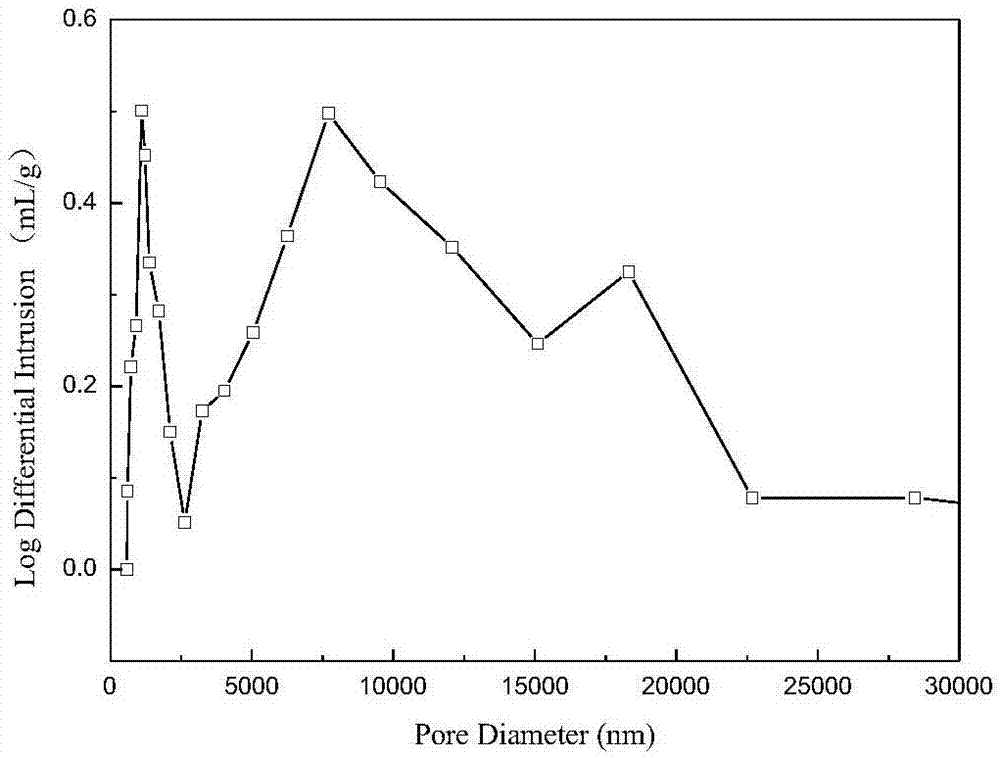
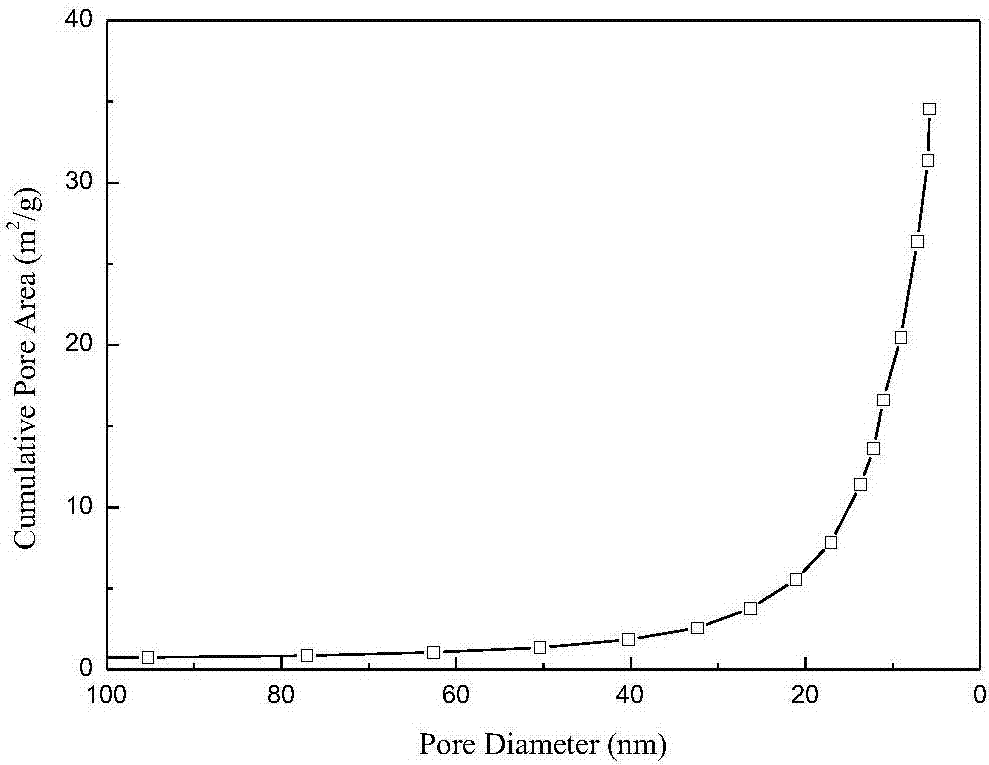
Preparation method of porous magnetic polymeric microspheres containing active polymerization sites
An active polymerization and polymer technology, which is applied in the field of preparation of porous magnetic polymer microspheres containing active polymerization sites, can solve the problems of easy loss and oxidation, unseen, poor magnetic stability, etc., and achieves a wide application value. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Example 1: Preparation of Porous Magnetic Polymer Microspheres Containing Active Polymerization Sites
[0029] Dissolve 0.06g of azobisisobutyronitrile in a mixture of 2.1g of glycidyl methacrylate and 3g of divinylbenzene; add 0.075g of 1,1-diphenylethylene, 1.5g of Span-80 and 0.225g of ferric oxide nanoparticles modified by oleic acid were fully mixed and ultrasonically dispersed to obtain the continuous phase; 27.84g of calcium chloride aqueous solution with a mass fraction of 5% was weighed as the dispersed phase; the continuous phase was placed In a three-necked flask, add the dispersed phase dropwise under mechanical stirring, and continue stirring for 30 minutes after the dropwise addition to obtain a water-in-oil type high internal emulsion. The dropping speed was controlled at 0.4mL / min, and the stirring speed was 500r / min; the obtained high internal emulsion was transferred to a syringe, and the emulsion was added dropwise to the aqueous solution of polyvinyl...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Example 2: Preparation of Porous Magnetic Polymer Microspheres Containing Active Polymerization Sites
[0031] Dissolve 0.10g of azobisisobutyronitrile in a mixture of 2.0g of glycidyl methacrylate, 2.0g of methyl methacrylate and 4.5g of ethylene glycol dimethacrylate; add 0.20g of 1-phenyl-1-naphthylethylene, 3.0g of Span-60 and 4.8g of ferric oxide nanoparticles modified by oleic acid, fully mixed, and ultrasonically dispersed to obtain a continuous phase; weigh 49.8g with a mass fraction of 4 % calcium chloride aqueous solution is used as the dispersed phase; the continuous phase is placed in a three-necked flask, and the dispersed phase is added dropwise to it under mechanical stirring, and the stirring is continued for 30 minutes after the addition is completed to obtain a water-in-oil type high internal emulsion. The dropping speed was controlled at 0.3mL / min, and the stirring speed was 400r / min; the obtained high internal emulsion was transferred to a syringe, a...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Example 3: Preparation of Porous Magnetic Polymer Microspheres Containing Active Polymerization Sites
[0033] Dissolve 0.06g of azobisisobutyronitrile in a mixture of 3.0g of methyl methacrylate and 3.6g of 1,1-diphenylethylene; add 0.06g of 1-phenyl-1- Naphthylethylene, 1.5g of Tween-60 and 0.24g of ferric oxide nanoparticles modified by oleic acid were mixed thoroughly and ultrasonically dispersed to obtain a continuous phase; 42.3g of calcium chloride aqueous solution with a mass fraction of 7% was weighed as a dispersion phase; the continuous phase was placed in a three-necked flask, and the dispersed phase was added dropwise to it under mechanical stirring, and the stirring was continued for 30 minutes after the dropwise addition was completed to obtain a water-in-oil type high internal emulsion. The dropping rate was controlled at 0.6mL / min, and the stirring speed was 450r / min; the obtained high internal emulsion was transferred to a syringe, and the emulsion was...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com