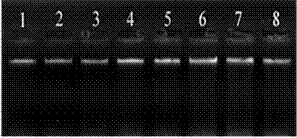
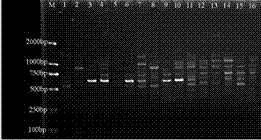
Method for extracting DNA from Xinjiang garlic wild relative species
An extraction method and technology of related species, applied in the field of plant molecular biology research, to achieve the effects of low environmental risk, short time consumption, and cost reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Example 1 A method for extracting genomic DNA from seeds of wild relatives of garlic in Xinjiang, referring to the method of Wang Zifeng with slight modifications, includes the following steps:
[0037] (1) From early to mid-August, in the original environment of Tianchi Lake in Tianshan Mountains (43°54′2.41″N, 88°07′18″E; altitude 1891m), the seeds of wild relatives of garlic (Garlicum prismatica) were used as materials, and the phenology The stage is in the fruit ripening stage. When the capsules are cracked and the pericarp is withered yellow, collect the mature seeds, put them in a kraft paper bag (envelope), bring them back to the laboratory, and dry them at room temperature for 7 days.
[0038] (2) Determination of seed water content: Randomly select the collected seeds, weigh them with an electronic balance, and record it as W 1 , and then put the seeds in an oven at 120°C, take them out every 4 hours and weigh them after the temperature drops to room temperatur...
Embodiment 2
[0050] The mensuration of embodiment 2 seed water content
[0051] 1. Materials
[0052] Randomly select about 1000 grains of rib-leaved garlic seeds that are uniform in size, plump, and dried naturally, and weighed with an electronic balance, recorded as W 1 , and then put the seeds in an oven at 120°C, take them out every 4 hours and weigh them after the temperature drops to room temperature, and repeat it several times until the weight of the seeds remains constant after drying, which is recorded as W 2 , thus calculate the seed water content (%) = (W 1 -W 2 ) / W 1 ×100%. Each treatment was repeated 5 times, and the average value was taken.
[0053] 2. Result analysis
[0054] Table 1 shows the water content of seeds
[0055] repeat
[0056] It can be seen from the table that the thousand-grain weight of garlic with ribbed leaves is 0.4924g, and the average water content is 8.328%.
Embodiment 3
[0057] Example 3 A method for extracting genomic DNA from leaves of wild relatives of garlic, slightly modified with reference to the method of Shi C, including the following steps:
[0058] (1) Use the dried leaves of the wild relative species of garlic (Allium prismatica) as materials, pick fresh leaves during the leaf-expansion stage, put them in a ziplock bag with silica gel, and dry them for 15-30 days.
[0059] (2) Weigh 2 g of completely dried leaves, grind them into powder quickly under liquid nitrogen conditions, and transfer them to a centrifuge tube.
[0060] (3) Add 65°C preheated SDS extraction buffer (same as in Example 1) to the tube, add 20 μL of precooled β-hydroxyethanol, and quickly vortex to mix.
[0061] (4) Place the centrifuge tube in a 65°C water bath and keep it warm for 60 minutes, during which time it is mixed slowly 8 times.
[0062] (5) Take out the centrifuge tube and cool it to room temperature, wipe off the water droplets on the outer wall of t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com