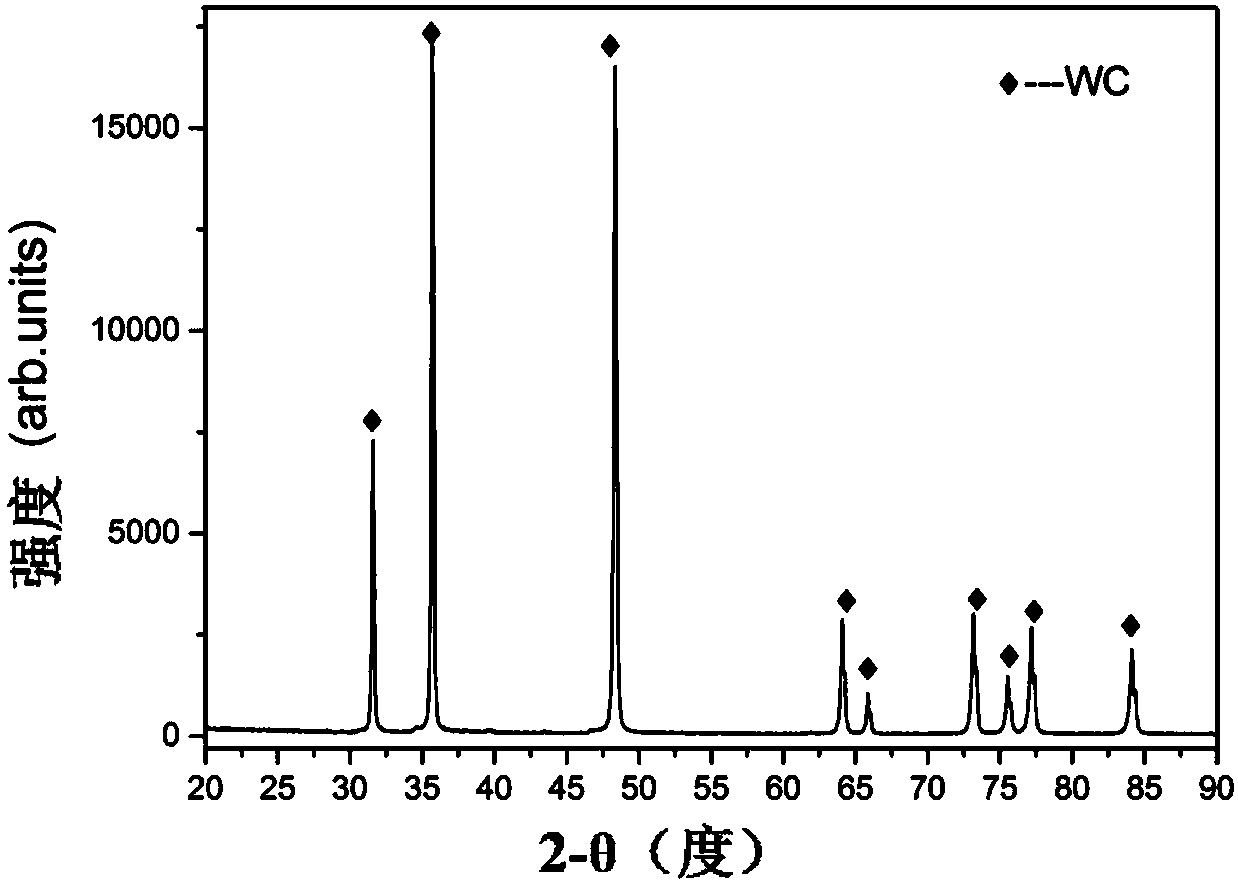
Preparation method for non-bonding-phase pure-carbonation tungsten target material
A tungsten carbide, non-adhesive technology, applied in the field of materials, can solve the problems that cannot meet the requirements of large-scale, batch-scale industrial production, size restrictions, poor stability, etc., and achieve improved arc discharge phenomenon, dense coating, and performance stable effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
[0030] A specific embodiment of the method for preparing a binder-free pure tungsten carbide target provided by the present invention includes the following steps:
[0031] Step A: Prepare materials, choose Fibonacci average particle size of 0.6-5 μm (such as 0.7 μm, 0.8 μm, 1.0 μm, 1.5 μm, 2.0 μm, 2.5 μm, 3.0 μm, 3.5 μm, 4.0 μm, 4.5 μm, 4.8 μm), Pure tungsten carbide powder with a purity of more than 99.9% is used as the raw material powder, and passed through a 100-mesh sieve to break the agglomeration and disperse the raw material powder to control the uniformity of the powder particle size. After sieving, take the undersieve and fill it into the mould.
[0032] Step B: mold loading, uniformly fill the powder obtained in step A into a special graphite mold according to a certain filling method. When filling, it is necessary to control the uniformity of the filling powder. If the uniformity of the powder filling is poor, it will easily lead to uneven density of the pressed ...
Embodiment 1-10
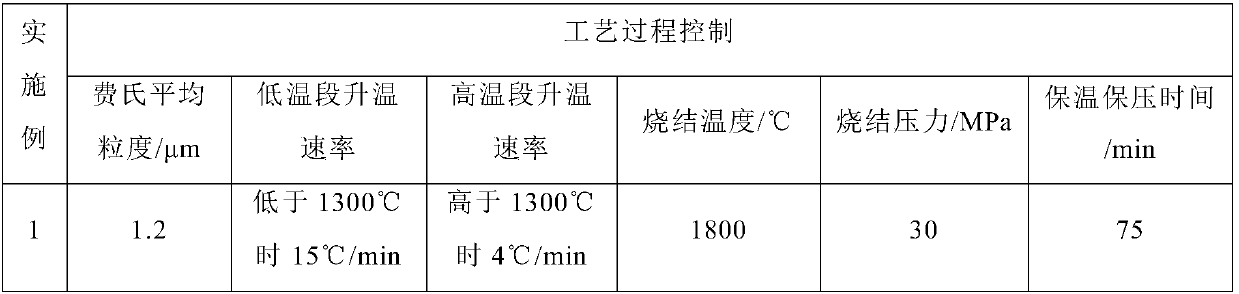
[0039] Table 1 has listed the raw material composition of embodiment 1-10, preparation process parameter, and concrete preparation steps are as follows:
[0040] (1) Prepare materials, pass the above-mentioned pure tungsten carbide raw material powder through a 100-mesh sieve, take the under-sieve powder for the next step, see Table 1 for the Fischer average particle size of the under-sieve powder, and sieve can control the uniformity of the powder particle size;
[0041] (2) moulding, the powder that step (1) obtains is evenly filled in the isostatic graphite mould;
[0042] (3) Hot-press sintering, place the powdered isostatic graphite mold in step (2) in a hot-press furnace, evacuate to below 5Pa, heat up to the sintering temperature, and carry out hot-press sintering, specific sintering parameters See Table 1;
[0043] (4) Demoulding. After sintering, the mold is air-cooled with the furnace, and after the temperature in the furnace is lower than 200°C, it is released from...
Embodiment 10-14
[0053] In Examples 10-14, except that the particle size of the powder is different from that of Example 4, other process parameters are the same as those of Example 4. See Table 3 for the particle size of pure tungsten carbide powder and target performance parameters in Examples 10-14.
[0054] Raw material composition, preparation process parameter of table 3 embodiment 10-14
[0055]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com