An ultra-low-field magnetic detection method for measuring cell adhesion and cell migration rate
A technology of cell migration and adhesion, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of failing to achieve high throughput, and achieve the effect of wide application range and sensitive detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
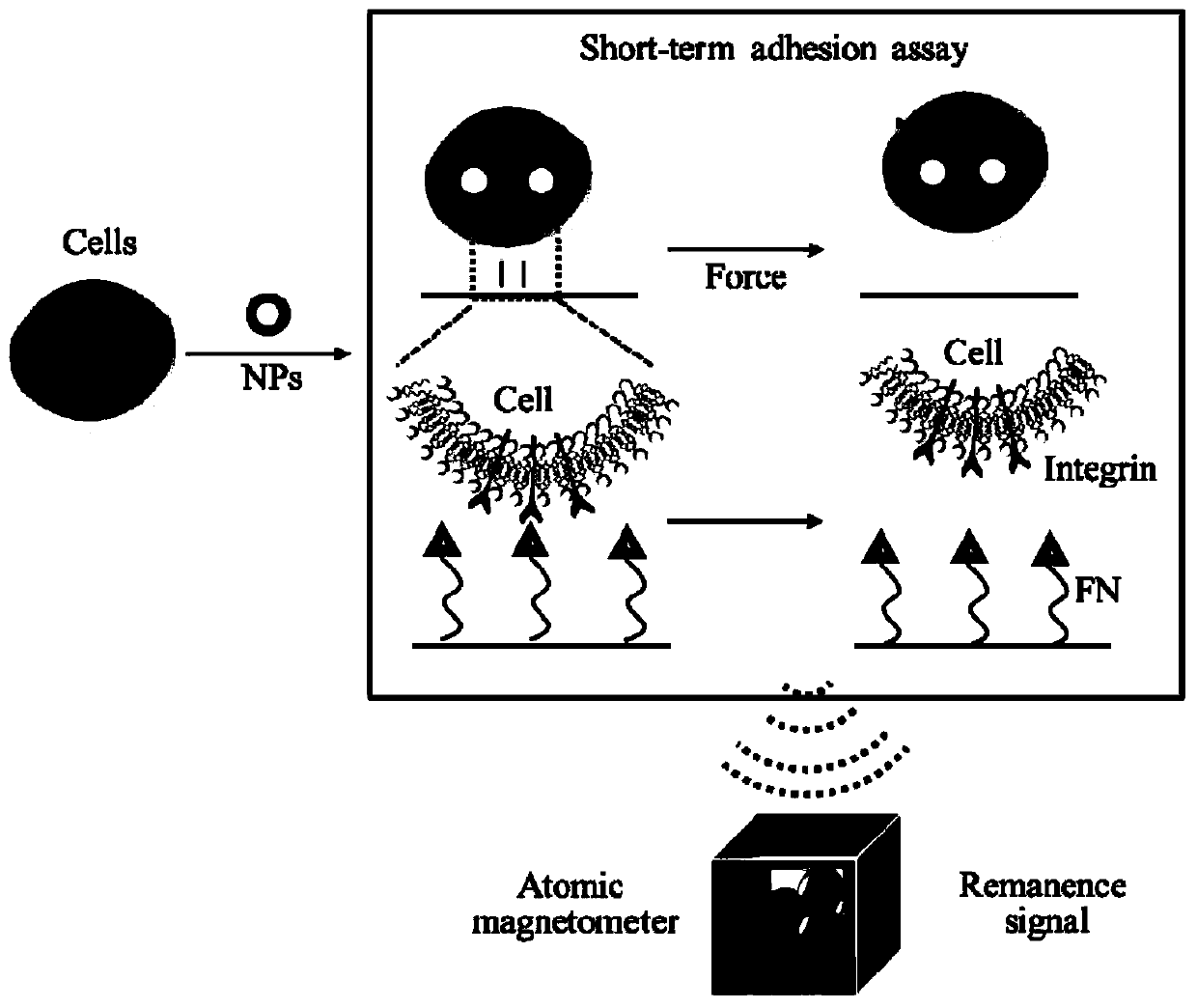
[0055] The modification of the extracellular matrix protein FN of embodiment 1, FIRMS chip
[0056] Prepare a polydimethylsilane (PDMS) cuboid with a length, width and height of 1.4 cm, 0.6 cm and 0.2 cm respectively. In the middle of the cuboid is a circular depression with a diameter of 0.4 cm, wherein the concave part is the FIRMS detection part. Place the FIRMS chip with the concave side facing up in the Petri dish, and clean the chip with plasma for 40s. After the surface of the chip is activated, a 2% volume fraction of 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES) absolute ethanol solution is quickly dropped. After reacting for 4 hours, the solution was discarded, and the chip was washed 5 times with absolute ethanol, and then washed 5 times with deionized water. Store in a desiccator after drying with nitrogen gas. Glutaraldehyde aqueous solution (1%, v / v) was added to the aminated chip, and after reacting for 3 hours, it was washed 5 times with deionized water and 5 times wi...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Embodiment 2, the magnetic labeling of cell
[0058] Will 1×10 6 Human lung cancer cells (A549) cells were inoculated in a 6-well cell culture plate, and after culturing for 17 hours, the cell culture medium was discarded. Cells were washed 3 times with serum-free culture. Serum-free medium dispersed with magnetic probes (20ug / mL) was added to continue culturing for 4h. The culture medium containing the magnetic probe was sucked off, and the cells were washed 5 times with phosphate buffer solution. The cells that had internalized the magnetic probe were then digested with trypsin (0.25%) for 3 min. After the digested cells were centrifuged to separate the solution containing trypsin, the cells were blown completely into the complete medium for later use.
Embodiment 3
[0059] Embodiment 3, FIRMS feasibility verification
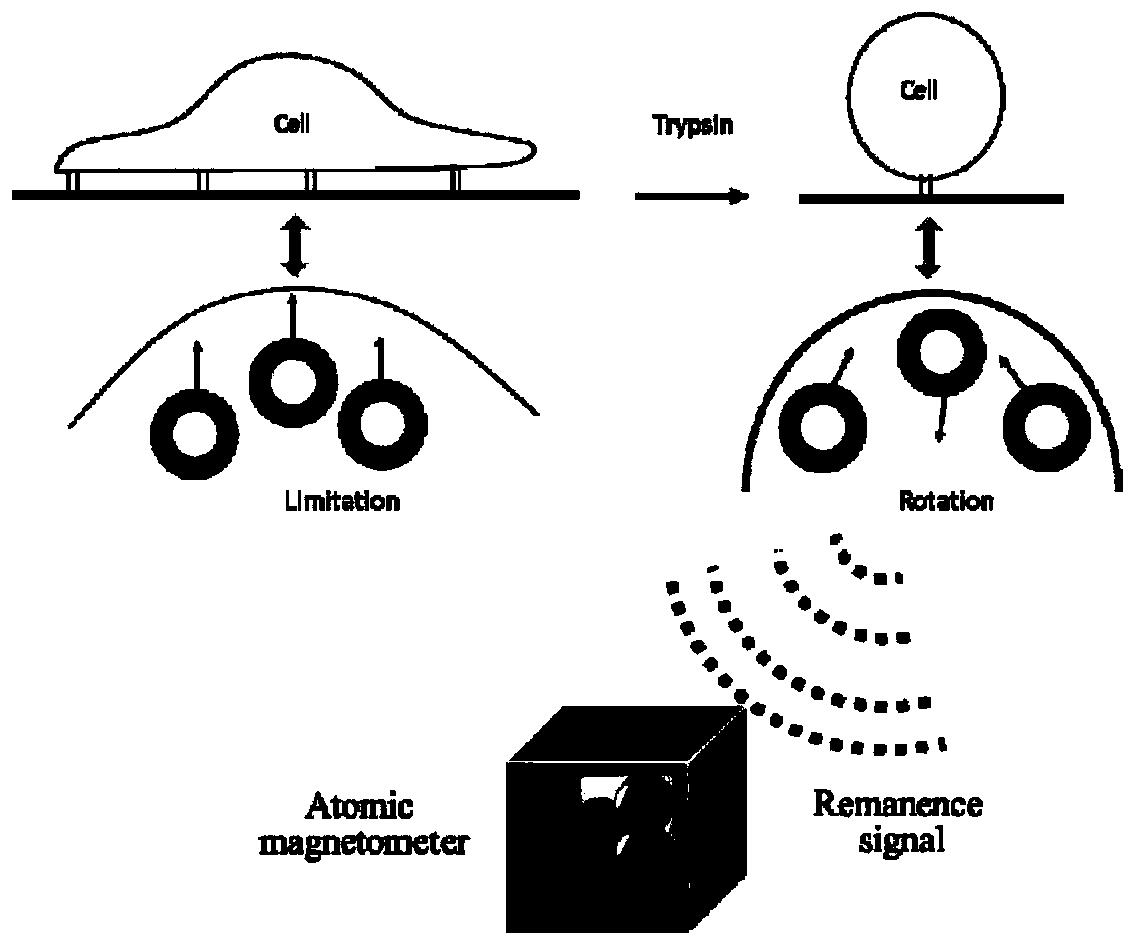
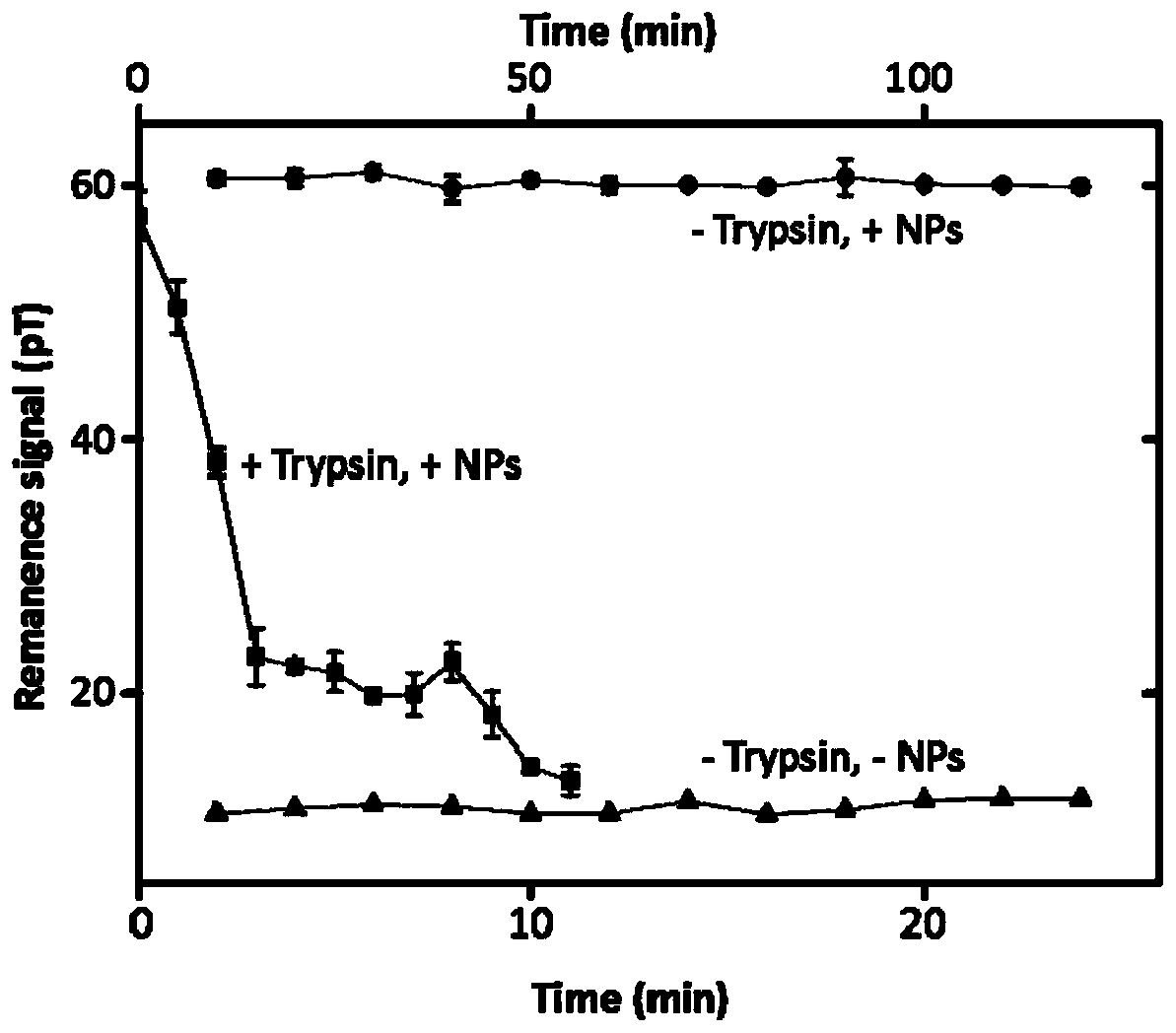
[0060] Such as figure 1 As shown, in order to verify that FIRMS can sensitively respond to external force interference or changes in the remanence signal caused by the cell's own migration, the cells were first cultured on the FIRMS chip. After culturing for 17 hours, the complete medium was discarded and washed with serum-free medium. The cells were added twice and incubated for 4 hours with the addition of a magnetic probe. After washing away the magnetic probes that are not endocytosed by the cells or adsorbed on the cell surface, the intracellular probes are magnetized for 2 min (the strength of the magnet is 1T). After adding 0.25% trypsin, quickly use FIRMS to record the contraction process of the cells under trypsinization, from the spreading state to the spherical shape until finally the decrease of the residual magnetic signal caused by the cells detaching from the substrate. Compared with the residual magnetic s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com