Method for producing super wet fabric
A fabric and supercritical technology, applied in non-woven fabrics, textiles and papermaking, fiber types, etc., can solve problems such as high cost, complex process, damage to mechanical properties of fabrics, etc., to achieve wide applicability, simple operation, extended functions and effect of use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
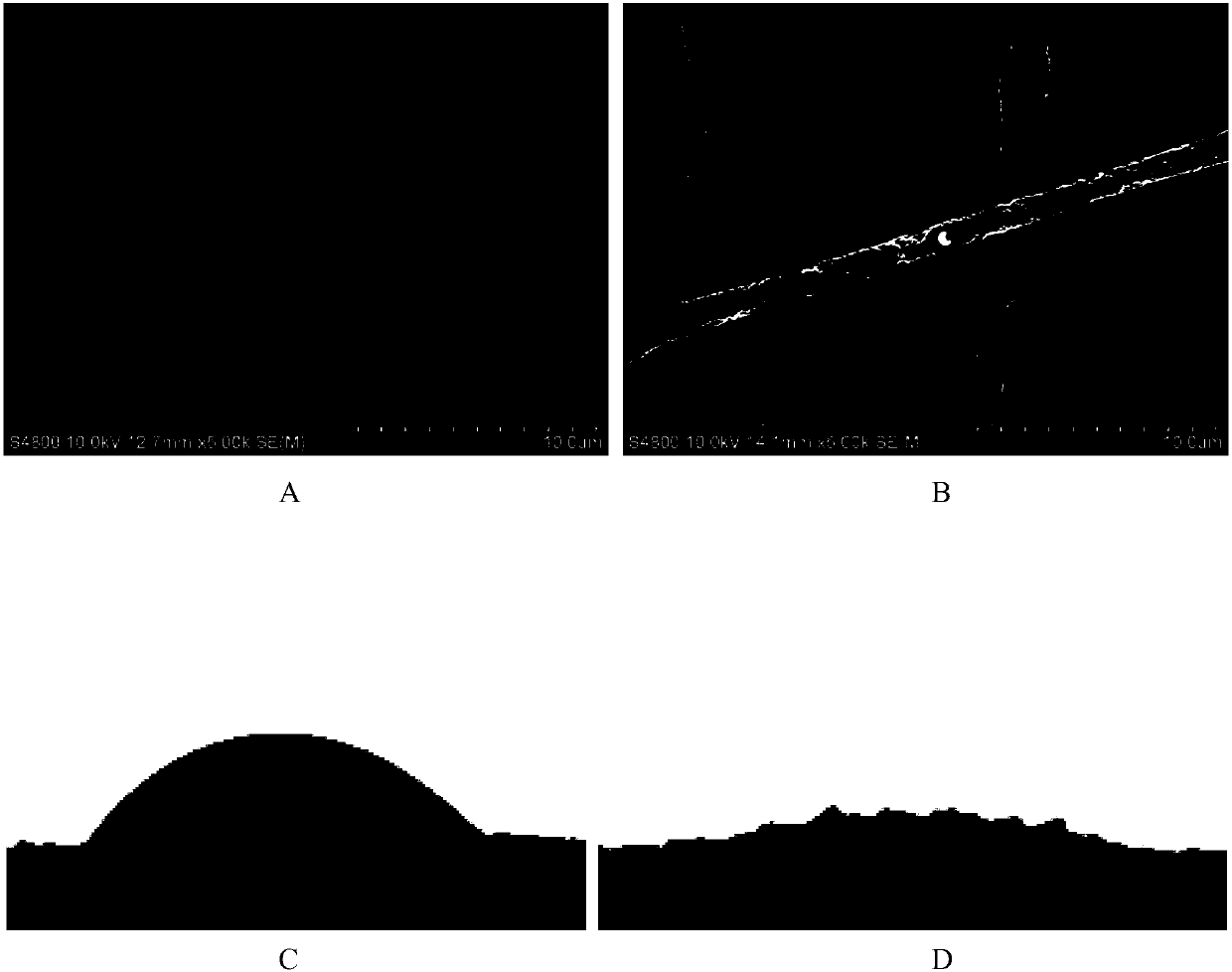
[0031] The electrospinning method is used to prepare PVP non-woven fabrics. The preparation process conditions are: use ethanol as the solvent, the concentration of the spinning solution: 25wt%, the voltage: 20KV, the distance between the injection needle and the receiving plate: 10cm, and the obtained hydrophilic The fiber diameter of the electrospun non-woven fabric of permanent polymer is 1~2μm, and the diameter of the hole formed by the overlapping of fibers in the nonwoven fabric is 5~20μm.
[0032] Put the prepared PVP non-woven fabric into the autoclave, under the supercritical CO with a pressure of 12MPa and a temperature of 30°C 2 Soak in medium for 30min, and then quickly reduce the pressure (pressure release rate: 8MPa / s), foam the PVP fiber, and manufacture PVP fiber with nanopores. The water contact angle test shows that before and after the non-woven fabric is foamed, the contact angle changes from 45° to almost completely spread, realizing superhydrophilicity ( ...
Embodiment 2
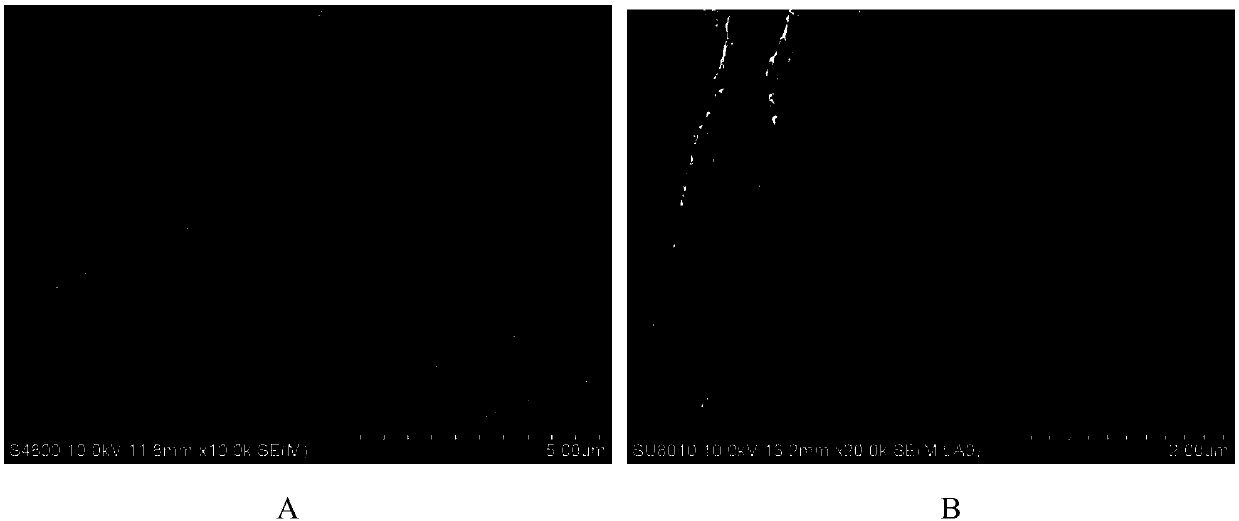
[0035] The electrospinning method is used to prepare PMMA nonwoven fabrics. The preparation process conditions are: using dichloromethane as a solvent, spinning solution concentration: 15wt%, voltage: 20KV, distance between the injection needle and the receiving plate: 15cm, the obtained The fiber diameter of the hydrophobic polymer electrospun non-woven fabric is 1-5 μm, and the diameter of the hole formed by the fiber lap in the non-woven fabric is 2-20 μm.
[0036] Put the prepared PMMA non-woven fabric into the autoclave, under the pressure of 15MPa, the temperature is 100 ℃ supercritical CO 2 Soak in medium for 60min, and then quickly reduce the pressure (pressure release rate: 7MPa / s), foam the PMMA fibers, and produce PMMA fibers with nanopores. The water contact angle test shows that before and after the non-woven fabric is foamed, the contact angle changes from 90° to 160°, realizing superhydrophobicity ( figure 2 ).
Embodiment 3
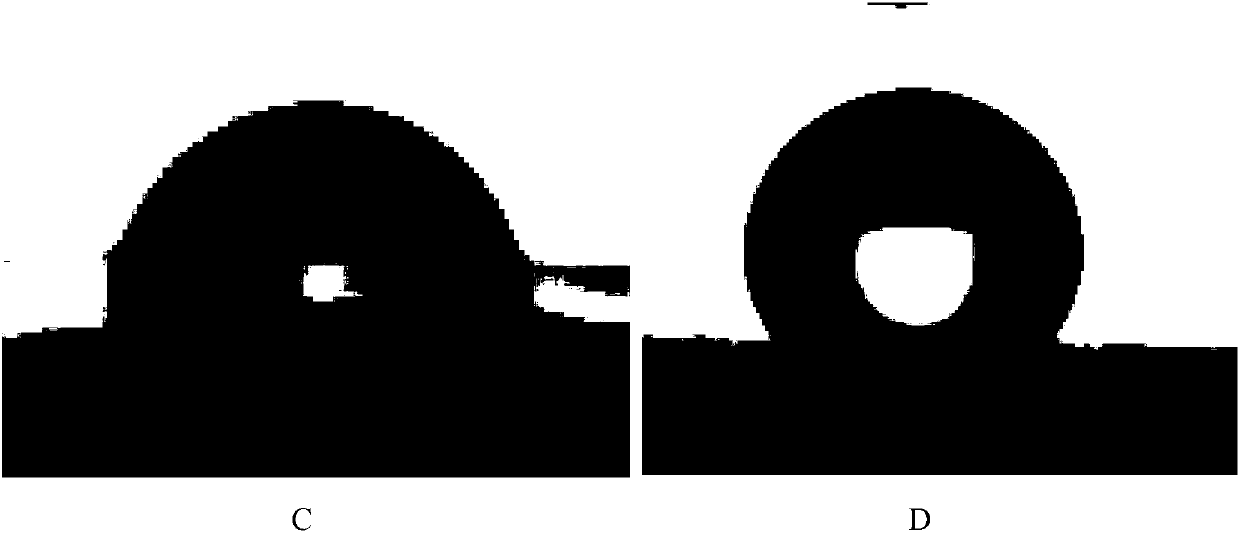
[0038] Put the purchased PP non-woven fabric into the high-pressure reactor, under the pressure of 15MPa, the temperature is 130℃ supercritical CO 2 Soak in medium for 120min, and then quickly reduce the pressure (pressure release rate: 7MPa / s), foam the PP fiber, and produce PP fiber with nanopores. The water contact angle test shows that before and after the non-woven fabric is foamed, the contact angle changes from 100° to 153°, realizing superhydrophobicity ( image 3 ).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com