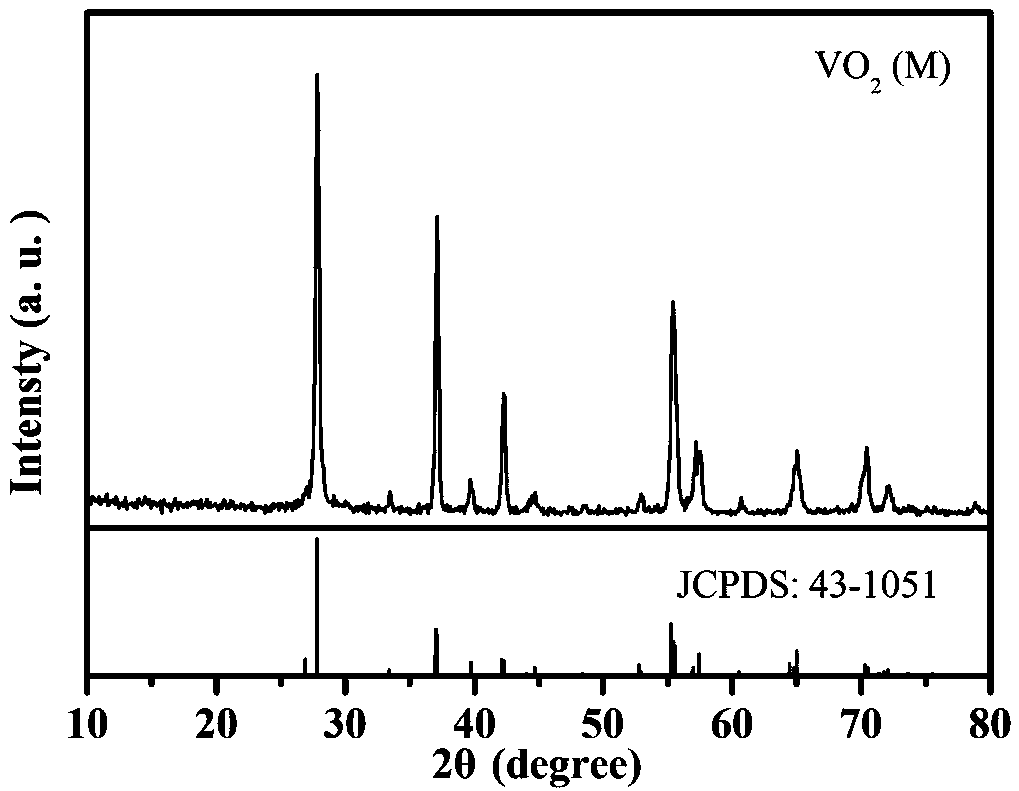
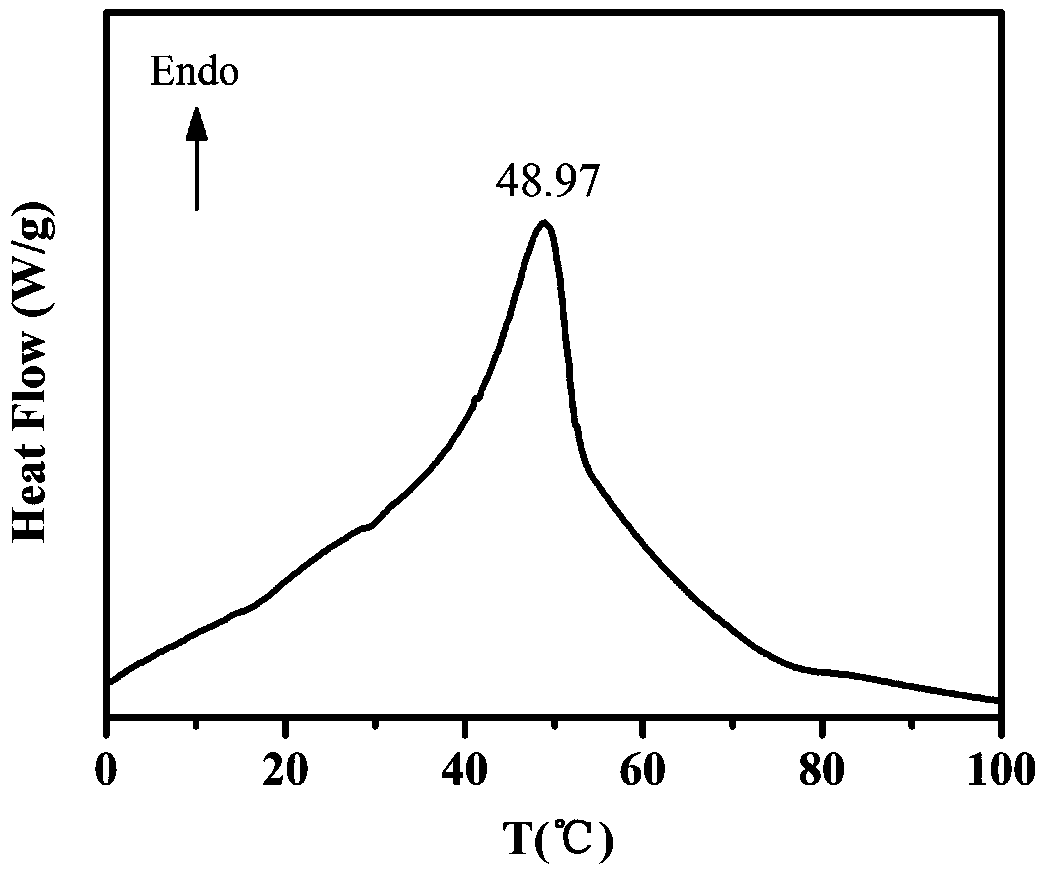
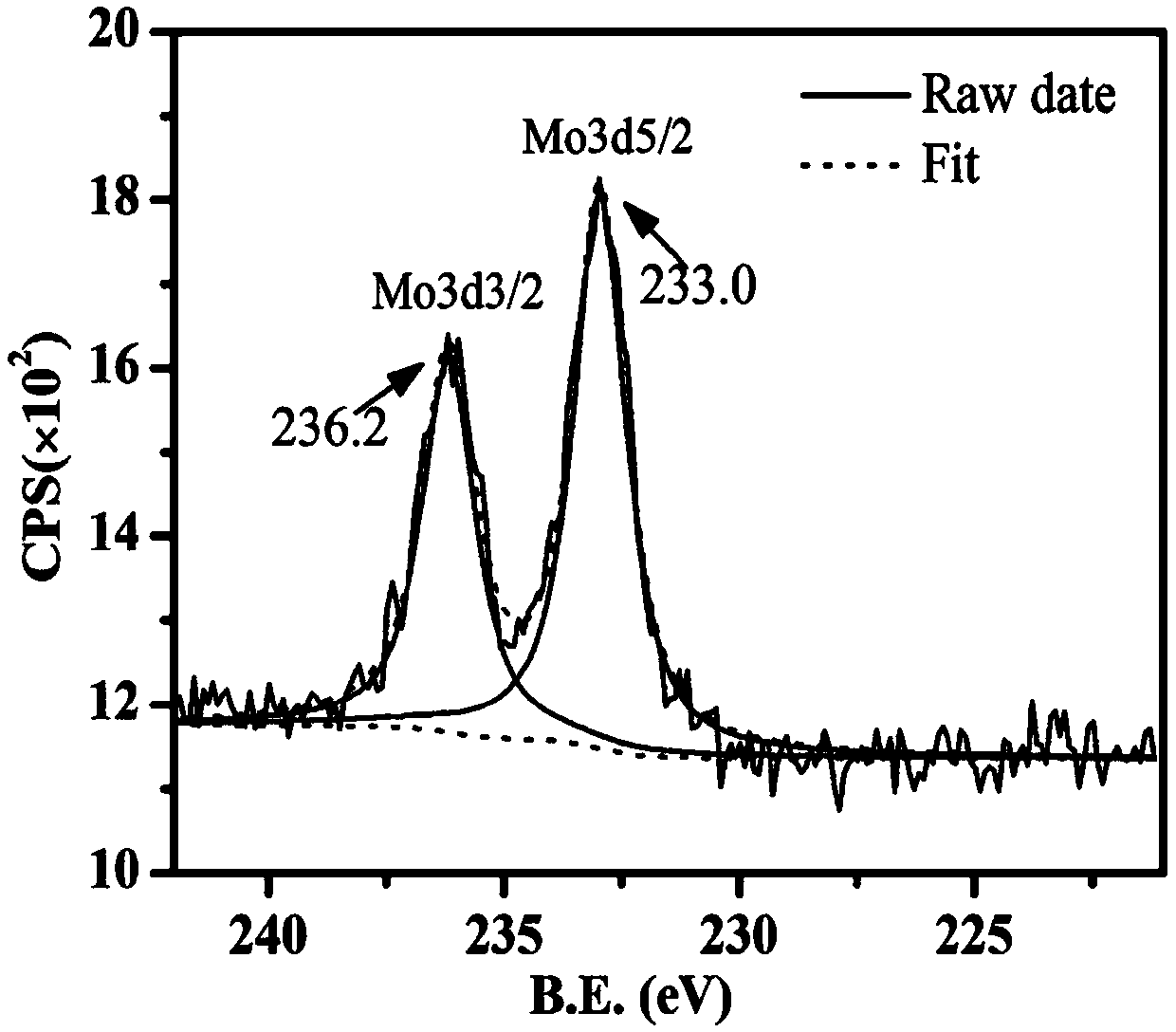
One-step hydrothermal method for preparing molybdenum-doped VO2 (M) powder by aid of tartaric acid used as reducing agent
A technology of tartaric acid and reducing agent, applied in vanadium oxide and other directions, can solve the problems of affecting thermally induced phase change performance, powder agglomeration, complex process and other problems, and achieve the effects of good crystallinity, low cost and simple operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] (1) Put 1.092 g V 2 o 5 , 0.18 g of tartaric acid, 1.5 at % ammonium molybdate, and 70 ml of deionized water were put into a beaker, and magnetically stirred at room temperature for 1 hour.
[0025] (2) Transfer the mixed solution to a 100 ml polytetrafluoroethylene autoclave and react at 240 °C for 48 hours.
[0026] (3) Synthesized by hydrothermal reaction, after naturally cooling to room temperature, the precipitate obtained from the reaction was centrifuged and washed three times with deionized water and absolute ethanol respectively.
[0027] (4) Put the washings in an oven and dry at 60 °C for 12 h to obtain the final product.
Embodiment 2
[0029] (1) Put 1.092 g V 2 o 5 , 0.36 g of tartaric acid, 1 at % ammonium molybdate, and 70 ml of deionized water were put into a beaker, and magnetically stirred at room temperature for 2 hours.
[0030] (2) Transfer the mixed solution to a 100 ml polytetrafluoroethylene autoclave and react at 220 °C for 72 hours.
[0031] (3) Synthesized by hydrothermal reaction, after naturally cooling to room temperature, the precipitate obtained from the reaction was washed by centrifugation twice with deionized water and absolute ethanol respectively.
[0032] (4) Put the washings into an oven and dry at 80°C for 10 hours to obtain the final product.
Embodiment 3
[0034] (1) Put 1.092 g V 2 o 5 , 0.36 g of tartaric acid, 2 at % ammonium molybdate, and 80 ml of deionized water were put into a beaker, and magnetically stirred at room temperature for one hour.
[0035] (2) Transfer the mixed solution to a 100 ml polytetrafluoroethylene autoclave and react at 240 °C for 48 hours.
[0036] (3) Synthesized by hydrothermal reaction, after naturally cooling to room temperature, the precipitate obtained from the reaction was centrifuged and washed three times with deionized water and absolute ethanol respectively.
[0037] (4) Put the washings into an oven and dry at 70°C for 10 hours to obtain the final product.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| phase transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| phase transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com