Preparation method of microcarrier used for cell three dimensional multiplication culture
A technology of amplifying culture and microcarriers, which is applied in the field of tissue engineering materials to achieve the effect of good biological performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
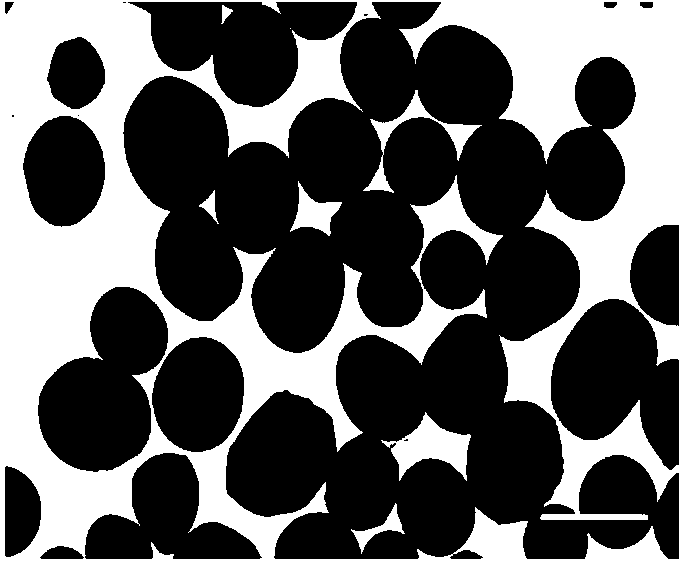
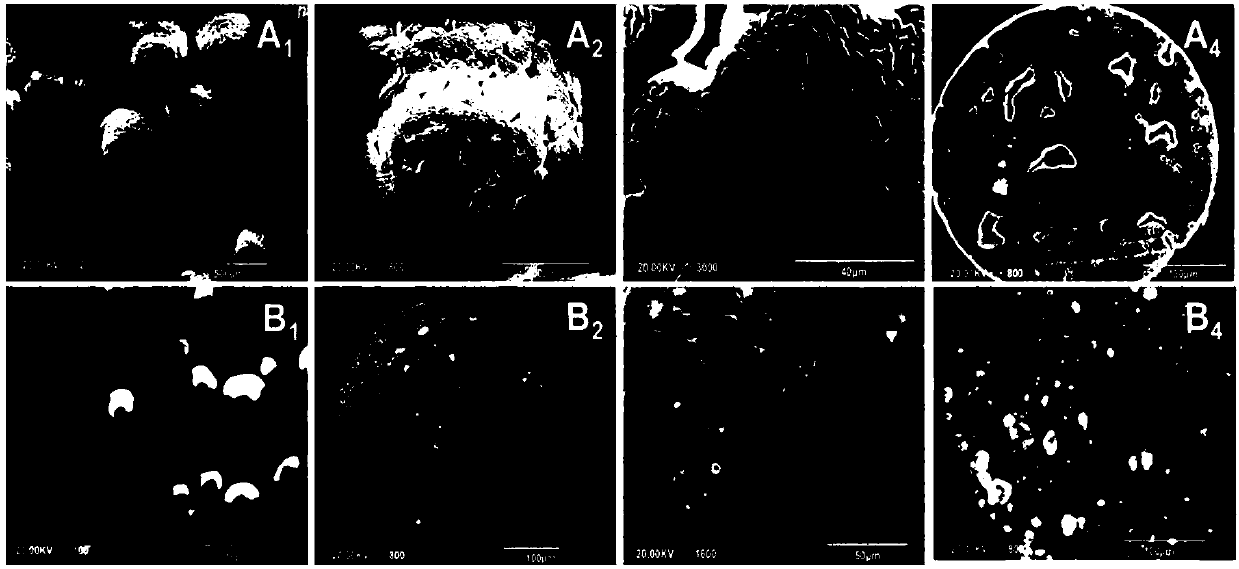
[0030] Example 1 Preparation of L-polylactic acid microspheres and biocompatibility detection (comparative example, the concentration of L-polylactic acid in the dichloromethane solution of L-lactic acid is 10g / mL, and the amount of gelatin is: gelatin / L-lactic acid mass ratio 1:40, mixing speed 150rpm / min / min)
[0031] First, weigh 10.0g of poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA) and add it to 100mL of dichloromethane solution, stir in a fume hood for 4h until PLLA dissolves to obtain PLLA in dichloromethane solution; then weigh 0.25g of gelatin and add it to 100mL of distilled water, Seal and stir for 3 hours to obtain a gelatin dispersant; add the PLLA dichloromethane solution to the gelatin dispersant solution, and stir for 7 hours in a fume hood at a speed of 150 rpm / min. During the stirring process, the liquid microspheres gradually solidify as the organic solvent volatilizes , into balls, and precipitate at the bottom of the beaker; stand for 30 minutes to separate the phases, separa...
Embodiment 2
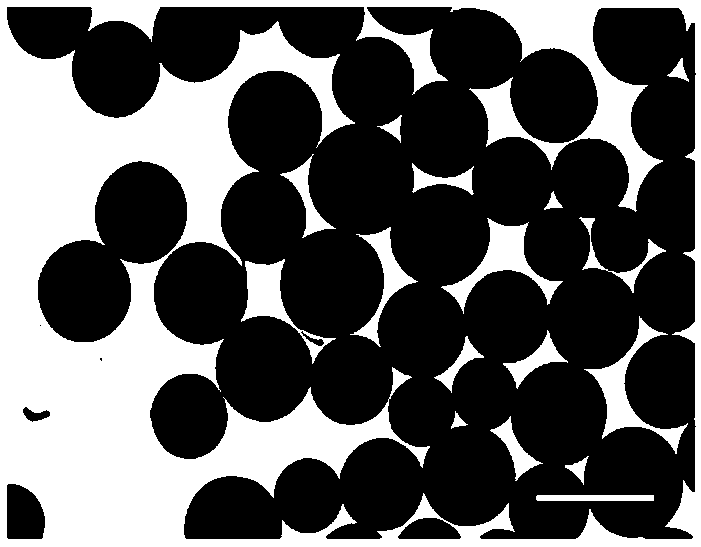
[0033] Example 2 Preparation of L-polylactic acid / nanometer hydroxyapatite (mass ratio 5:1) composite microspheres (polylactic acid dichloromethane solution concentration 5g / mL, gelatin dosage: gelatin / L-polylactic acid mass ratio 1:20, Mixing speed 200rpm / min)
[0034] Weigh 5.0g of L-polylactic acid (PLLA), add it into 100mL of dichloromethane, and stir magnetically for 3h under water bath conditions until PLLA is completely dissolved in dichloromethane to obtain PLLA dichloromethane solution; weigh 1.0g of nano Hydroxyapatite (nHAp), add it to the above PLLA dichloromethane solution, seal it, stir rapidly on a magnetic stirrer for premixing, and further ultrasonically disperse and mix for 30min in an ultrasonic oscillator until nHAp is evenly dispersed in the solution , to obtain PLLA / nHAp dichloromethane solution; weigh 0.25g gelatin, add it to 100mL distilled water, seal and stir for 2h until the gelatin dissolves, and obtain a gelatin dispersant; add the prepared PLLA / nH...
Embodiment 3
[0035] Example 3 Preparation of L-polylactic acid / nanometer hydroxyapatite (mass ratio 5:1) composite microspheres (polylactic acid dichloromethane solution concentration 10g / mL, gelatin dosage: gelatin / L-polylactic acid mass ratio 1:40, Mixing speed 200rpm / min)
[0036] Weigh 10.0g of L-polylactic acid (PLLA), add it to 100mL of dichloromethane, and stir magnetically for 4h under water bath conditions until PLLA is completely dissolved in dichloromethane to obtain PLLA dichloromethane solution; weigh 2.0g of nano Add hydroxyapatite (nHAp) to the above-mentioned PLLA dichloromethane solution, seal it, stir rapidly on a magnetic stirrer for premixing, and further ultrasonically disperse and mix in an ultrasonic oscillator for 50 minutes until nHAp is evenly dispersed in the solution. Obtain PLLA / nHAp dichloromethane solution; Weigh 0.25g of gelatin, add it to 100mL distilled water, seal and stir for 2h until the gelatin is dissolved, and obtain a gelatin dispersant; add the pre...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com