Magnesium alloy anode rolled board and preparing method and application thereof
A magnesium alloy and plate technology, which is applied in the field of chemical power electrode materials, can solve the problems of positive displacement of metal particles, decreased discharge performance, shedding, etc., and achieves the effects of small and uniform grain size, low dislocation density, and simple method.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] 1. The nominal composition of the zinc and manganese modified AP65 magnesium alloy of the present embodiment is 5.5wt.% of Al, 4.5wt.% of Pb, 0.8wt.% of Zn, 0.1wt.% of Mn, 89.05wt.% of Mg. Among them, magnesium, aluminum, lead and zinc are all pure metals with a purity of 99.99wt.%, and manganese is added in the form of Al-30wt.%Mn master alloy.
[0031] 2. Put magnesium, aluminum, lead, zinc and manganese into a high-purity graphite crucible at one time, pump the air pressure in the furnace to 2.4Pa and then fill it with argon until the air pressure reaches 0.06MPa, and then put the fully stirred molten The body was cast in a stainless steel crucible in a furnace to obtain an as-cast zinc and manganese modified AP65 magnesium alloy ingot with a size of 400×200×40 mm.
[0032] 3. The as-cast AP65 magnesium alloy ingot was uniformly annealed at 400° C. for 24 hours in a box-type resistance furnace, and then quenched in water.
[0033] 4. Preheat the homogenized anneale...
Embodiment 2
[0038] 1. The preparation of the zinc and manganese modified AP65 magnesium alloy rolled plate in this embodiment is the same as in embodiment 1, except that the total rolling deformation in step 4 reaches 63%.
[0039] The microstructure characterization and electrochemical performance test of this embodiment are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
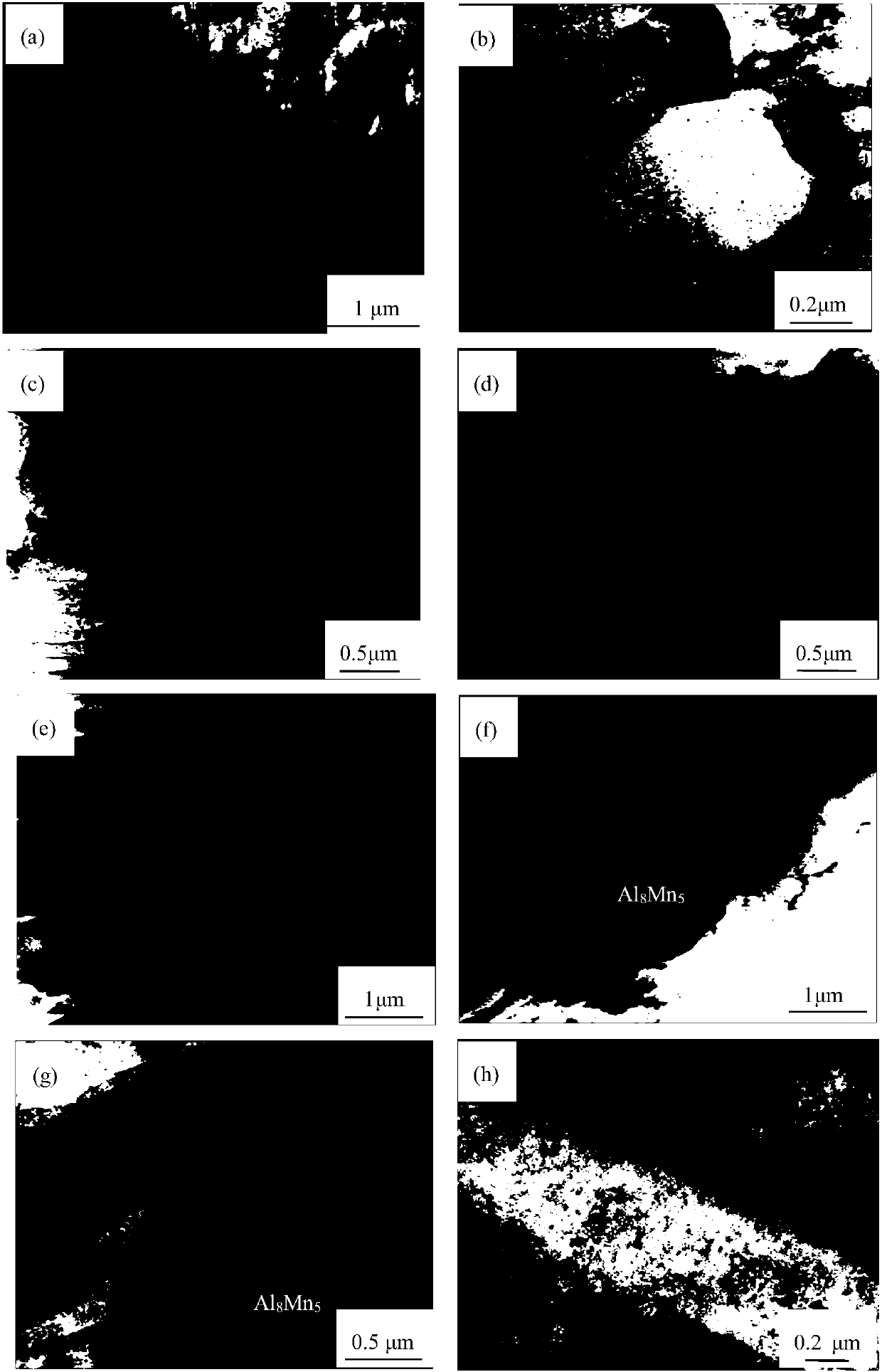
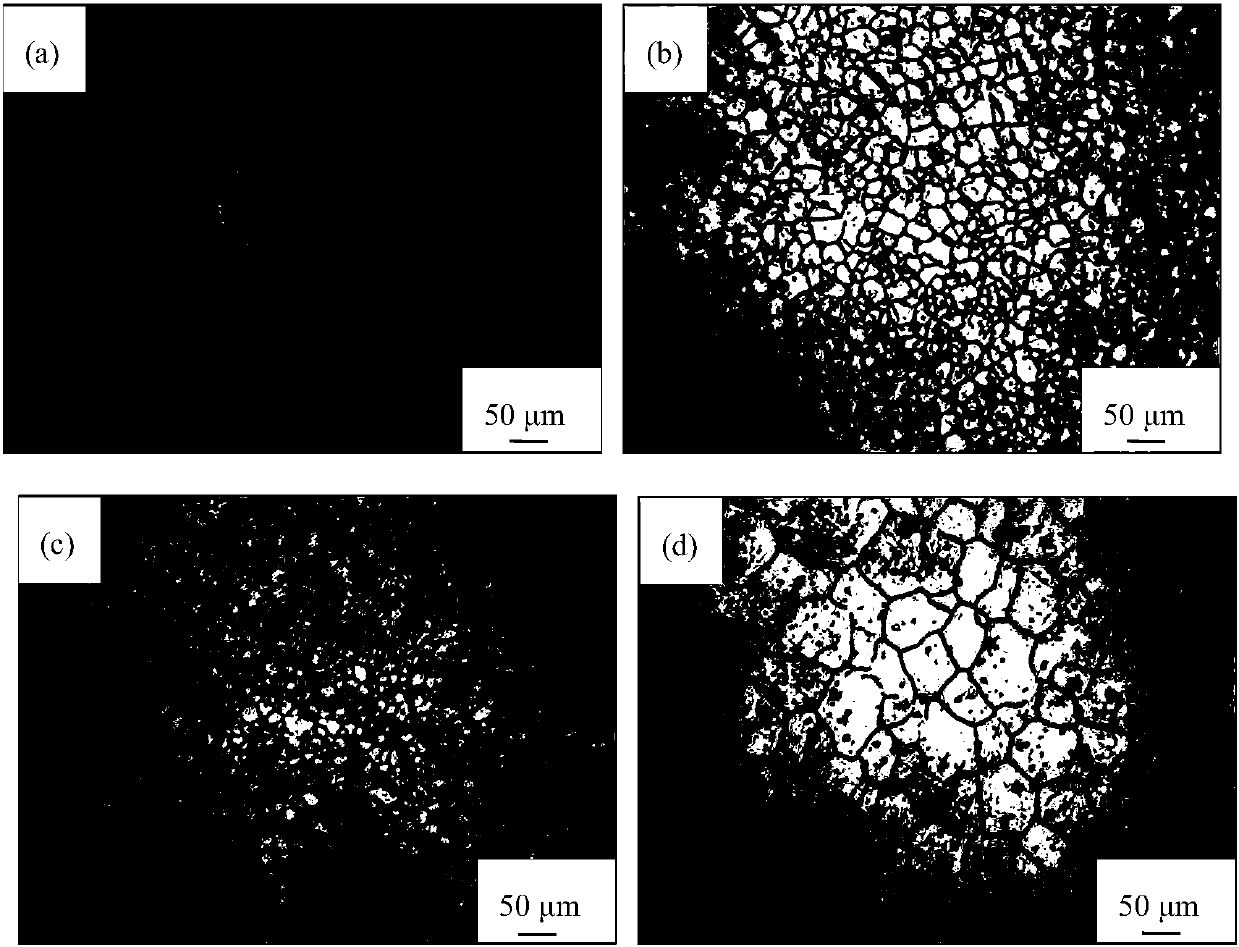
[0040] according to figure 1 The metallographic photograph of (b) shows that the AP65 magnesium alloy grain size of 63% rolling deformation is fine and uniform; figure 2 The TEM bright-field images shown in (c)-(d) show that the magnesium alloy has a low dislocation density and a certain number of twins.
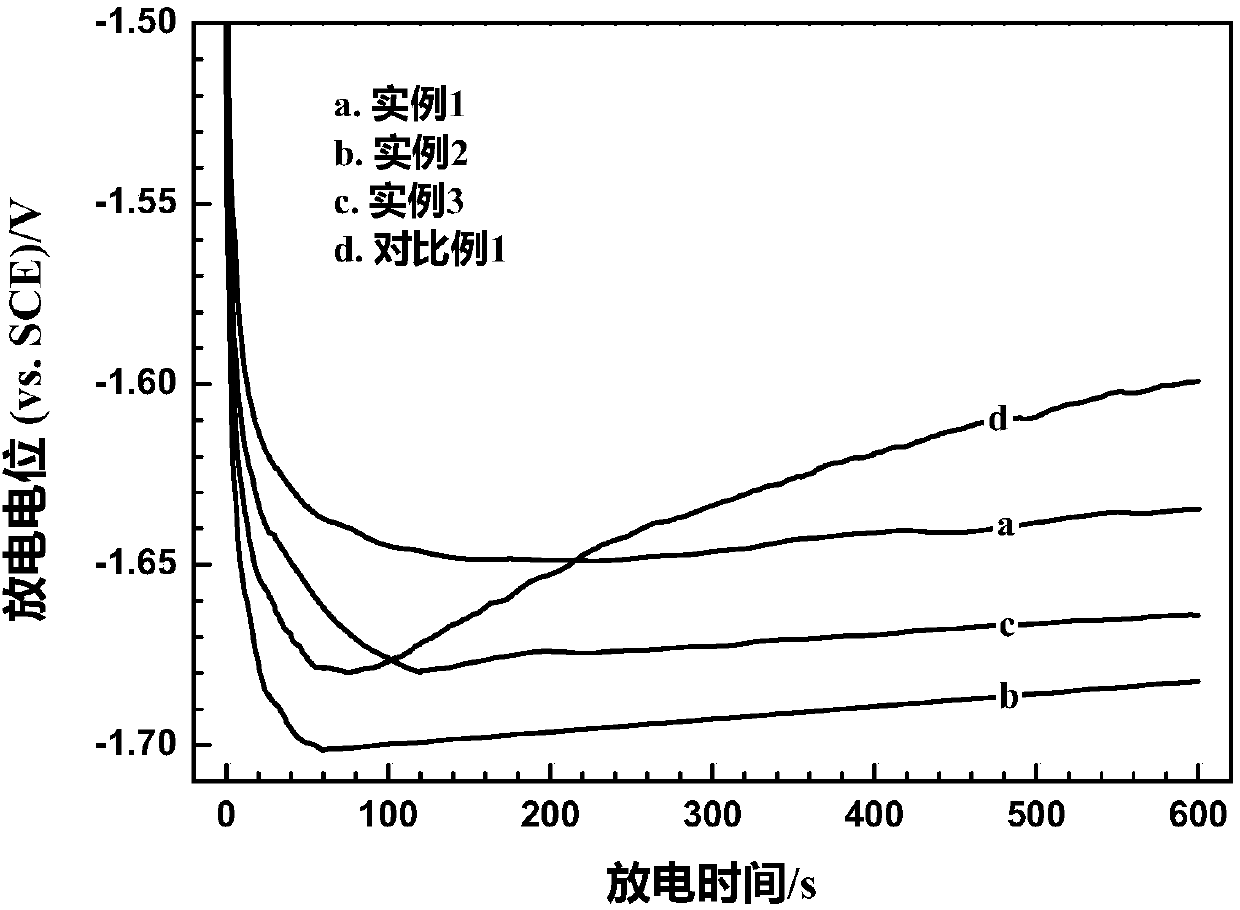
[0041] image 3 The shown potential-time curves show that the AP65 magnesium alloy with a rolling deformation of 63% is at 180mA cm -2 When the potential is relatively negative and stable.
[0042] Figure 4 (b) The scanning electron microscope secondary electron image shows that the AP65 magnesium alloy with a rolling def...
Embodiment 3
[0044] The preparation of the zinc and manganese modified AP65 magnesium alloy rolled plate in this example is the same as in Example 1, except that the total rolling deformation in step 4 reaches 86%.
[0045] The microstructure characterization and electrochemical performance test of this embodiment are the same as those in Embodiment 1. according to figure 1The metallographic photograph of (c) shows that the grain size of the AP65 magnesium alloy with a rolling deformation of 86% is further refined. figure 2 The TEM bright-field images shown in (e)-(f) show that the magnesium alloy has fine grains and high dislocation density, and the second phase Al 8 mn 5 Broken, twins disappear.
[0046] image 3 The shown potential-time curves show that the AP65 magnesium alloy with a rolling deformation of 86% is at 180mA cm -2 The time potential is slightly positive than that of the AP65 magnesium alloy with a rolling deformation of 63%. Figure 4 The SEM secondary electron ima...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com