Method for recycling wastewater containing sodium hypochlorite
A technology of sodium hypochlorite and sodium hypochlorite solution, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water pollutants, multi-stage water treatment, etc., can solve the problems of limited amount of oxidant and oxidation time, high total phosphorus concentration in wastewater, affecting the quality of effluent, etc. Convenient, low-cost, easy-to-control effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] This embodiment is a simulation experiment of a method for recovering waste water containing sodium hypochlorite.
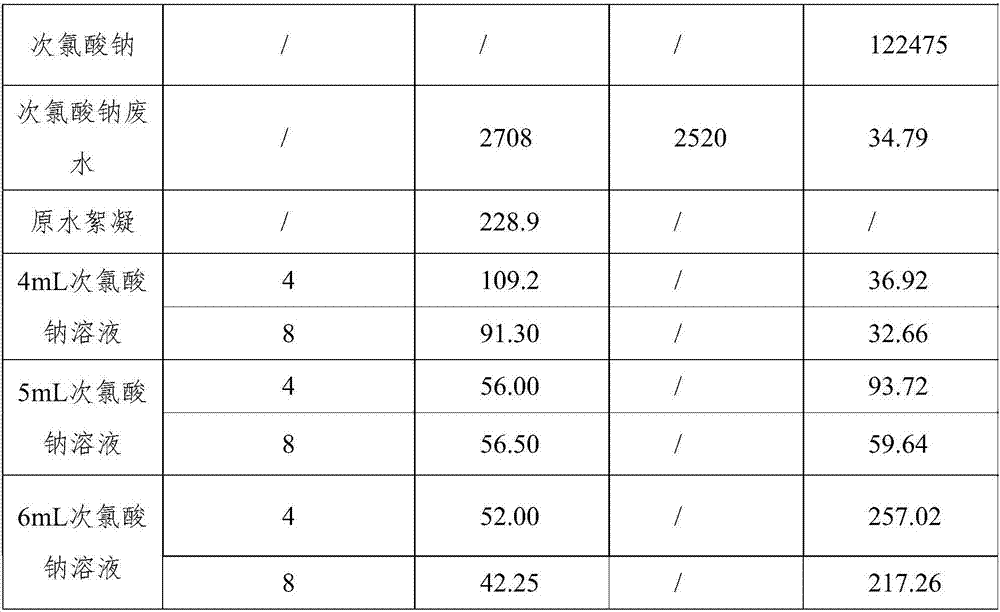
[0046] This test is divided into three groups, first add 500mL sodium hypochlorite wastewater into the beaker, then add 4mL, 5mL, 6mL sodium hypochlorite solution with a mass concentration of 10%, stir fully and react, and take samples after 4 hours and 8 hours.
[0047] Add 0.1 mL of PAC with a mass concentration of 0.1% to the sampled wastewater, and then add 0.1 mL of PAM with a mass concentration of 0.1% to remove orthophosphate.
[0048] Table 2 Test data
[0049]
[0050]
[0051] After adding 4mL sodium hypochlorite, 5mL sodium hypochlorite, and 6mL sodium hypochlorite respectively, the residual chlorine in the water is calculated to be 1000mg / L, 1250mg / L, and 1500mg / L respectively.
[0052] It can be seen from Table 2 that when 5ml of sodium hypochlorite is added, the content of total phosphorus has a small difference between sampling at 4 hou...
Embodiment 2
[0054] This embodiment uses the same simulation experiment as in Embodiment 1 to provide a method for recovering waste water containing sodium hypochlorite.
[0055] This test is divided into three groups, first add 500mL sodium hypochlorite wastewater into the beaker, add 5mL sodium hypochlorite solution with a mass concentration of 10%, stir and take a sample every 4 hours and 8 hours. The water samples were subjected to coagulation and sedimentation treatment, and PAM and ferric chloride with mass ratios of 1:1, 2:1, 2.15:1, and 3:1 were added to the oxidized water samples for treatment, and the removal of phosphorus was investigated. Effect.
[0056] Table 3 Test data
[0057]
[0058] It can be seen from the above table that after using the combination of PAM and ferric chloride, the removal effect of total phosphorus is better than that of PAC and PAM.
[0059] Phosphorus content in sodium hypochlorite wastewater fluctuates greatly. When the total phosphorus content...
Embodiment 3
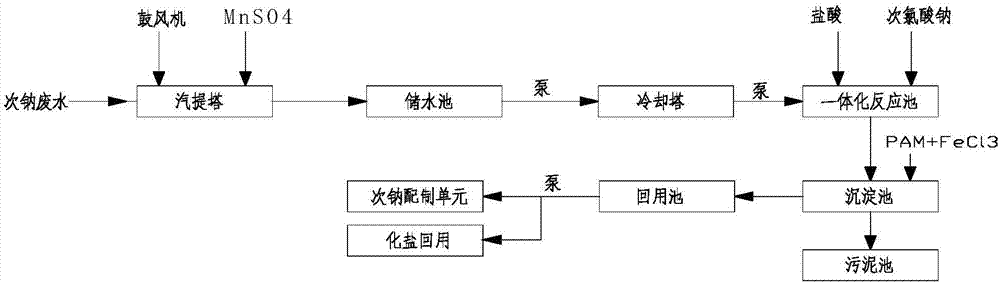
[0063] A system for recovering waste water containing sodium hypochlorite, comprising a stripping tower connected in series, a water storage tank, a cooling tower, an integrated reaction tank, a sedimentation tank, and a reuse tank; the sludge outlet of the sedimentation tank is connected with a sludge tank; The outlet of the reuse pool is connected in parallel with the preparation unit of sodium hypochlorite and the salt recovery unit; and the addition of catalyst, sodium hypochlorite solution and flocculant is controlled by the DCS control system; figure 1 The flowchart shown.
[0064] Wherein, the stripping tower is provided with a blower and a catalyst addition inlet; the integrated reaction tank is provided with a sodium hypochlorite solution addition inlet; and the sedimentation tank is provided with a flocculant addition inlet.
[0065] The method for processing phosphorus in the waste water may further comprise the steps:
[0066] 1) the waste water flows into the str...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com