High Cr Cast Roadheader Tool Steel and Its Manufacturing Process
A manufacturing process and technology of roadheading machines, which are applied in the field of tool steel manufacturing, can solve problems such as difficult access to imported tools, and achieve the effects of saving processing hours, reducing production costs, and improving stability against high temperature tempering
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] (1) The chemical composition of the new high-Cr cast roadheader tool steel is by weight percentage:
[0046] C: 0.307; Cr: 8.151; Mo: 1.272; Ni: 0.564; V: 0.665; Mn: 0.131; Si: 0.648;
[0047] (2) The heat treatment process scheme and mechanical properties of this embodiment are shown in Table 4.
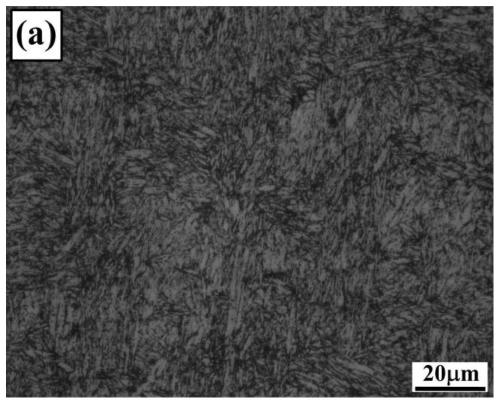
[0048] The high-Cr cast roadheader tool steel is mainly composed of lath martensite and retained austenite after heat treatment in schemes 2 to 4, and its mechanical properties have reached or exceeded that of forged high-carbon H13 roadheader tool steel. Among them, after the heat treatment of process plan 3, the impact toughness is increased by 19.4%, the tensile strength is increased by 6.8%, the yield strength is increased by 12.7%, and the elongation is increased by 18.0%. Oxidation at 550°C for 60 hours in the air environment increases the weight of forging. 42.4% of H13 steel; after 10,000 thermal cycles at 550°C → 25°C, the length and number of thermal fatigue cracks...
Embodiment 2
[0057] (1) The chemical composition of high-Cr cast roadheader tool steel is by weight percentage:
[0058] C: 0.415; Cr: 10.163; Mo: 2.171; Ni: 1.233; V: 0.804; Mn: 0.235; Si: 0.706;
[0059] (2) The heat treatment process characteristics of the new high-Cr cast roadheader tool steel are shown in Table 6.
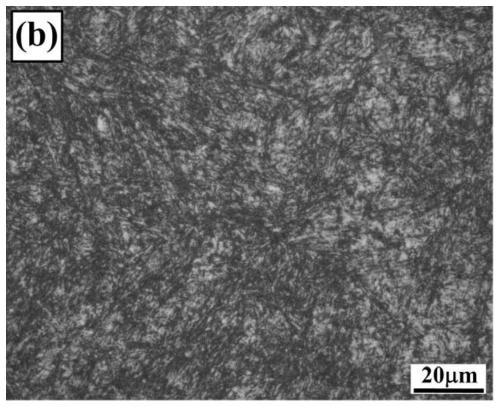
[0060] After the heat treatment of the new high-Cr cast roadheader tool steel in schemes 2 to 4, the microstructure is mainly lath martensite and retained austenite, and its mechanical properties have met or exceeded that of forged high-carbon H13 roadheader tool steel. Among them, after the heat treatment process scheme 3, the hardness increased by 1.5HRC, the impact toughness increased by 17.8%, the tensile strength increased by 13.5%, the yield strength increased by 19.5%, and the elongation increased by 13.8%. Oxidation at 550°C in the air environment 60-hour oxidation weight gain is 40.5% of that of forged H13 steel; after 10,000 thermal cycles at 550°C → 25°C, the o...
Embodiment 3
[0067] (1) The chemical composition of the new high-Cr cast roadheader tool steel is by weight percentage:
[0068] C: 0.547; Cr: 11.89; Mo: 2.880; Ni: 1.692; V: 0.947; Mn: 0.384; Si: 0.771;
[0069] (2) The heat treatment process characteristics of the new high-Cr cast roadheader tool steel are shown in Table 8.
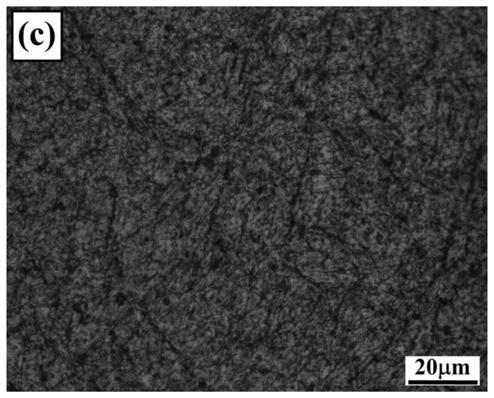
[0070] After the heat treatment of the new high-Cr cast roadheader tool steel through heat treatment schemes 1 to 3, the structure is mainly lath martensite, and at the same time, high-carbon acicular martensite appears in different degrees, and the plasticity and toughness decrease. Compared with forged high-carbon H13 roadheader tool steel, the hardness is increased by 2-3HRC, the tensile strength is increased by 8.3%-11.5%, and the yield strength is increased by 13.2%-19.5%. When the quenching temperature is higher than 1100 °C, quenching cracks on the surface of the sample are more obvious. Oxidation at 550°C for 60 hours in an air environment is 50.7% of that...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com