Method for producing n-hexane through raffinate oil
A technology for n-hexane and raffinate oil, which is applied in the field of reforming raffinate oil recovery and utilization, can solve problems such as difficult separation, and achieve the effects of wide adaptability and reduced energy consumption.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
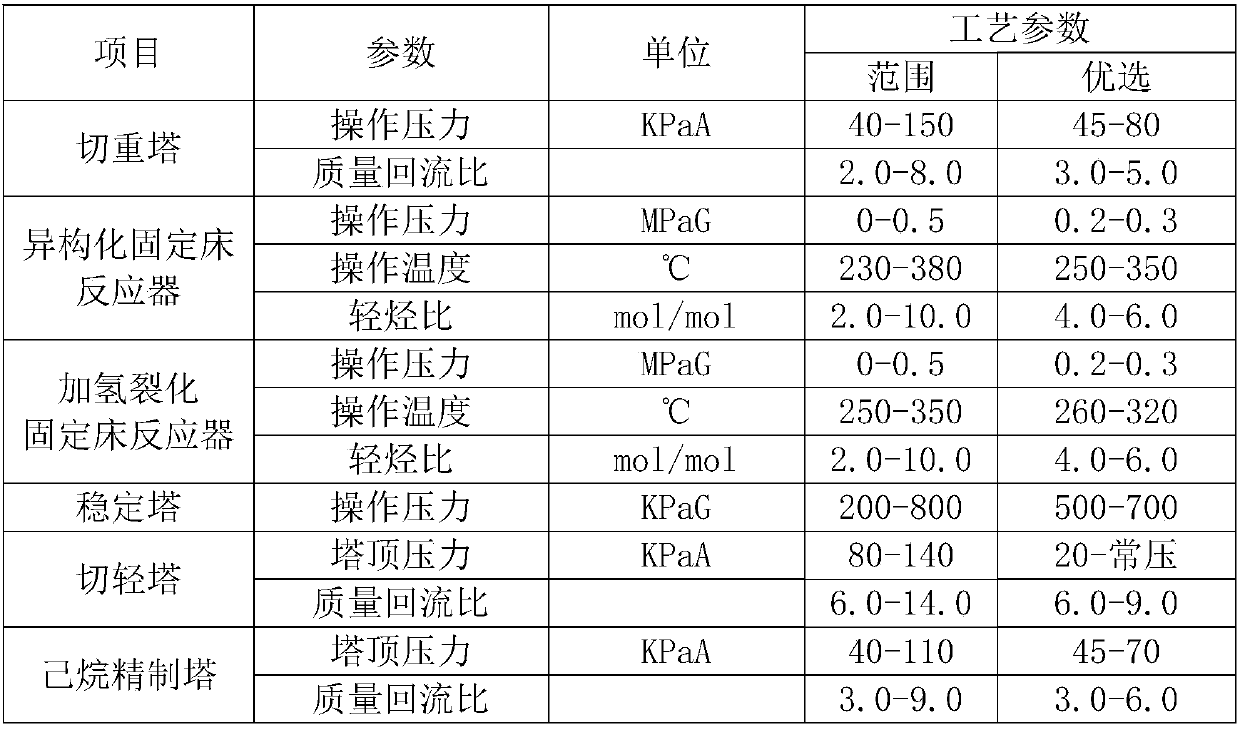
[0049] The complete composition of the reformed raffinate in the catalytic reforming unit of a petrochemical company is shown in Table 1. The company's raffinate contains more C5 components and a certain amount of heavy components. According to the full composition of the raffinate oil in Table 1, the content of methylcyclopentane is relatively high, and the isomerization reaction should be selected to obtain cyclohexane and benzene with relatively higher industrial value.
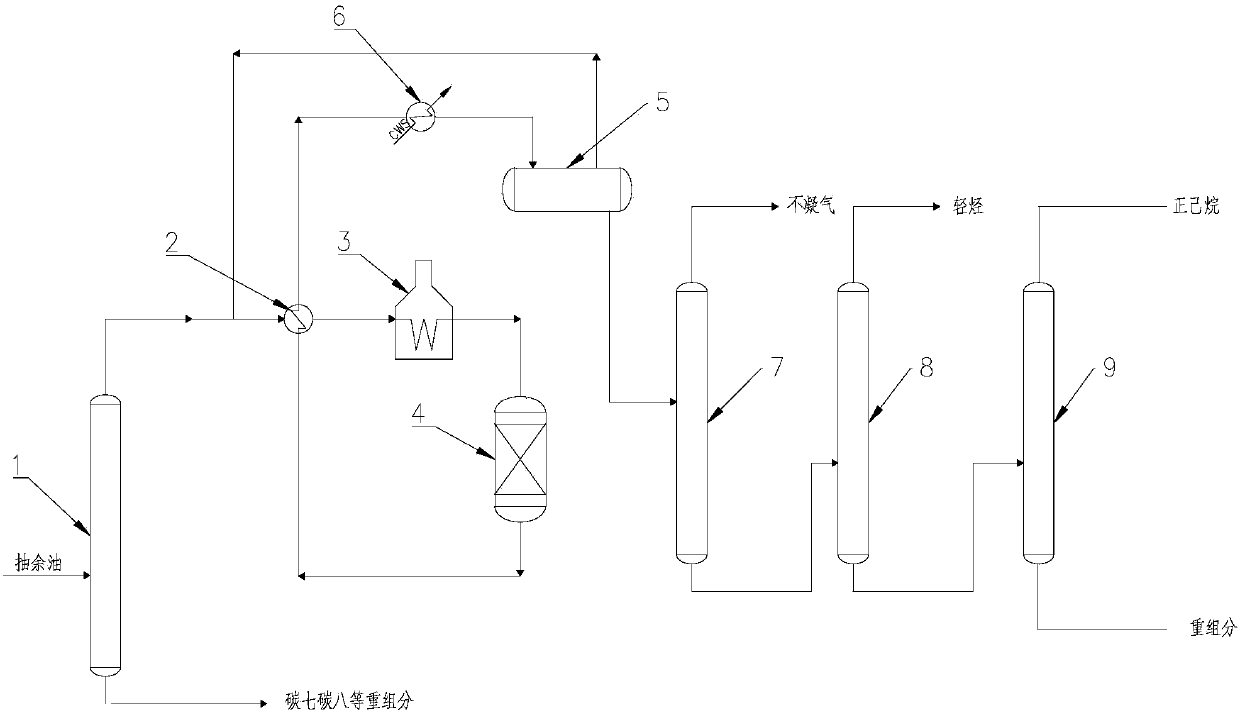
[0050] Such as figure 1 Shown is the schematic process flow diagram of embodiment 1. The raffinate oil is exchanged with the material in the bottom of the weight-shearing tower and then sent to the weight-shearing tower. C5 and C6 components are distilled from the top of the tower, and heavy components such as C7 and C8 are extracted from the bottom of the tower.
[0051] The C5C6 components distilled from the top of the weight-shear tower are first mixed with the circulating hydrogen, and then exchanged...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Table 2 shows the PONA group composition of reformed raffinate oil from a catalytic reforming unit of a Sinopec company. The company's raffinate oil is mainly composed of C6-C7 isoparaffins and normal paraffins, basically free of olefins and aromatics, of which n-hexane accounts for 93.7% of the total content of normal paraffins. According to the PONA group composition of raffinate oil in Table 2, the content of methylcyclopentane is relatively low, and hydrocracking reaction should be used. The cracking reaction mainly produces small molecular light hydrocarbons of C1-C5, which has greater relative volatility and is easier to realize. The separation from n-hexane, the implementation process of the hydrocracking reaction is described below.
[0061] The implementation process is implemented according to the schematic diagram of the technological process of Example 1, and the difference is that the fixed-bed reactor of Example 1 is an isomerization fixed-bed reactor, and...
Embodiment 3
[0068] The complete composition of No. 6 solvent oil is shown in Table 3. According to Table 3, it can be seen that the content of methylcyclopentane is relatively high, and the isomerization reaction should be selected to obtain cyclohexane and benzene with relatively higher industrial value. The implementation process was carried out according to the schematic process flow diagram of Example 1, and the operating temperature of the fixed-bed reactor was 270°C. At this operating temperature, the selectivity of cyclohexane was greater than that of benzene.
[0069] Table 3 The complete composition of No. 6 solvent oil
[0070] components
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com