A method for synergistically catalyzing the one-step conversion of cellulose to 1,4-sorbitol
A technology of sorbitan and synergistic catalysis, which is applied in the field of catalysis to achieve the effects of avoiding corrosion and environmental problems, reducing costs and reducing dosage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
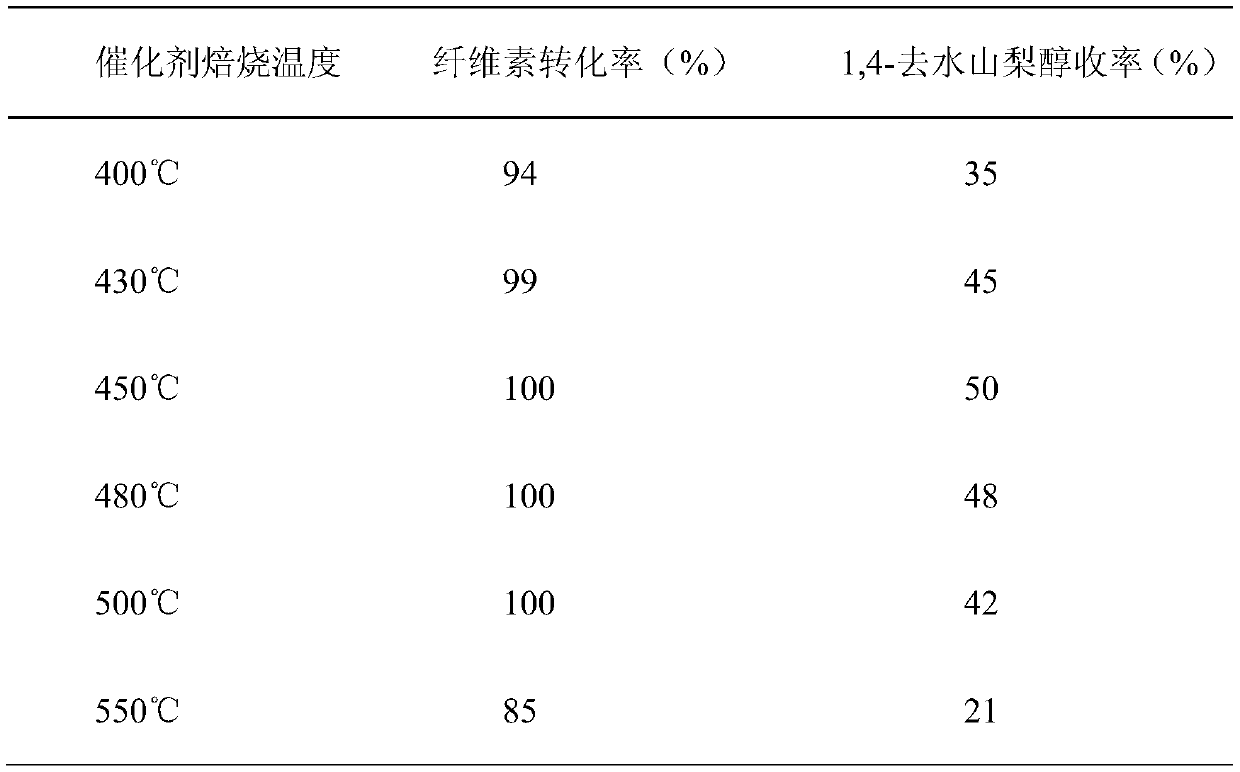
[0022] Example 1: Evaluation of the catalytic performance of niobium phosphate obtained at different calcination temperatures to catalyze the conversion of cellulose into 1,4-sorbitan.
[0023] Add 30ml of water into the reaction kettle as a solvent, add 0.3g of α-cellulose as a raw material, add 0.03g of Ru / C (5wt%, Aladdin), 0.3g of niobium phosphate catalyst, and react at 220°C for 3h under a hydrogen atmosphere of 5MPa. After the reaction was cooled down, the liquid phase product was detected and quantitatively analyzed by high performance liquid chromatography.
[0024] Described niobium phosphate catalyst is prepared by hydrothermal method, and its preparation method comprises the following steps:
[0025] Step 1: Preparation of niobium hydroxide: hydrofluoric acid with a molar ratio of 5:1 and niobium pentoxide heated in water at 100°C for 12 hours to obtain niobium fluoride solution; after cooling, titrate with ammonia water until alkaline to obtain niobium hydroxide p...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Embodiment 2: change the catalytic performance evaluation of reacting to the catalyst dosage of niobium phosphate
[0032] The difference between this example and Example 1 is that niobium phosphate (calcined at 450° C.) with better catalytic effect is selected as the catalyst, and the amount of the niobium phosphate catalyst is different.
[0033] Catalytic Performance Evaluation:
[0034] Add 30ml of water as a solvent, 0.3g of α-cellulose as a raw material, 0.03g of Ru / C, and 0.1-0.7g of niobium phosphate as a catalyst in the reaction kettle, and react at 220°C for 3 hours under a 5MPa hydrogen atmosphere. The catalytic effect is shown in Table 2:
[0035] Table 2 Catalytic Performance Evaluation of Different Niobium Phosphate Catalyst Consumption on Reaction
[0036]
Embodiment 3
[0037] Embodiment 3: change Ru / C catalyst consumption to the catalytic performance evaluation of reaction
[0038]The difference between this example and Example 1 is that niobium phosphate (calcined at 450° C.) with better catalytic effect is selected as the acid catalyst, but the amount of Ru / C catalyst is different.
[0039] Catalytic Performance Evaluation:
[0040] Add 30ml of water as a solvent, 0.3g of α-cellulose as a raw material, 0.3g of niobium phosphate, and 0.02-0.07g of Ru / C into the reaction kettle, and react at 220°C for 3 hours under a 5MPa hydrogen atmosphere. The catalytic effect is shown in Table 3:
[0041] Table 3 Catalytic performance evaluation of Ru / C catalyst dosage on the conversion of cellulose to 1,4-sorbitol
[0042]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com