Method for producing hollow porous microspheres
A technique for porous microspheres and a manufacturing method, which is applied in the field of scaffolds for tissue engineering in biological tissues, which can solve the problems of reduced production efficiency, low pore uniformity, and high loss rate, and achieve simplified production processes and excellent stomatal uniformity Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] [Example 1] Production of hollow porous microspheres 1
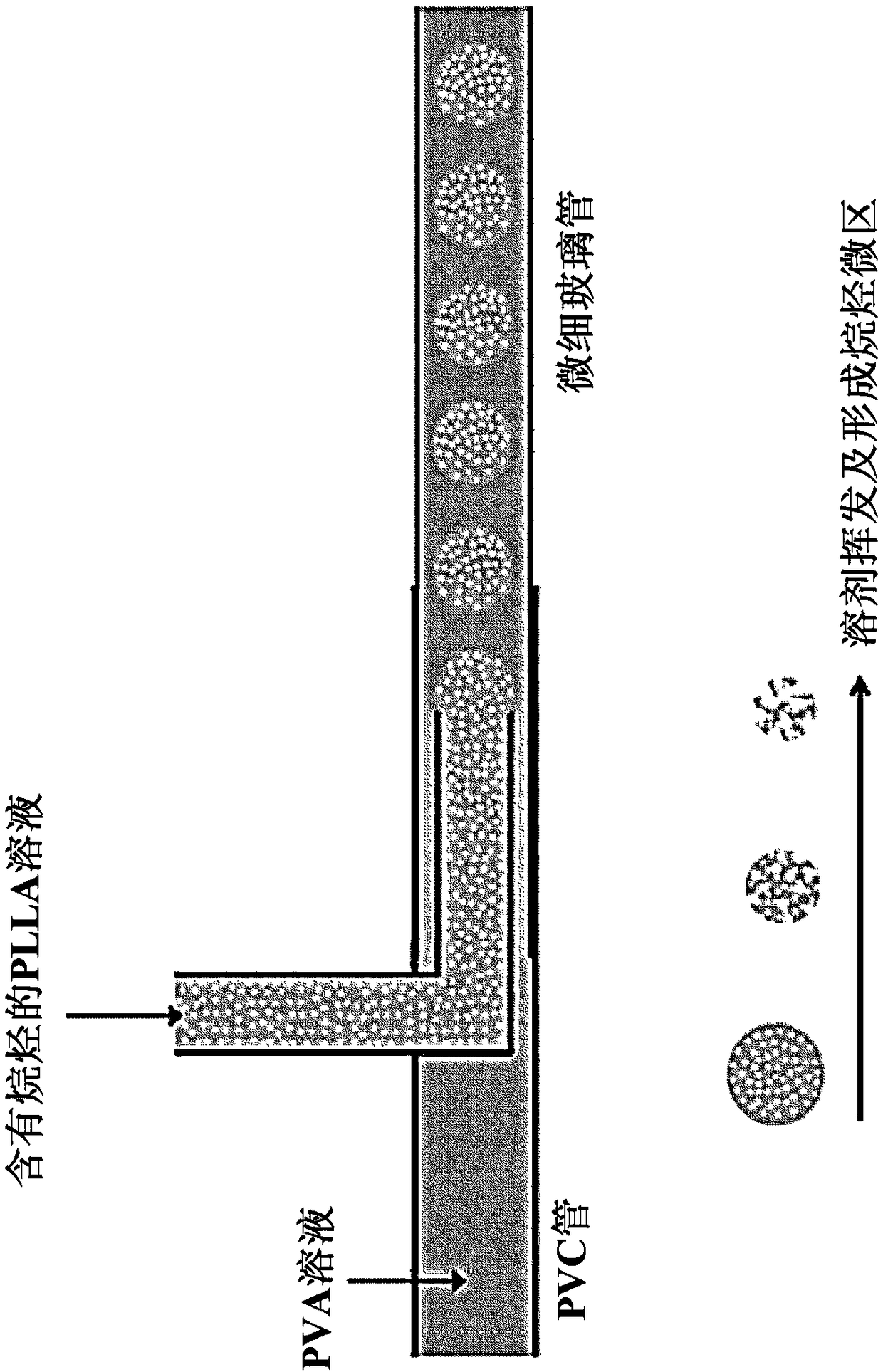
[0042] Hollow porous microspheres according to an embodiment of the present invention have been manufactured by the following method (refer to figure 1 ).
[0043] Step 1: Fabrication of a simple fluidic device
[0044] A 30-gauge injection needle bent at 90° was placed in a PVC tube, and a microfluidic device was fabricated by inserting a fine glass tube between the injection needle and the PVC tube. The fabricated microfluidic device uses epoxy adhesive to plug the tiny gaps.
[0045] Step 2: Preparation of PLLA solution containing alkanes
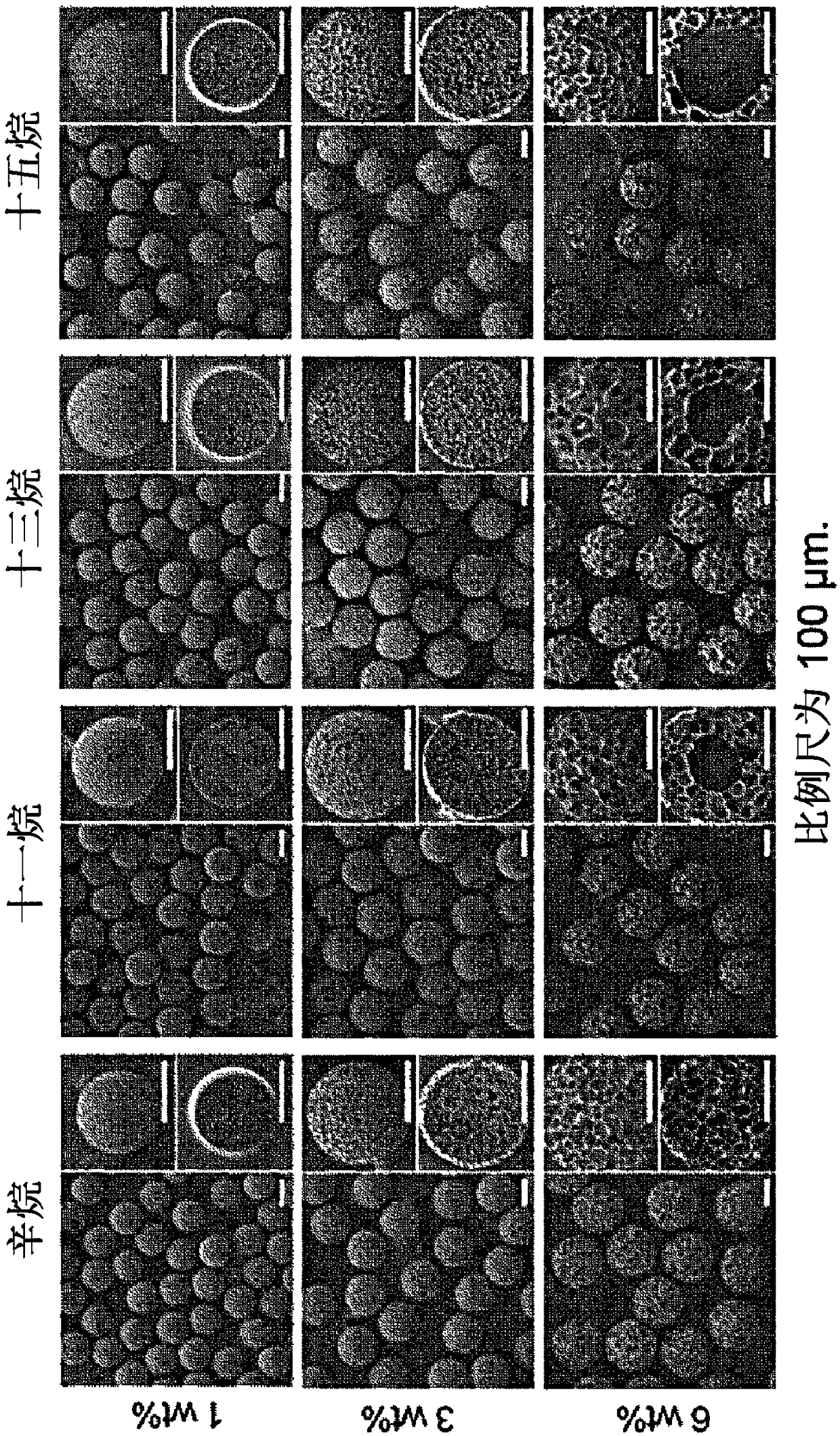
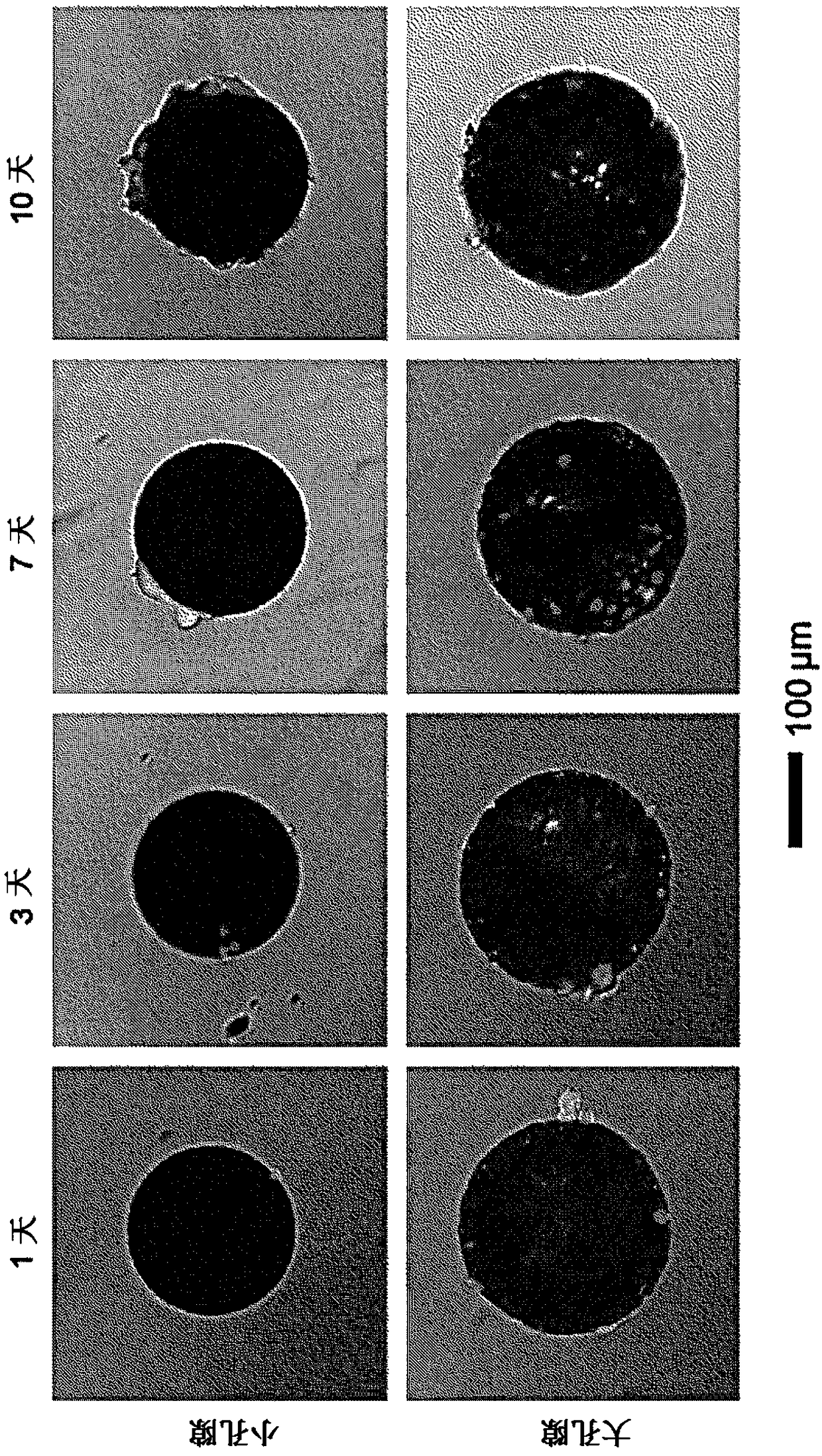
[0046] 0.1 g of PLLA (RESOMER LR 704S, Evonik Industries AG) as a hydrophobic biodegradable polymer, 10 g of dichloromethane (Dichloromethane; 34355-0350, Junsei) as a volatile solvent, and alkanes as a stomatal formation inducing substance Substances, specifically octane (Octane, 412236, Sigma-aldrich) or undecane (U407, Sigma-aldrich) or tridecane (T57401, Sigma-aldric...
Embodiment 2
[0054] [Example 2] Production of hollow porous microspheres 2
[0055] Hollow porous microspheres according to an example of the present invention were manufactured by the following method.
[0056] Step 1: Fabrication of a simple fluidic device
[0057] A 30-gauge injection needle bent at 90° was placed in a PVC tube, and a microfluidic device was fabricated by inserting a fine glass tube between the injection needle and the PVC tube. The fabricated microfluidic device uses epoxy adhesive to plug the tiny gaps.
[0058] Step 2: Manufacture of PLLA solution containing vegetable oil
[0059] Mix 0.1 g of PLLA (RESOMER LR 704S, Evonik Industries AG) as a hydrophobic biodegradable polymer, 10 g of methylene chloride (34355-0350, Junsei), and 0.5 g each of cottonseed oil or soybean oil as a stomatal formation inducing substance , thus making a hydrophobic biodegradable polymer (PLLA) solution.
[0060] Step 3: Create a uniform PLLA emulsion
[0061] Use the PLLA solution obta...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com