Knitted fabric having excellent heat-retaining properties and production method therefor
A manufacturing method and technology of knitted fabrics, which are applied in knitting, weft knitting, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve problems such as movement barriers, insufficient thermal insulation, increased knitted fabric mesh, cloth thickness, etc., and achieve excellent thermal insulation, Excellent hand feel and good dimensional stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
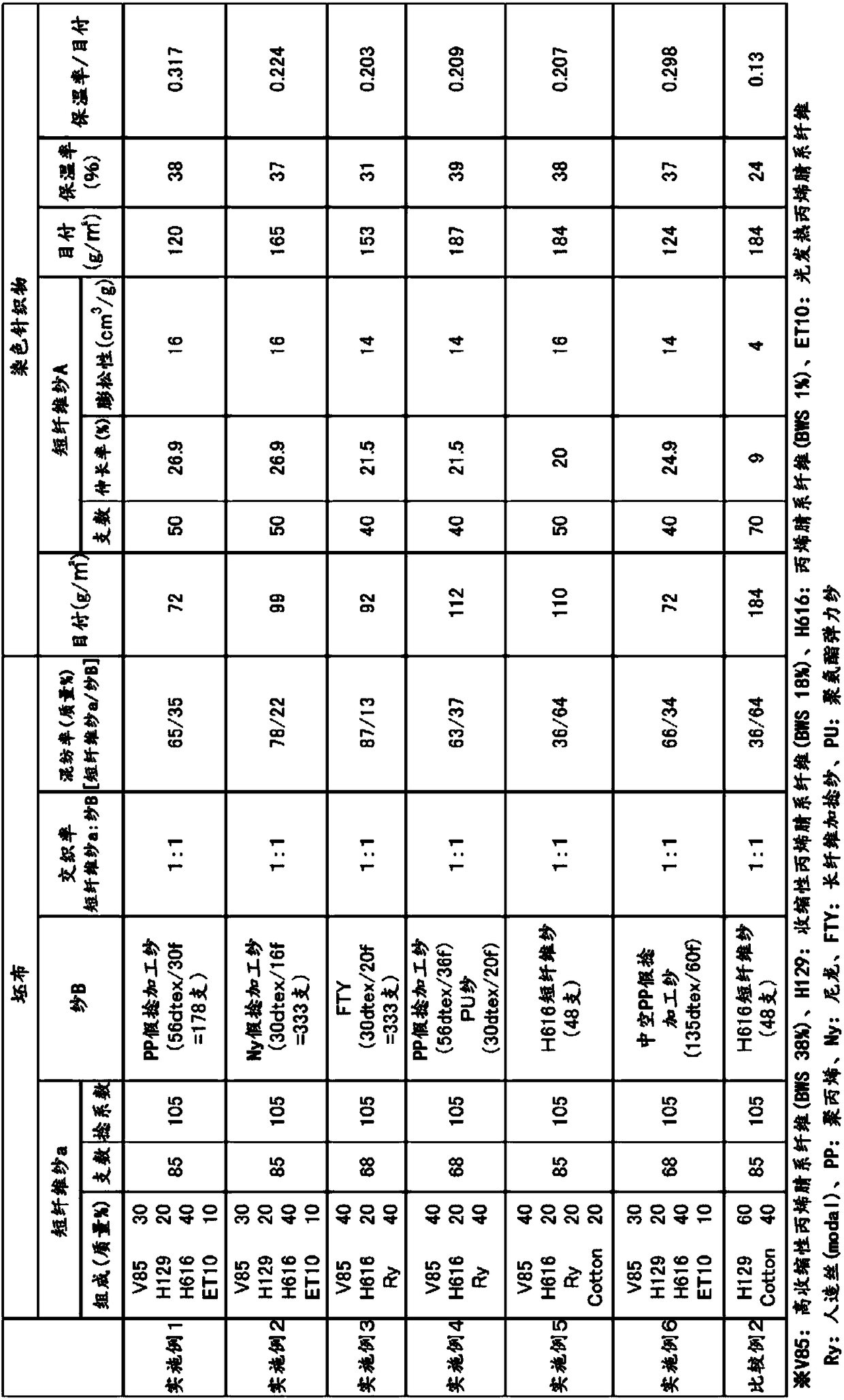
[0107] An acrylonitrile copolymer comprising 91% by mass of acrylonitrile and 9% by mass of vinyl acetate obtained by an aqueous suspension polymerization method was dissolved in dimethylacetamide to obtain a spinning dope having a polymer concentration of 20% by mass. This spinning dope was discharged into a coagulation bath having a composition of 60% by mass of dimethylacetamide, 40% by mass of water, and a temperature of 40° C. using a spinneret having circular discharge holes for spinning. In addition, for the spinneret, a nozzle die having a discharge hole of 0.008 mm in diameter and 15,000 holes was used. Next, after washing the solvent in boiling water, stretch it to 5 times, then attach the oil agent, dry it with a hot roll at 150°C, perform a heat relaxation treatment, and perform a steam stretching process of 1.8 times in order to obtain the target shrinkage rate, and then cut it. The fiber-forming length was 38 mm, and the acrylic fiber whose cross-sectional shape ...
Embodiment 2
[0110] Using a circular knitting machine with 12 needles (G) and 24 mouths, the twist coefficient made in Example 1 is 105 and the staple fiber yarn a of 85 counted as the yarn count and the nylon false twist processed yarn (30dtex / 16f ) yarn B interweaves the knitted fabric of the double rib structure at an interlacing ratio of 1:1, and obtains the aforementioned 85-count staple fiber yarn a with a blending ratio of 78% by mass and a mesh weight of 99 g / m 2 woven fabric. This woven fabric was dyed in the same manner as in Example 1. The net weight of the knitted fabric obtained is 165g / m 2 , With regard to the spun yarn A constituting the knitted fabric, the above-mentioned 85-count spun-staple yarn a shrunk to become a thick dyed yarn of 50 metric counts. In addition, the heat retention rate of the obtained knitted fabric was 37%, which was excellent in heat retention.
Embodiment 3
[0112] 40% by mass of the highly shrinkable acrylic fiber (V85) produced in Example 1, 20% by mass of the same acrylic fiber (H616) as used in Example 1, and rayon with a single fiber fineness of 1.3 dtex After the yarn (Ry) was blended at 40% by mass, a staple yarn a with a twist coefficient of 105 and a metric count of 68 was produced through a cotton spinning process. Using a circular knitting machine with 12 needles (G) and 24 mouths, the spun yarn a of 68 counted in metric count and the yarn B of FTY (30dtex / 20f) are interleaved with plain stitches at an interweaving ratio of 1:1 In the knitted fabric of the structure, the blending rate of the above-mentioned 68 staple yarn a was 87% by mass and the mesh weight was 92g / m. 2 woven fabric. This woven fabric was dyed in the same manner as in Example 1. The net weight of the knitted fabric of gained is 153g / m 2 , With regard to the spun yarn A constituting the knitted fabric, the above-mentioned 68-count spun-staple yarn a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| elongation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| twist factor | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| shrinkage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com