Application of narrowly distributed chitosan oligosaccharides in the preparation of functional foods for the prevention of long-term high-fat diet-induced hyperglycemia
A technology of functional food and chitosan oligosaccharides, which is applied to the functions of food ingredients, medical preparations containing active ingredients, applications, etc., to achieve the effects of reducing fasting blood sugar, reducing insulin resistance index, and restoring pancreatic tissue structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
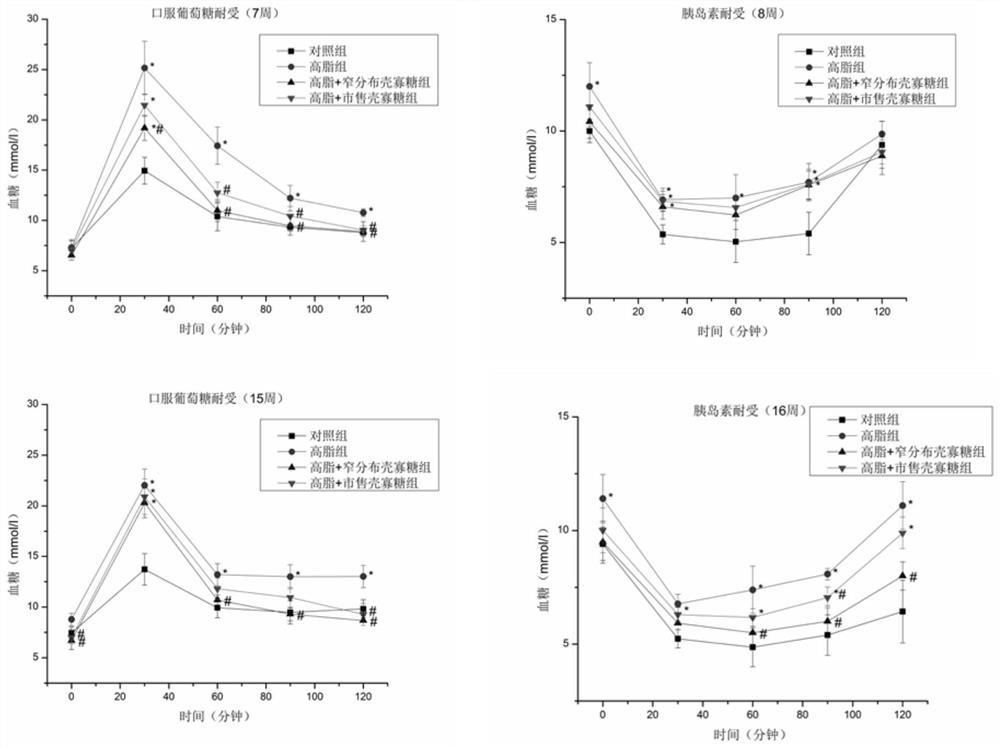
[0052] Example 1: Effects of narrowly distributed chitosan oligosaccharides on oral glucose tolerance and insulin tolerance in long-term high-fat diet mice
[0053] The oral glucose tolerance (OGTT) test was performed on the 7th and 15th week of mouse feeding, and the insulin tolerance (ITT) test was performed on the 8th and 16th week. figure 1 It can be known that the addition of the narrow-distribution chitosan oligosaccharide of the present invention can significantly improve the oral glucose tolerance and insulin tolerance of mice with hyperglycemia induced by a high-fat diet (P<0.05). And it is better than the chitosan oligosaccharide with a commercially available average molecular weight of 3000.
Embodiment 2
[0054] Example 2: Effects of narrowly distributed chitosan oligosaccharides on fasting blood glucose and insulin levels in long-term high-fat diet mice
[0055] Table 2 Effects of narrowly distributed chitosan oligosaccharides on fasting blood glucose and insulin levels in long-term high-fat diet mice
[0056]
[0057] As shown in Table 2, the high-fat diet for 16 weeks significantly increased the fasting blood glucose, and the fasting blood glucose value of the mice in the narrow distribution chitosan oligosaccharide group significantly decreased. The insulin content of the mice in the high fat group was slightly lower than that in the normal group, but there was no significant difference. Insulin content in the narrowly distributed chitosan oligosaccharide group was significantly higher than in the fat group, indicating that this is an important compensatory response for the body to maintain blood sugar at normal levels after high-fat diet feeding. Insulin resistance ind...
Embodiment 3
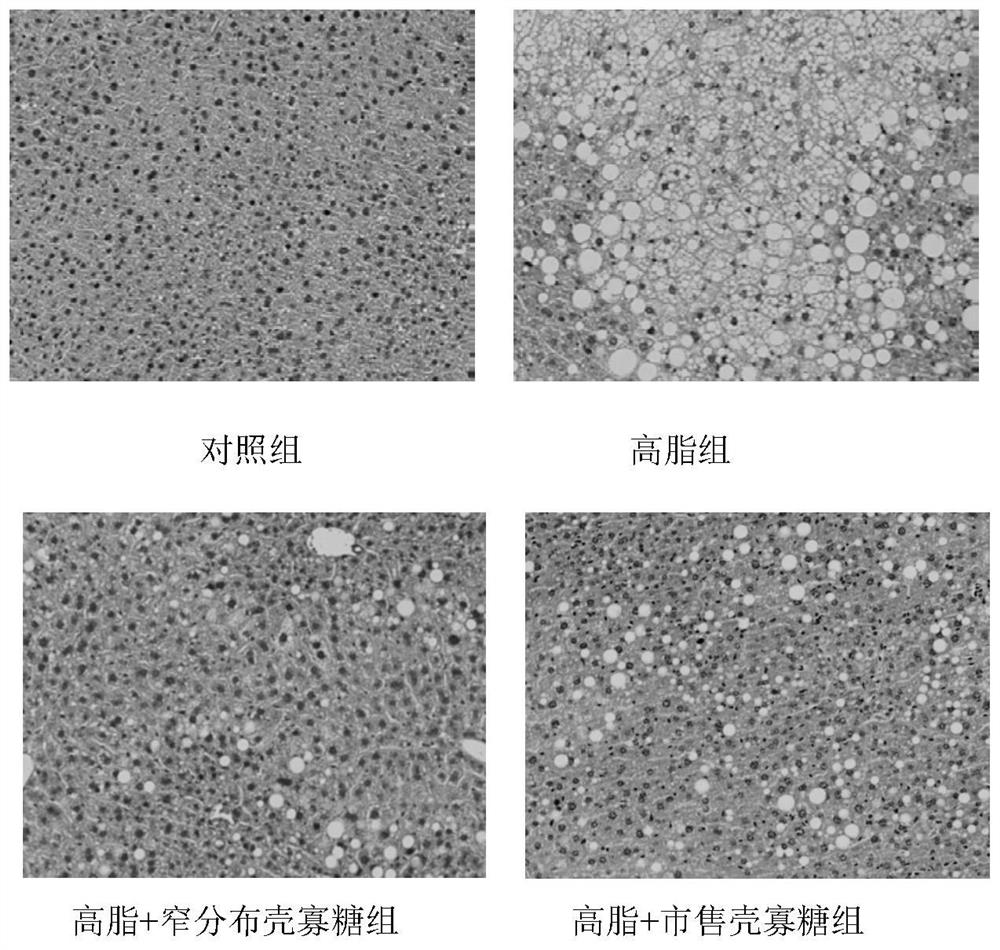
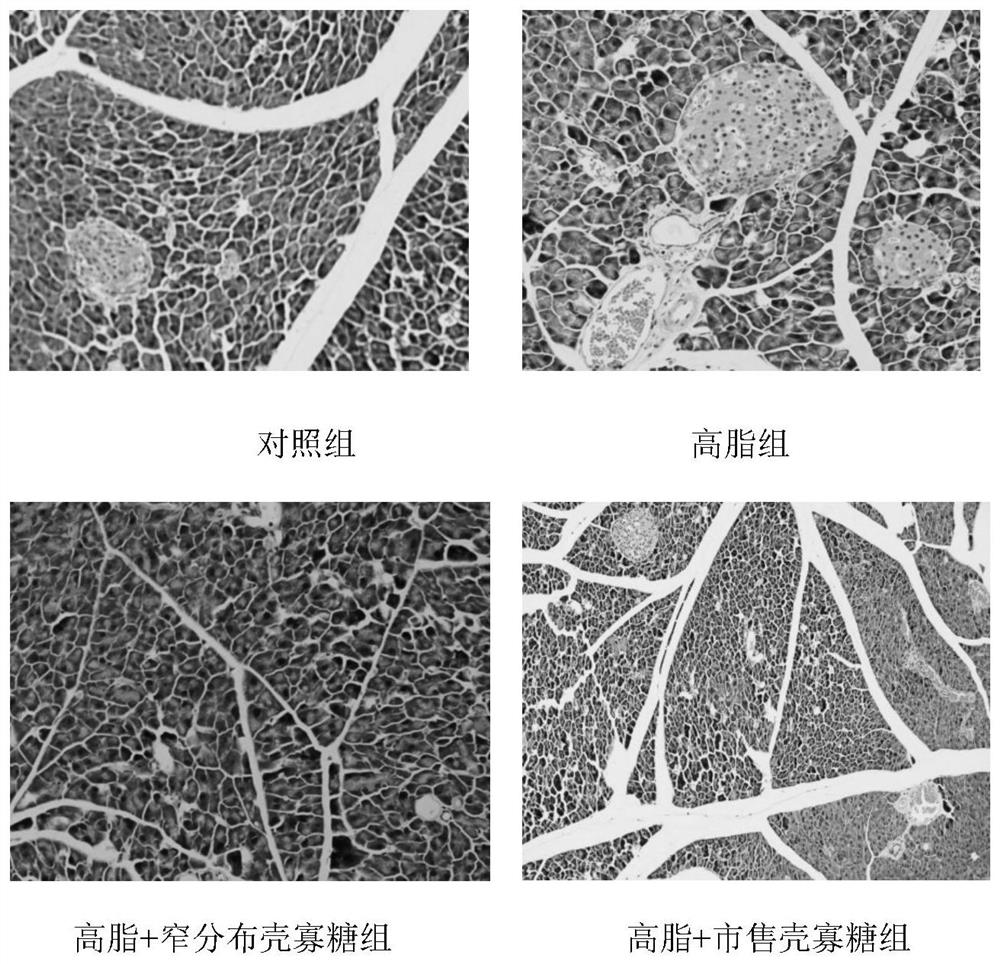
[0058] Example 3: Effects of narrowly distributed chitosan oligosaccharides on liver fat infiltration in mice with long-term high-fat diet
[0059] refer to figure 2 It can be seen that, compared with the normal group, the liver of high-fat diet mice showed significant fat infiltration, the cytoplasm was occupied by a large number of fat vacuoles, and the cell boundaries became blurred, indicating that high-fat diet disrupted the normal metabolism of liver lipids in mice , a large accumulation of fat in the liver. The shape of liver cells in the mice in the narrow distribution chitosan oligosaccharide group was significantly restored, the fat vacuoles in the liver cells became smaller and smaller, the accumulation of lipids was reduced, and the fatty degeneration of the liver tissue was significantly reduced in the fat group. Compared with the high-fat diet mice, the commercially available chitosan oligosaccharide group with an average molecular weight of 3000 has reduced fa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com