Ketoreductase and method for catalytic preparation of (S)-1-(2-chlorophenyl)ethanol by ketoreductase
A technology for catalytic preparation and reductase, applied in oxidoreductase, fermentation and other directions, can solve the problems of low substrate concentration, low conversion rate, hindering industrial production, etc., achieve good catalytic performance, and simplify the production process and cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] Example 1 Preparation of ketoreductase
[0066] Inoculate the genetically engineered bacteria (vector pET21a, host cell E.Coli BL21(DE3)) containing the coding gene (SEQ ID No.1) of ketoreductase into 5 mL of ampicillin-containing LB test tube medium for activation culture (37° C. Cultivate for 12h), transfer the activated culture to 400mL LB liquid medium containing ampicillin according to 1% inoculum size, culture at 37°C to OD to 0.6-0.8, add IPTG (final concentration 0.1mM) and induce culture at 25°C for 16h. Collect the cells by centrifugation to obtain ketone reductase cells, resuspend the cells in 40 mL of distilled water, and ultrasonically break in an ice-water bath for 15 minutes, collect the supernatant by centrifugation, pre-freeze at -20°C, freeze-dry in vacuum for 48 hours, and crush to obtain recombinant ketones Reductase Enzyme Powder.
Embodiment 2
[0067] Example 2 Preparation of gram-grade (S)-1-(2-chlorophenyl)ethanol
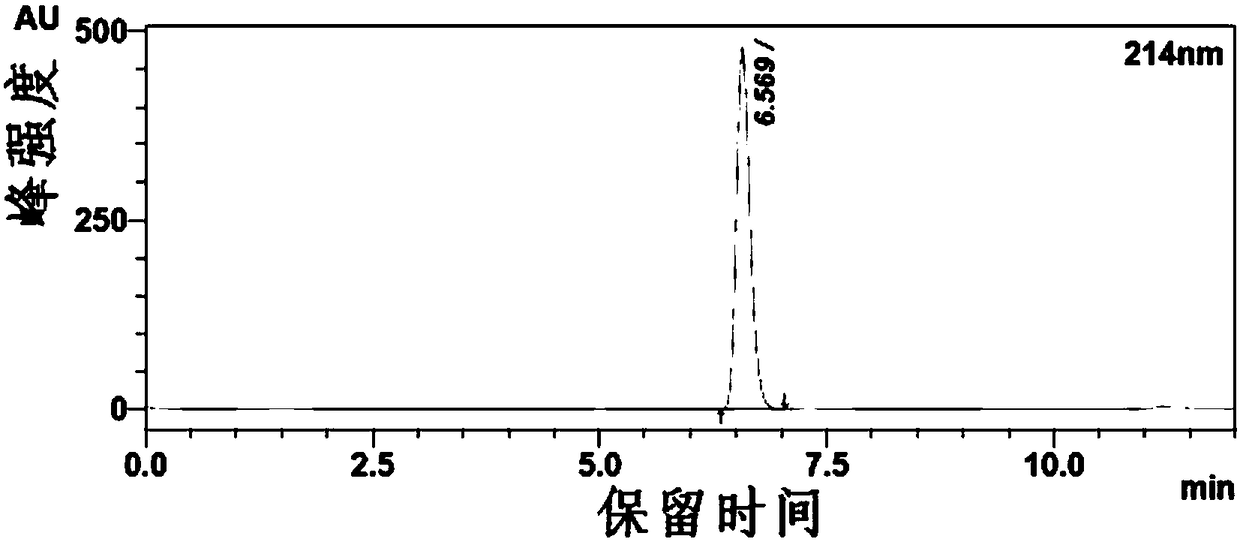
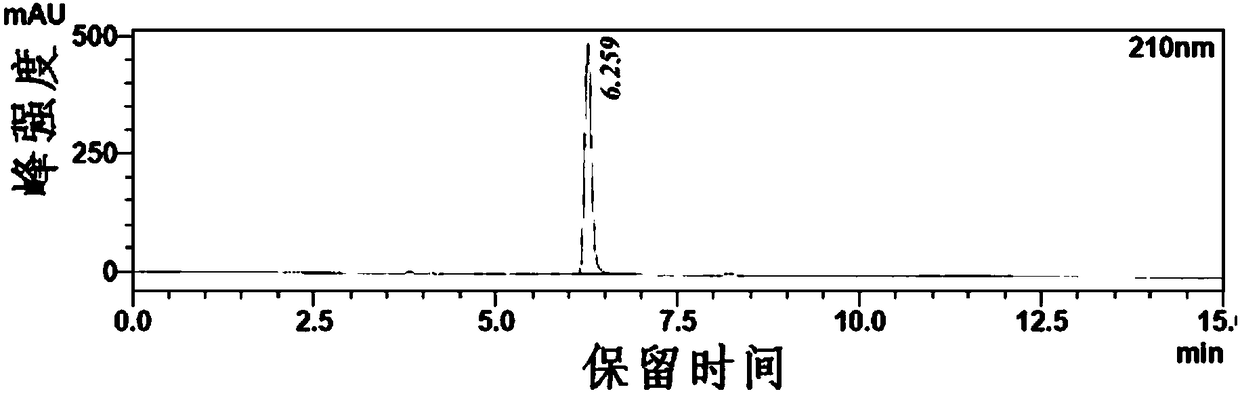
[0068] Add isopropanol (5mL) and substrate o-chloroacetophenone (1.5g) into the reaction vessel, stir well and then add enzyme powder 0.1g, coenzyme NADP + Finally, dilute the volume of 1 mg to 10 mL with pure water, stir the reaction under magnetic force at 30°C, and monitor the progress of the reaction by TLC. After 6 hours, the reaction was completed, the reaction solution was filtered with diatomaceous earth, the liquid phase was extracted three times with the organic phase, the organic phases were combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and spin-dried under reduced pressure to obtain the product. The conventional HPLC profile of the substrate before the reaction solution starts to react is as follows: figure 1 Shown, the chiral HPLC spectrogram of substrate is as attached figure 2 Shown; The 1-(2-chlorophenyl) ethanol chiral HPLC of racemate is as attached image 3 Shown; The chiral HPLC...
Embodiment 3
[0069] Example 3 Preparation of gram-level (S)-1-(2-chlorophenyl)ethanol
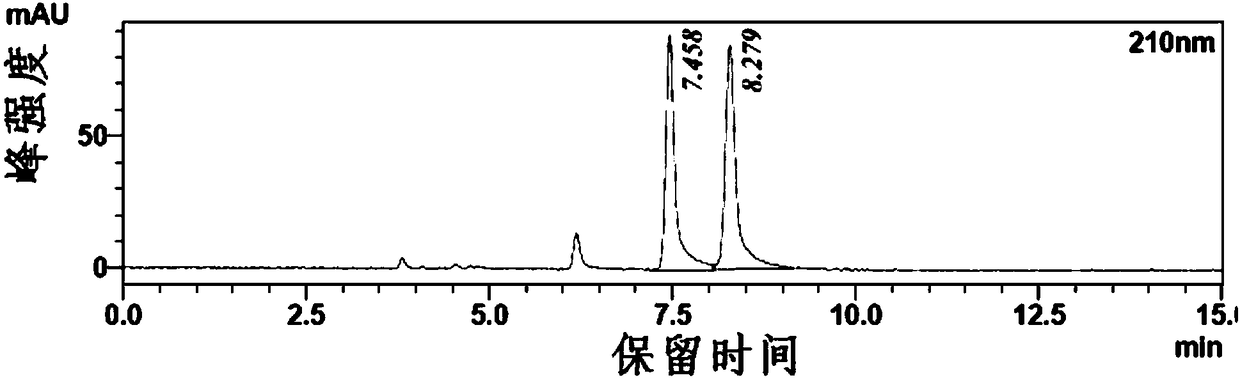
[0070] Add isopropanol (6.4mL) and substrate o-chloroacetophenone (2.8g) into the reaction vessel, stir well and add 0.26g of ketoreductase cells, coenzyme NADP + 1.2mg, finally dilute to 10mL with pure water, stir the reaction with magnetic force at 29°C, and detect the progress of the reaction by TLC at the same time. After 6 hours of reaction, diatomaceous earth was filtered, the liquid phase was extracted three times with the organic phase, the organic phases were combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and spin-dried under reduced pressure to obtain the product. Chiral HPLC of the reaction solution such as Figure 12 , The routine HPLC spectrogram detection of reaction solution is as attached Figure 6 , with Figure 12 and 6 The detection of the ee value and conversion rate of the product shows that: the substrate conversion rate=99.5%, and the ee value of the S-type product=99.9%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com