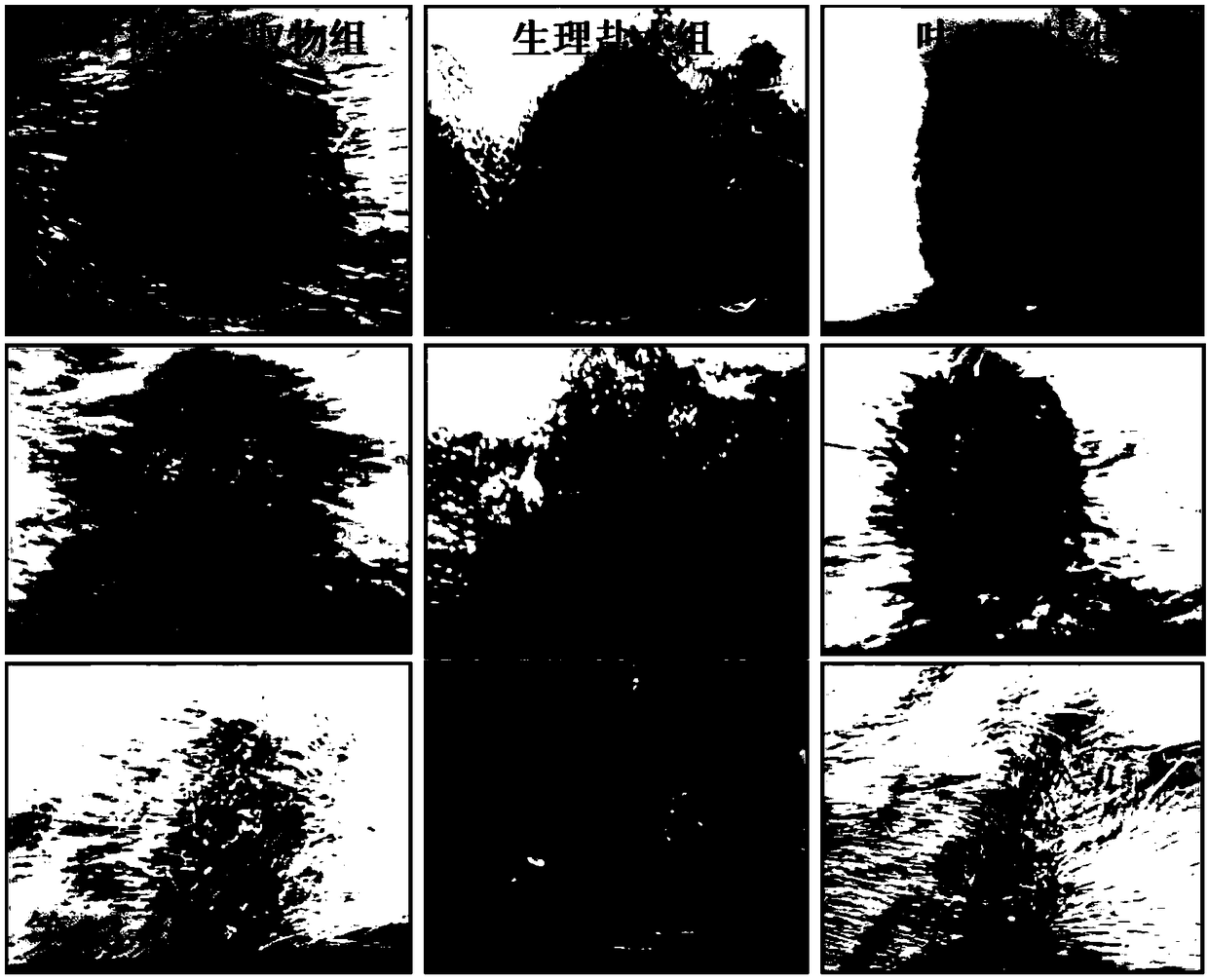
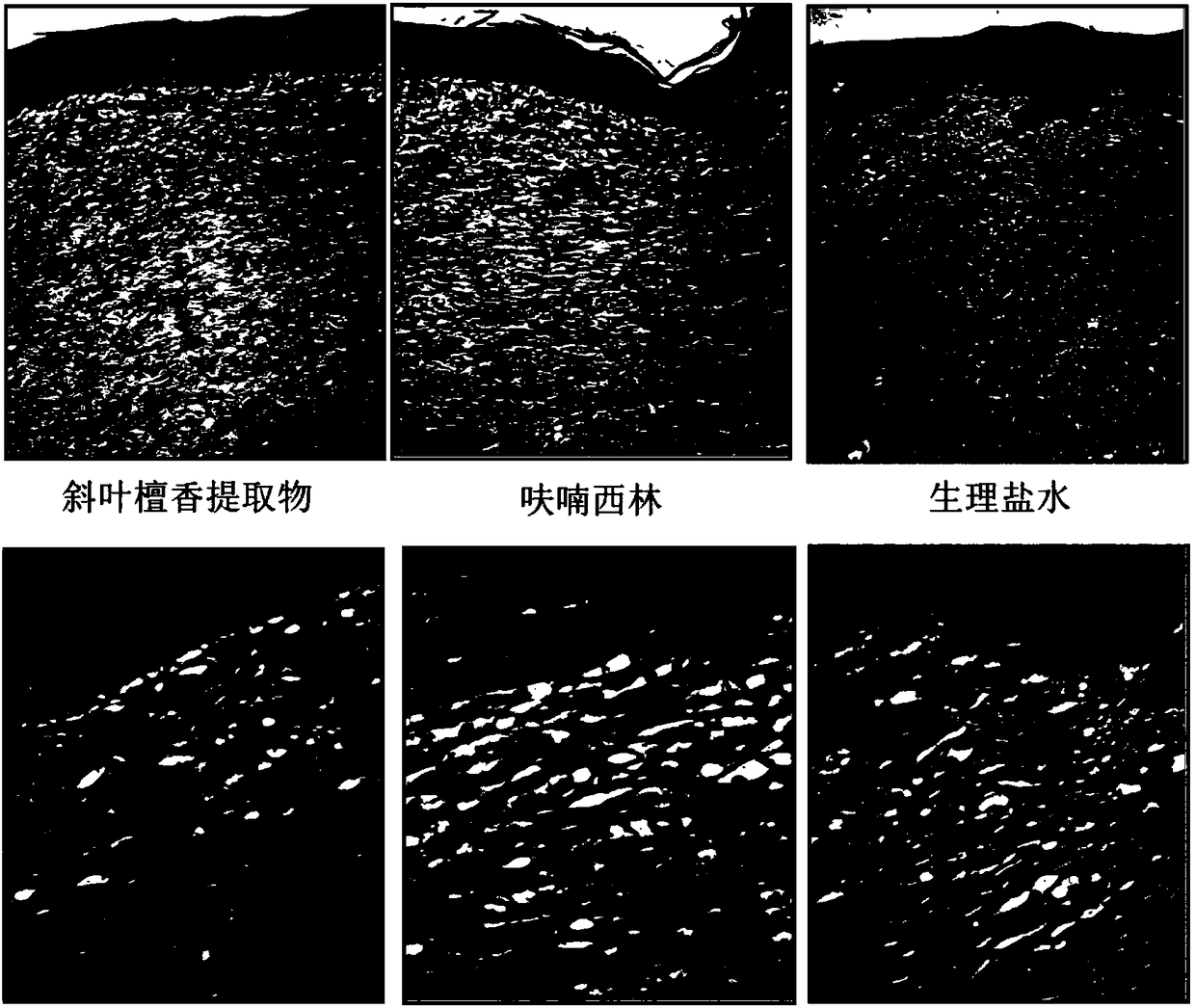
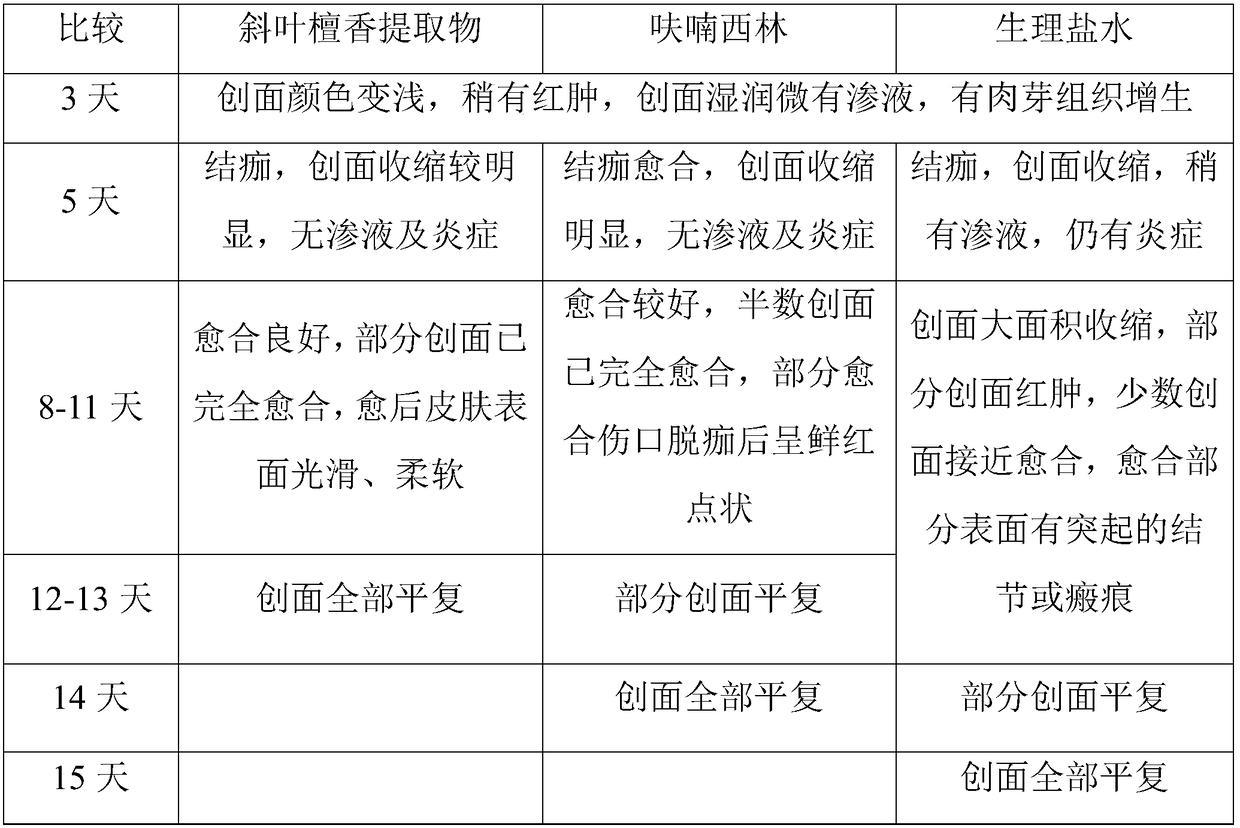
Application of extract of dalbergia pinnata in preparing drug for healing skin wound
A skin wound and extract technology, applied in the field of medicine, can solve the problems of no research report on the extraction method and use of the alcohol extract of oblique leaf sandalwood, and achieve the effects of promoting the proliferation of vascular endothelial cells, accelerating the healing speed and having broad prospects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] The present embodiment provides the preparation method of sandalwood oblique leaf extract, and the steps are as follows:
[0028] Crush 1 kg of oblique-leaved sandalwood cane, pass through a 20-mesh sieve, add 5000 mL of ethanol solution with a mass concentration of 95% and ultrasonically extract twice, each extraction time is 2 hours, filter, and combine the filtrates at -0.07 MPa at a temperature of Ethanol is recovered under reduced pressure at 50°C, concentrated to an extract, and then vacuum-dried at 60°C to obtain the Sandalwood oblique leaf extract of the present invention.
[0029] According to the method for determining the total flavonoid content specified in the 2015 edition of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia, the total flavonoid content in the Sandalwood oblique leaf extract was measured, and the total flavonoid content in the Sandalwood oblique leaf extract obtained under the extraction method was 20.8%.
Embodiment 2
[0030] Example 2 Preparation of cataplasm of sandalwood oblique leaf extract
[0031] Weigh 0.8g of CMC-Na, add an appropriate amount of purified water, heat and dissolve in a water bath to make a 20% solution, add an appropriate amount of glycerin, stir well, and form A phase; prepare 10% PVA aqueous solution and 10% gelatin aqueous solution by the same method, respectively Phase B and Phase C: first mix Phase B and Phase C, then add to Phase A, stir evenly, add finely powdered silica gel and preheated sandalwood extract, and apply it on the non-woven fabric while it is hot. Place it in an electric constant temperature drying oven, and dry it at 70°C for 2 hours to obtain a poultice of Sandalwood oblique leaf extract.
Embodiment 3
[0032] Embodiment 3 preparation of sandalwood oblique leaf extract gel
[0033] Weigh 2.5g of Carbomer-940, moisten it with 11mL of glycerin and add 60mL of distilled water to swell, leave it overnight at room temperature for later use (I); weigh 5g of Sandalwood oblique leaf extract, add absolute ethanol to dissolve it completely, and set aside for later use (II) ;Weigh 20g of urea, add 20mL of distilled water to dissolve, and set aside (Ⅲ); Mix I, II, and III, slowly add 1.0g of Tween-80, add an appropriate amount of triethanolamine to adjust the pH value to 7.0, and finally add distilled water to 200g, stir Uniform, degassed, sterilized, potted, that is.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com