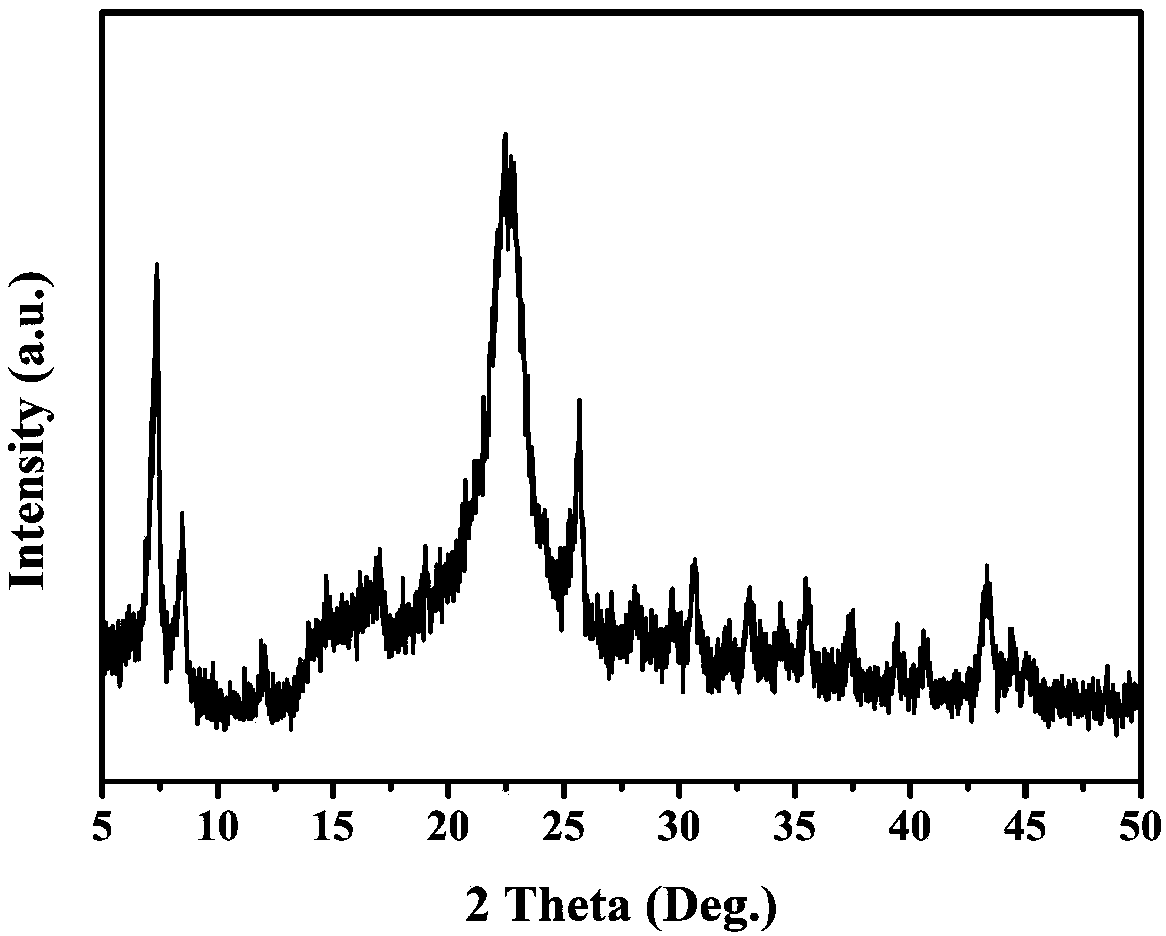
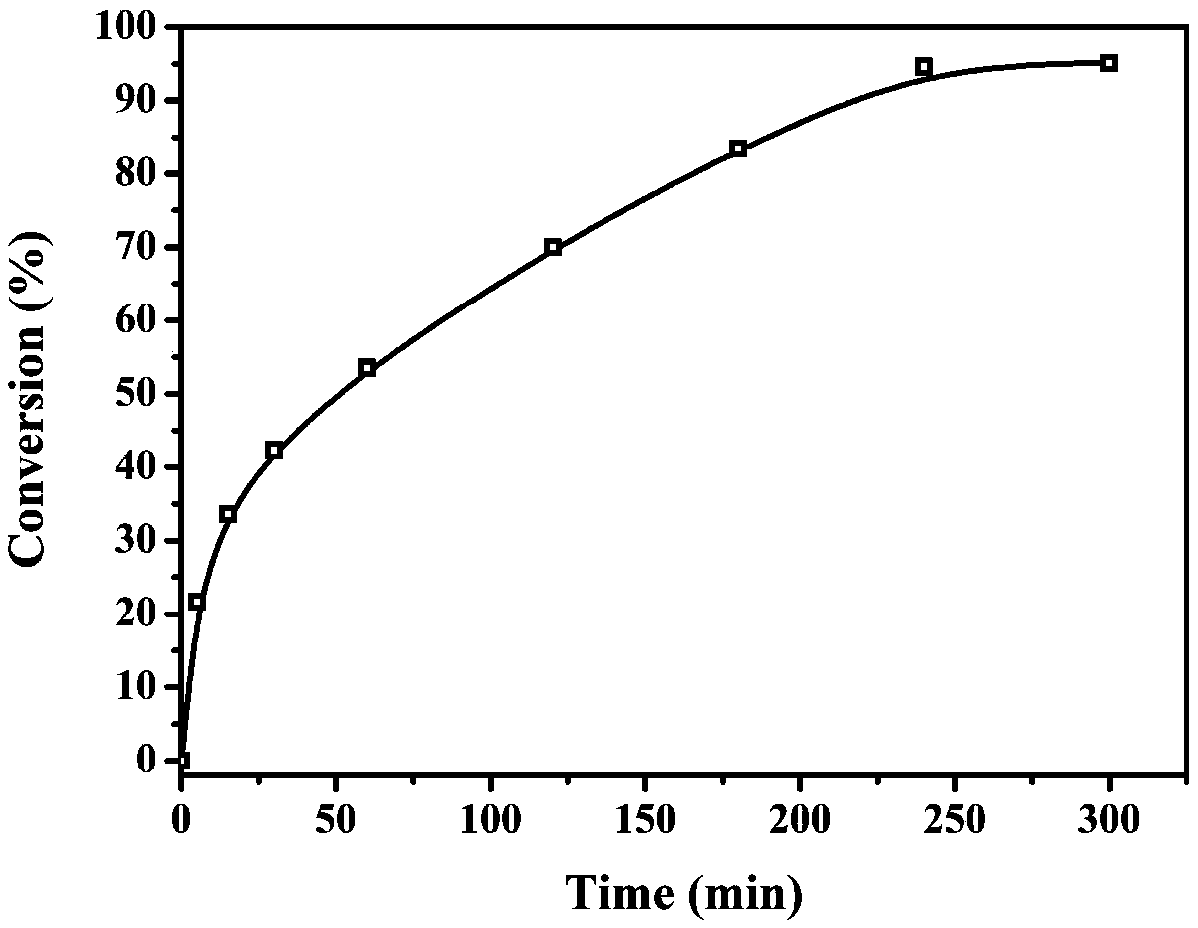
Cellulose/UiO-66-NH2 porous material capable of degrading organophosphate biochemical toxic agent and preparation method thereof
A uio-66-nh2, organic phosphate ester technology, applied in organic compound/hydride/coordination complex catalysts, chemical instruments and methods, fiber processing, etc., can solve the problem of large specific surface area, high porosity and low density and other problems, to achieve the effect of good degradation effect and good mechanical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
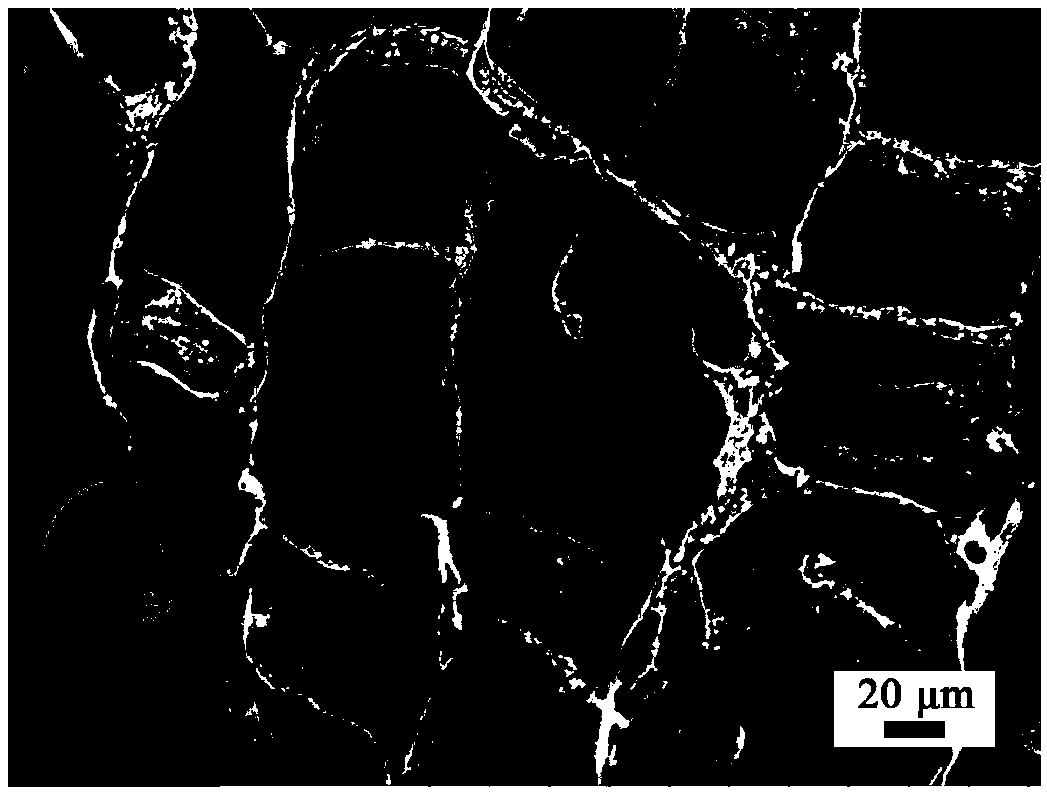
[0039] (1) Add 0.06g of silane coupling agent KH560 to 5g of wood pulp nanocellulose suspension with a solid content of 1.2wt%, and magnetically stir for 4h at room temperature to obtain a hydrolyzate of cellulose nanowires and silane coupling agent KH560 Suspension; placed in liquid nitrogen for rapid cooling for 15 minutes, the cooling method is bottom-up directional cooling to obtain ice gel; then placed in a freeze dryer at -40°C, 25 Pa, freeze-dried for 35 hours, and placed at 110 after drying Bake in an oven at ℃ for 30 minutes to obtain a cellulose porous material, which is stored in a ziplock bag for later use.
[0040] (2) Add 125mg of zirconium chloride powder to a 50ml sample bottle, add 1ml of hydrochloric acid and 5ml of N,N-dimethylformamide dropwise, sonicate for 5min to make the dispersion uniform, and then dropwise add 134mg of 2-aminoterephthalic acid And 10ml of N,N-dimethylformamide, ultrasonically 5min to disperse completely and transfer to a hydrothermal syn...
Embodiment 2
[0046] (1) Add 0.1g of silane coupling agent KH560 to 3.9g of wood pulp nanocellulose suspension with solid content of 1.28wt%, and magnetically stir for 5h at room temperature to obtain hydrolyzate of cellulose nanowires and silane coupling agent KH560 Suspension; placed in liquid nitrogen to quickly cool for 15 minutes, the cooling method is directional cooling from bottom to top to obtain ice gel; then placed in -40 ℃, 25 Pa freeze dryer freeze-drying for 30 hours, placed after drying Bake in an oven at 110°C for 30 minutes to obtain a cellulose porous material, which is stored in a ziplock bag for later use.
[0047] (2) Add 80mg of zirconium chloride powder to a 50ml sample bottle, add 0.71ml of hydrochloric acid and 4ml of N,N-dimethylformamide dropwise, sonicate for 5min to make it evenly dispersed, and then dropwise add 65mg of 2-aminoterephthalene Formic acid and 8ml N,N-dimethylformamide, ultrasonically 5min to disperse completely, transfer to a hydrothermal synthesis r...
Embodiment 3
[0050] (1) Add 0.1g of silane coupling agent KH560 to 10g of wood pulp nanocellulose suspension with a solid content of 1.0wt%, and magnetically stir for 4h at room temperature to obtain a hydrolyzate of cellulose nanowires and silane coupling agent KH560 Suspension; placed in liquid nitrogen for rapid cooling for 20 minutes, the cooling method is bottom-up directional cooling to obtain ice gel; then placed in a freeze dryer at -40°C, 25Pa, freeze-dried for 30h, and placed at 110 after drying Bake in an oven at ℃ for 30 minutes to obtain a cellulose porous material, which is stored in a ziplock bag for later use.
[0051] (2) Add 125mg of zirconium chloride powder to a 50ml sample bottle, add 1ml of hydrochloric acid and 5ml of N,N-dimethylformamide dropwise, sonicate for 5min to make the dispersion uniform, and then dropwise add 134mg of 2-aminoterephthalic acid And 10ml of N,N-dimethylformamide, ultrasonic for 5min to disperse completely, transfer to a hydrothermal synthesis re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com