Long-acting sustained-release cardiovascular coating material integrating double functions of resisting calcification and hyperplasia and preparation method of long-acting sustained-release cardiovascular coating material
A coating material and cardiovascular technology, applied in the field of medical materials, can solve the problems of easy drug release and low drug loading, achieve high research and application value, and enhance the effect of mechanical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
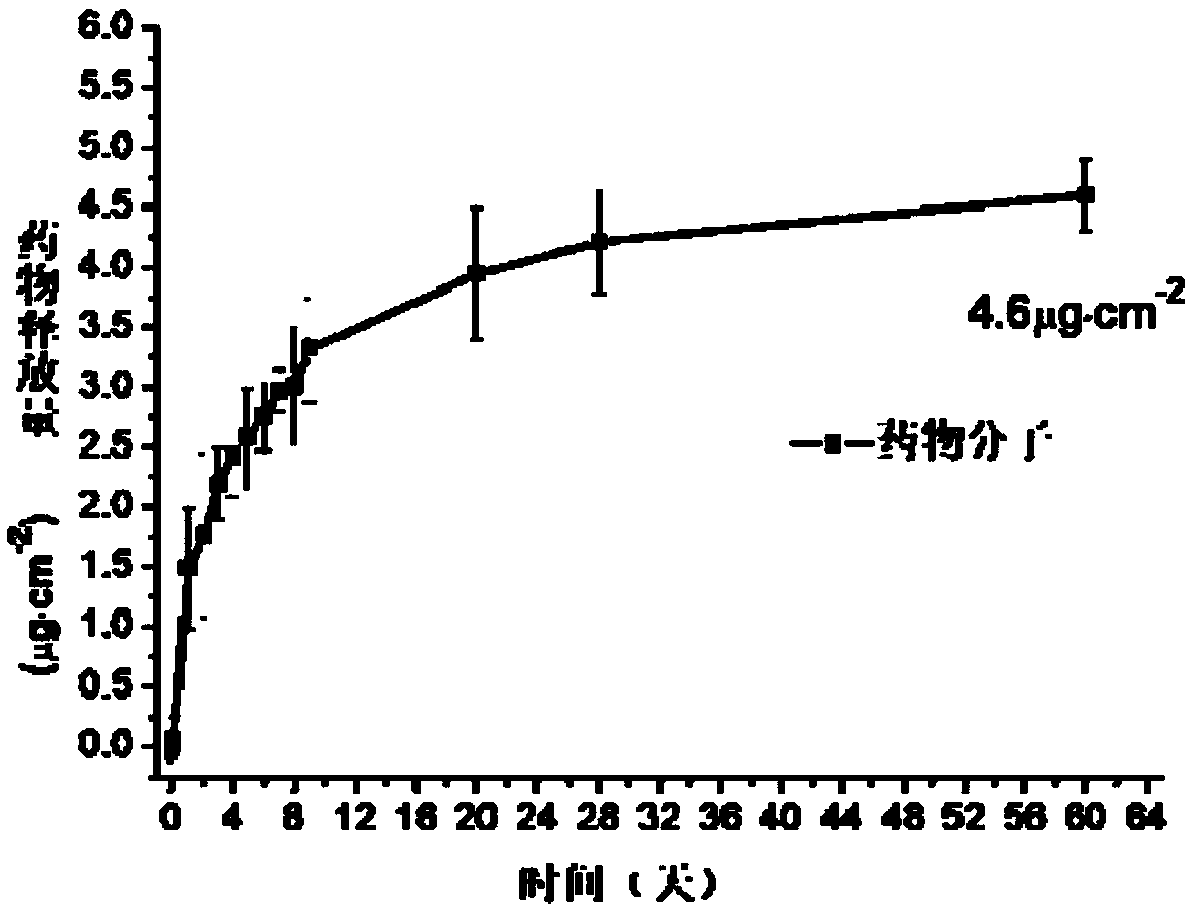
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0028] Aiming at the problems that cardiovascular stent materials are easy to cause restenosis at the implantation site after being implanted into the human body, and the amount of anti-calcification and anti-proliferation drugs of organic coating materials in the prior art is too low and the drug release rate is too fast, the present invention proposes a A new coating material preparation method, which introduces calcification drugs and anti-proliferation drugs into the coating material through layer-by-layer self-assembly technology, and binds the drug-loaded micelles on the membrane through various intermolecular interactions. To achieve the purpose of slow drug release. The preparation method mainly comprises the following steps:
[0029] 1), preparation of polycation electrolyte solution
[0030] The polyanolyte among the present invention preferably adopts the polyamino compound of catechol group modification, and this is because catechol compounds are easily oxidized a...
Embodiment 1
[0044] A method for preparing a long-acting sustained-release cardiovascular coating material with dual functions of anti-calcification and anti-proliferation, which is realized based on mussel bionics and phenylboronic acid modification, comprising the following steps:
[0045] A. Use 3,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde to modify dimethyl ammonium chloride to obtain positively charged biomacromolecules modified by catechol derivatives. During modification, dimethyl ammonium chloride and 3,4-dimethyl ammonium chloride The molar ratio of hydroxybenzaldehyde is 2:1; after the modification is completed, the modification is configured into a solution with a concentration of 10 mg / ml and pH=6; the solution is used as a polycation electrolyte component for layer-by-layer self-assembly;
[0046] B, preparing negatively charged heparin into a solution with a concentration of 10 mg / ml and pH=6, which is used as a layer-by-layer self-assembled polyanion electrolyte component;
[0047] C. Weigh 2 ...
Embodiment 2
[0053] A preparation method for a long-acting sustained-release cardiovascular coating material with dual functions of anti-calcification and anti-proliferation, which is realized based on mussel bionics and phenylboronic acid modification, including the following steps:
[0054] A. Utilize 3,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde to modify polydiallyl polyhexyl violet nitrile to obtain positively charged biological macromolecules modified by catechol derivatives. During modification, polydiallyl polyhexyl violet nitrile The molar ratio to 3,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde is 1:1; after the modification is completed, the modification is configured into a solution with a concentration of 2mg / ml and pH=6; this solution is used as a polycation electrolyte component for layer-by-layer self-assembly ;
[0055] B, preparing negatively charged heparin into a solution with a concentration of 2 mg / ml and pH=6, which is used as a layer-by-layer self-assembled polyanion electrolyte component;
[0056] C. Weig...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com