Method for preparing adipose-derived ECM (extracellular matrix) through built-in ultrasonic waves
A technology of adipose-derived cells and extracellular matrix, applied in the field of preparation of adipose-derived extracellular matrix by built-in ultrasound, can solve the problems of cytokine loss, cumbersome operation, high cost, etc., achieve low preparation cost, increase survival rate, and broad application prospects Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
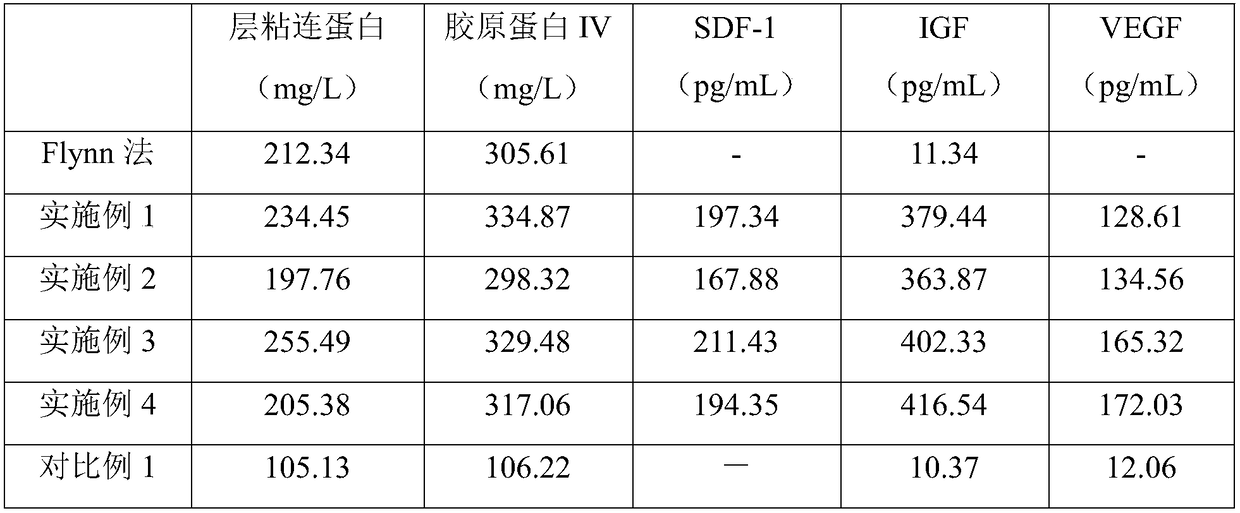
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] A method for preparing fat-derived extracellular matrix using built-in ultrasound, the specific steps are as follows:
[0034] (1) Centrifuge the obtained adipose tissue at 5000rpm for 2min, and discard the bottom blood after centrifugation (when pushing out the lower layer of swelling fluid, push the swelling fluid as clean as possible without losing fat, otherwise the final product will have Blood color), then pass through a 70-mesh screen (after filtering, the adipose tissue remaining in the filter should be sucked under negative pressure to avoid losing too much fat), and the filtrate is transferred to a sterile centrifuge tube (when transferring the middle and upper layer mixture, as much as possible Do not transfer the upper layer of grease into the centrifuge tube);
[0035] (2) Put the fat tissue into the ultrasonic cell disruptor, adjust the power to 45W and time for 25s for ultrasonic disruption; then continue ultrasonic disruption, the ultrasonic disruption condit...
Embodiment 2
[0039] A method for preparing fat-derived extracellular matrix using built-in ultrasound, the specific steps are as follows:
[0040] (1) Centrifuge the obtained adipose tissue at 4000 rpm for 5 minutes, and discard the bottom blood after centrifugation (when pushing out the lower swelling fluid, push the swelling fluid as clean as possible without losing fat, otherwise the final product will have Blood color), then pass through a 60-mesh screen (after filtering, the adipose tissue remaining in the filter should be sucked under negative pressure to avoid losing too much fat), and the filtrate is transferred to a sterile centrifuge tube (when transferring the middle and upper layer mixture, as much as possible Do not transfer the upper layer of grease into the centrifuge tube);
[0041] (2) Put the fat tissue into the ultrasonic cell disruptor, adjust the power to 50W, and time for 15s for ultrasonic disruption; then continue ultrasonic disruption, the ultrasonic disruption conditio...
Embodiment 3
[0045] A method for preparing fat-derived extracellular matrix using built-in ultrasound, the specific steps are as follows:
[0046] (1) Centrifuge the obtained adipose tissue at 4000 rpm for 5 minutes, and discard the bottom blood after centrifugation (when pushing out the lower swelling fluid, push the swelling fluid as clean as possible without losing fat, otherwise the final product will have Blood color), then pass through an 80-mesh screen (after filtering, the adipose tissue remaining in the filter should be sucked under negative pressure to avoid losing too much fat), and the filtrate is transferred to a sterile centrifuge tube (when transferring the middle and upper mixture, as much as possible Do not transfer the upper layer of grease into the centrifuge tube);
[0047] (2) Put the fat tissue into the ultrasonic cell disruptor, adjust the power to 65W, and time for 10s to perform ultrasonic disruption; then continue ultrasonic disruption, the ultrasonic disruption condit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com