Method for capturing and identifying fetal nucleated red blood cells in a microfluidic chip
A microfluidic chip and nucleated red blood cell technology, which is applied in the field of capturing and identifying fetal nucleated red blood cells, can solve the problems of inability to distinguish the fetal origin of nucleated red blood cells, and achieve good application prospects, low price, and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
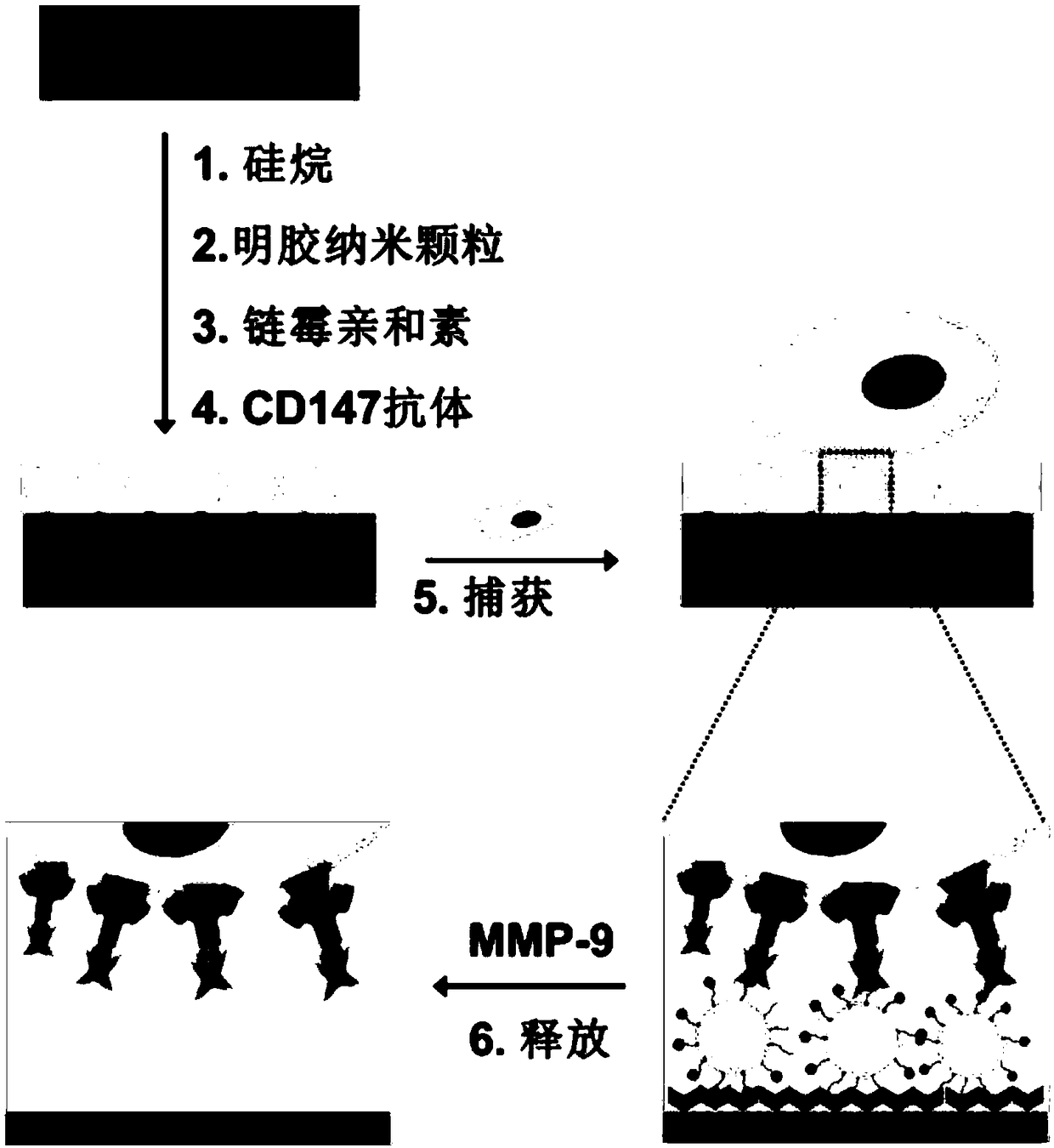
[0038] like figure 1 As shown, the specific steps of the method for capturing and identifying fetal nucleated red blood cells in the microfluidic chip provided in this embodiment are:
[0039] (1) Preparation of gelatin nanoparticles:
[0040] Weigh 0.625g B-type gelatin and dissolve it in 12.5mL deionized water, heat to dissolve at 50°C. Then 12.5 mL of acetone was added at a rate of 6 mL / h at 300 rpm, and after standing for 1 min, the supernatant was discarded. Add 12.5 mL of deionized water to the precipitate, and heat again at 50°C to dissolve. Use 2mol / L NaOH solution to adjust the pH of the reactant to 10, then slowly add about 45mL of acetone to the gelatin solution, and finally add glutaraldehyde (1.5%) solution, in situ cross-linking for 2 hours, and stop cross-linking by excess glycine couplet. The gelatin nanoparticles were recovered by centrifuging the above reaction solution at 10000 rpm for 10 min. Freeze-drying is carried out by a freeze dryer to remove res...
Embodiment 2
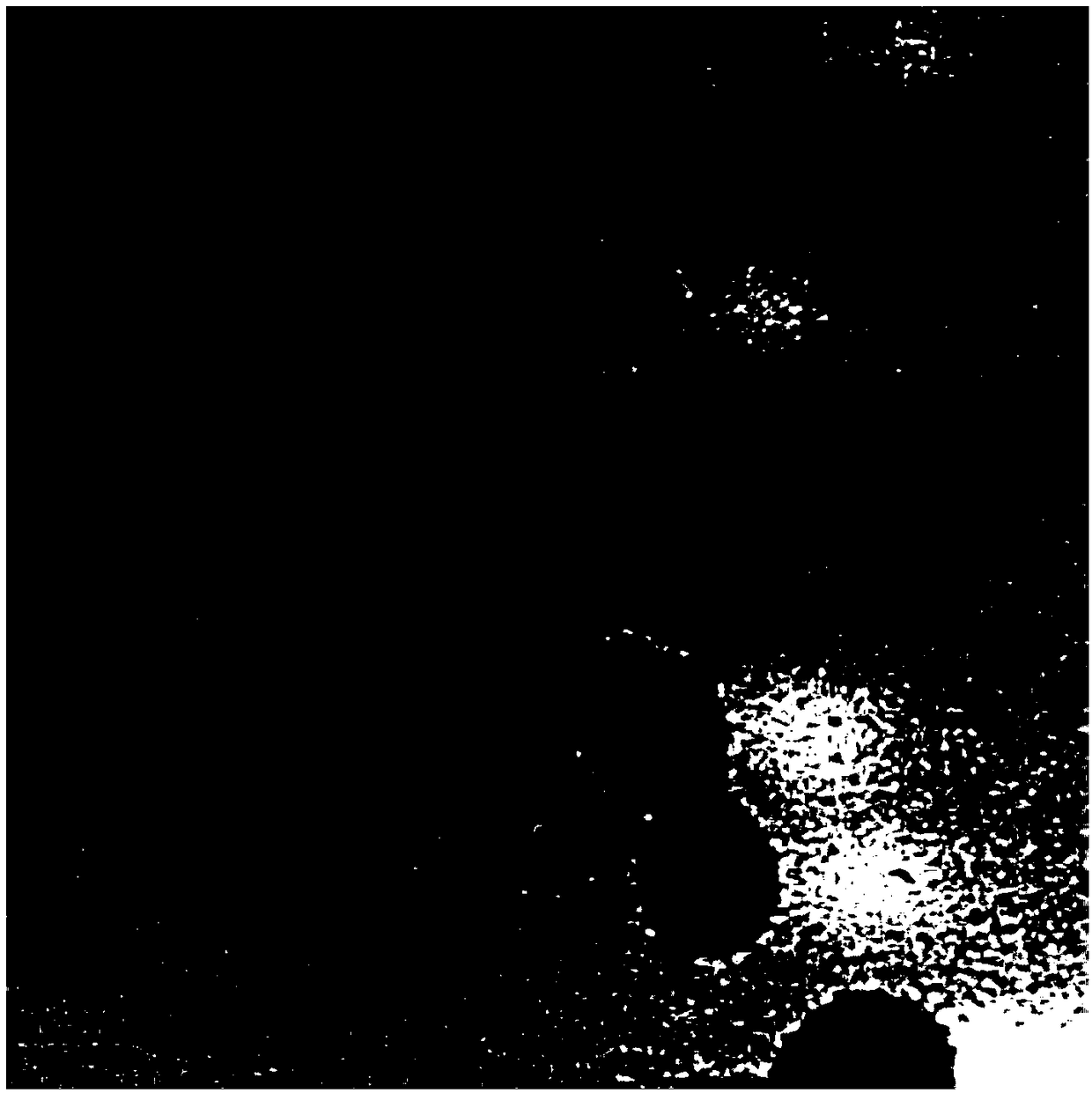
[0050] Dilute 2mL of maternal peripheral blood with PBS at a ratio of 1:1, then place it on a 4mL lymphocyte separation medium, centrifuge at 400g for 30min, obtain a mononuclear layer containing fetal nucleated red blood cells, and make 1mL of cell suspension. Then pass through the antibody-modified microfluidic chip 10, under the action of the fluid, the background interfering cells in the suspension are recovered from the outlet port along with the fluid, while the fetal nucleated red blood cells remain in the microfluidic chip through the specific recognition of the antigen antibody 10 internal, to achieve capture. like Figure 7 As shown, after the capture is completed, the fetal nucleated red blood cells are captured on the inner wall of the microfluidic chip 10 . like Figure 8 As shown, the cells spread out on the surface of the nano-coating and firmly adsorbed on the surface of the nano-coating.
Embodiment 3
[0052] To explore the effect of the concentration of gelatin nanoparticles on the efficiency of target cell sorting, the specific operation is: use different concentrations (1.0mg / mL, 1.5mg / mL, 2.0mg / mL, 2.5mg / mL) of gelatin nanoparticles in the microfluidic A nano-coating is formed inside the control chip 10 and modified with antibodies. A 1 mL sample of nucleated erythroid TF-1 cells at a concentration of 200 / mL was passed into the microfluidic chip 10 to complete capture. Observing and counting under the Olympus IX 81 microscope, the experimental results are as follows Figure 9 As shown, when the concentration of gelatin nanoparticles was 2.0 mg / mL, the capture efficiency was 81%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com