A kind of amino lyase mutant protein and its coding gene and application
An amino and gene technology, applied in amino lyase mutant protein and its coding gene and application field, can solve the problems of high raw material price, low stereoselectivity, poor stereoselectivity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0133] Example 1, Screening and Determination of Mutation Sites
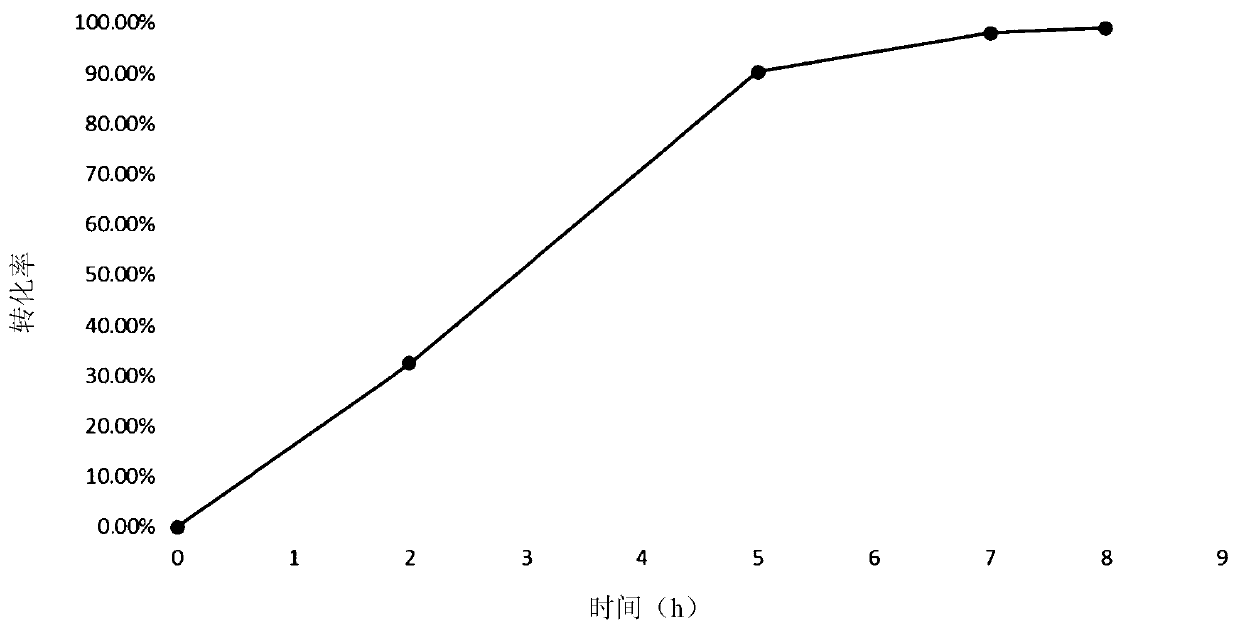
[0134] Sequence analysis, mutation and functional verification of the L-aspartate deaminase protein (aspB protein) derived from Bacillus subtilis revealed 37 amino acid sites. Four important amino acid sites were screened out. These 4 amino acid sites are mutated in different forms, and the obtained mutant proteins all have higher amino lyase activity, and can catalyze the hydrogenation reaction with trans-2-butenoic acid as the substrate at the same time, which can be used in the production of ( R) 1-propyl (2-amino) formic acid, the yield is high and meets the requirement of 100% stereoselectivity.
[0135] The aspB protein is shown in sequence 2 of the sequence listing, and the coding gene of the aspB protein (aspB gene) is shown in sequence 1 of the sequence listing.
[0136] The four amino acid sites and their mutant forms are shown in Table 1.
[0137] Table 14 amino acid sites and their mutant forms
...
Embodiment 2
[0139] Embodiment 2, the preparation of recombinant bacteria
[0140] The wild-type aspB protein is shown in sequence 2 of the sequence listing, and the coding gene (aspB gene) of the wild-type aspB protein is shown in sequence 1 of the sequence listing.
[0141] 1. Construction of wild-type recombinant expression vector
[0142] The double-stranded DNA molecule shown in Sequence 1 was inserted between the EcoR I and Not I restriction sites of the pET21a vector to obtain the recombinant expression vector pET21a-aspB (sequencing verification was correct). The DNA molecule shown in sequence 1 encodes the protein shown in sequence 2.
[0143] 2. Construction of mutant recombinant expression vector
[0144] 1. Insert the double-stranded DNA molecule 1 between the EcoR I and Not I restriction sites of the pET21a vector to obtain the recombinant expression vector pET21a-1 (sequence verification is correct). Double-stranded DNA molecule 1 is obtained by point-mutating the wild-typ...
Embodiment 3
[0181] Embodiment 3, the enzyme activity assay of aminoacidase mutant protein
[0182] Adopt the wild-type recombinant bacterium that embodiment 2 obtains and mutant recombinant bacterium 1-34 to carry out following experiment respectively:
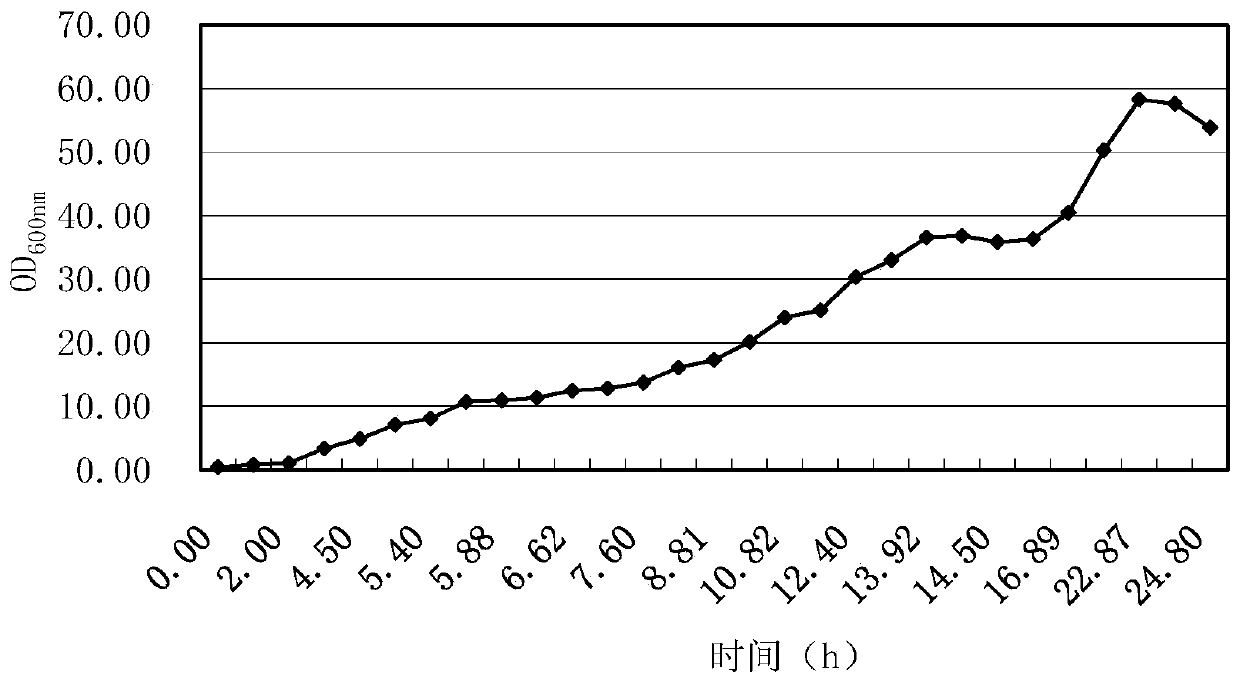
[0183] 1. Inoculate the bacteria to be tested into 5ml LB liquid medium (amphicillin resistance: 100μg / ml), shake at 37°C and 200rpm until the OD of the bacteria solution 600nm =1-2, add 30ppm IPTG, continue to culture at 30°C and 200rpm shaking until 24h.
[0184] 2. After completing step 1, collect the bacterial cells by centrifugation at 12000 rpm.
[0185] 3. Use 50mM Tris (pH 7.5), 2mM MgCl to the bacteria collected in step 2 2 After resuspending 1ml, ultrasonically (power 25W) disrupted for 30s to obtain the cell disrupted liquid.
[0186] 4. Heat the broken cell solution obtained in step 3 at 60°C for 30 minutes, then centrifuge at 12,000 rpm, and collect the supernatant, which is the protein solution.
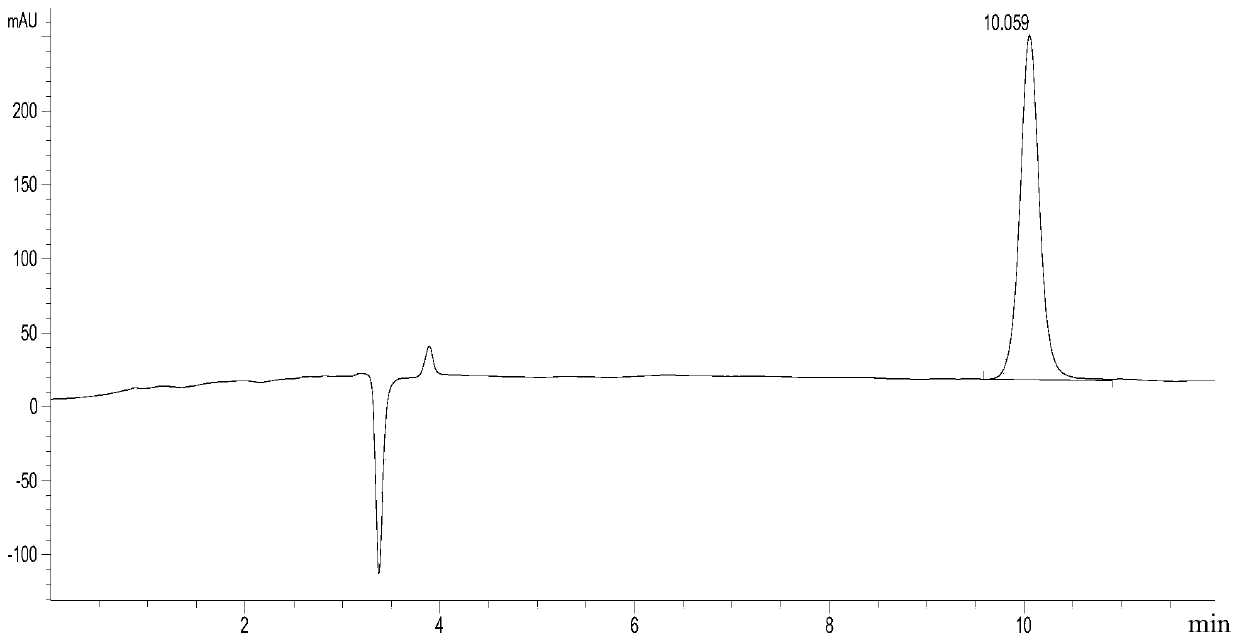
[0187] The protein sol...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com