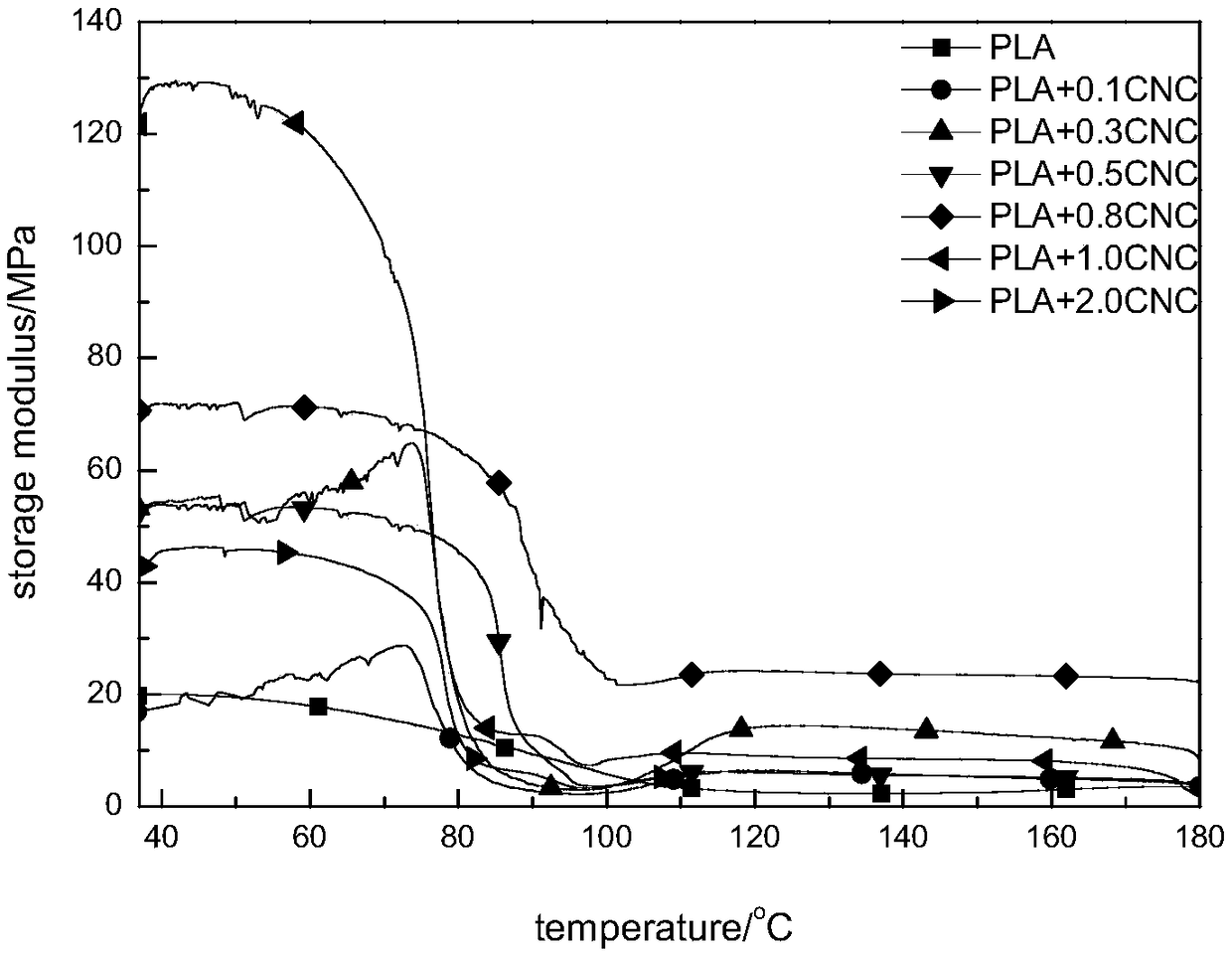
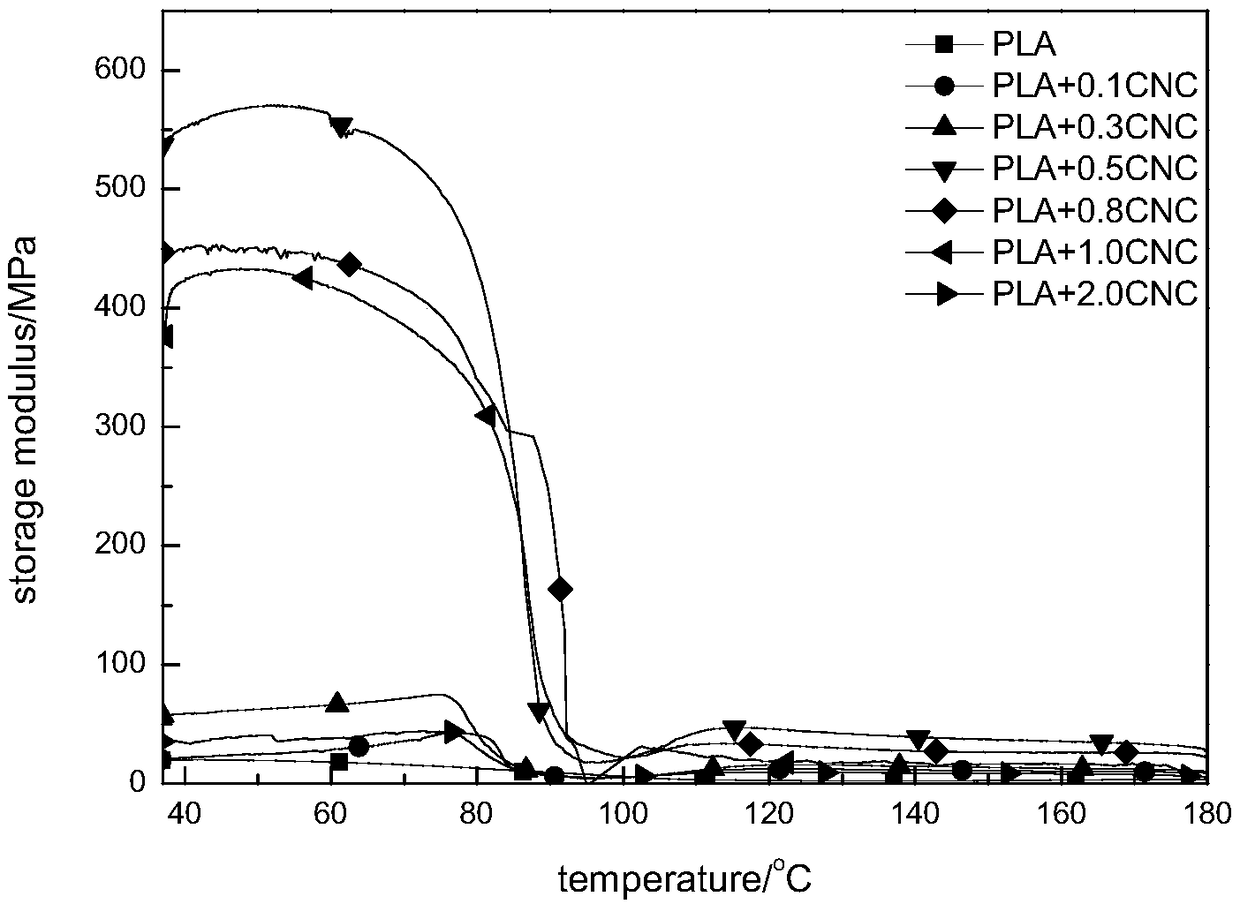
High-performance bio-based composite film and preparation method thereof
A composite film and bio-based technology, applied in the direction of conjugated synthetic polymer artificial filament, cellulose/protein conjugated artificial filament, non-woven fabric, etc., can solve the problem of non-renewable, biocompatibility and Degradability, medical materials are not easy to pass through cells, hinder drug release and absorption, etc., to achieve the effects of avoiding infection, adhesion and swelling, good blood compatibility, and increased storage modulus
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] (1) Add 0.025g of cellulose nanocrystals to 15ml of dichloromethane, place the solution on a stirring table and stir for 6h until a uniform cellulose nanocrystal mixture is obtained, and the cellulose nanocrystals in the cellulose nanocrystal mixture The mass fraction is 0.13%. (2) Add 2.04g polylactic acid to the cellulose nanocrystal mixture, and stir at room temperature for 12 hours to obtain a uniformly dispersed polylactic acid / cellulose nanocrystal mixture, and the fibers in the polylactic acid / cellulose nanocrystal mixture The mass fraction of prime nanocrystals is 0.12%, and the mass fraction of polylactic acid is 9.7%. (3) Add 5ml N-N dimethylformamide in polylactic acid / cellulose nanocrystal mixed solution, after stirring 2h, obtain spinning solution, the massfraction of cellulose nanocrystal in the spinning solution is 0.1%, polylactic acid The mass fraction is 8.0%. The film was spun under the technological conditions of spinning voltage 15kv, spinning dis...
Embodiment 2
[0032] (1) Add 0.076g of cellulose nanocrystals to 15ml of dichloromethane, place the solution on a stirring table and stir for 6h until a uniform cellulose nanocrystal mixture is obtained, and the cellulose nanocrystals in the cellulose nanocrystal mixture The mass fraction is 0.40%. (2) Add 2.29g polylactic acid to the cellulose nanocrystal mixed solution, and stir at room temperature for 24 hours to obtain a uniformly dispersed polylactic acid / cellulose nanocrystalline mixed solution, and the fibers in the polylactic acid / cellulose nanocrystalline mixed solution The mass fraction of prime nanocrystals is 0.36%, and the mass fraction of polylactic acid is 10.8%. (3) Add 5ml N-N dimethylformamide in polylactic acid / cellulose nanocrystal mixed solution, after stirring 3h, obtain spinning solution, the massfraction of cellulose nanocrystal in the spinning solution is 0.3%, polylactic acid The mass fraction is 9.0%. The film was spun under the conditions of a spinning voltage ...
Embodiment 3
[0035] (1) Add 0.126g of cellulose nanocrystals to 15ml of dichloromethane, place the solution on a stirring table and stir for 6h until a uniform cellulose nanocrystal mixture is obtained, and the cellulose nanocrystals in the cellulose nanocrystal mixture The mass fraction is 0.66%. (2) Add 2.29g polylactic acid to the cellulose nanocrystal mixed solution, and stir at room temperature for 24 hours to obtain a uniformly dispersed polylactic acid / cellulose nanocrystalline mixed solution, and the fibers in the polylactic acid / cellulose nanocrystalline mixed solution The mass fraction of prime nanocrystals is 0.59%, and the mass fraction of polylactic acid is 10.8%. (3) Add 5ml N-N dimethylformamide in polylactic acid / cellulose nanocrystal mixed solution, after stirring 3h, obtain spinning solution, the massfraction of cellulose nanocrystal in the spinning solution is 0.5%, polylactic acid The mass fraction is 9.0%. The spinning conditions are the same as in Example 2, and the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| storage modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| storage modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| storage modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com