Construction and application of engineering strains that co-utilize glucose and xylose to produce xylitol
A glucose and xylitol technology, applied to the biological field, can solve the problem of not fully utilizing the glucose and xylose co-utilization ability of heat-resistant yeast
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0062] Example 1. Preparation of strains:
[0063] 1. Construction of a heat-resistant yeast strain produced by glucose and xylose to produce xylitol:
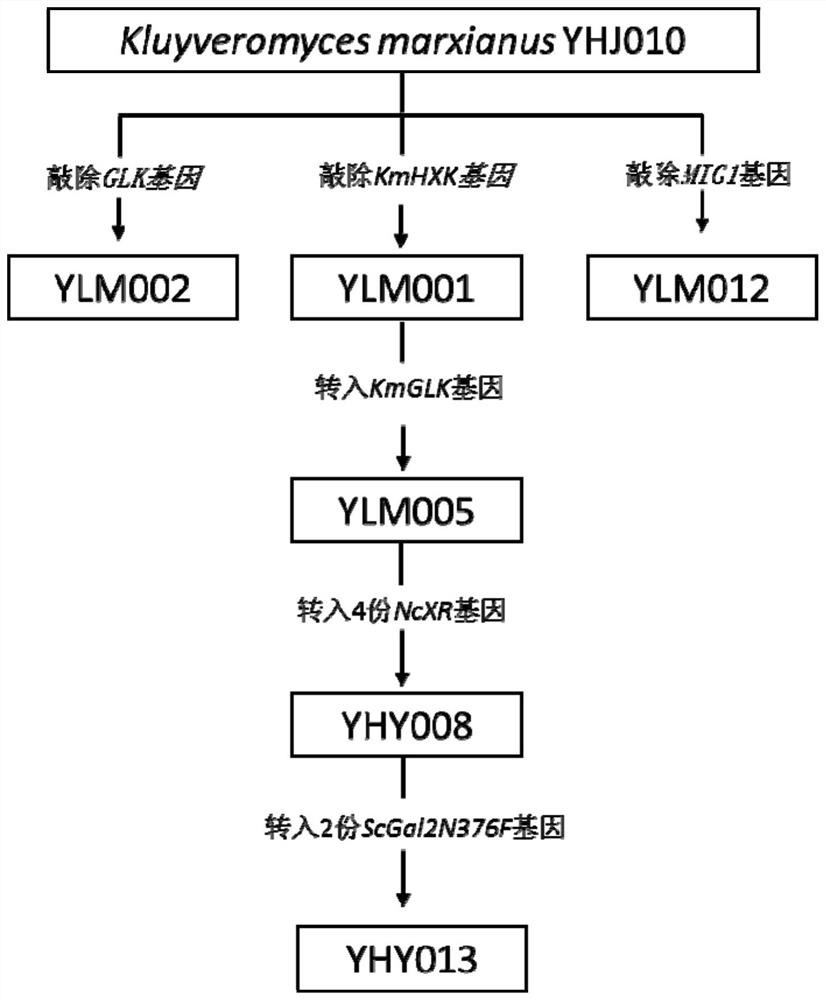
[0064] Reconstruction of genetically modified strains is performed by heat-resistant yeast YHJ010 (see HONG ET Al., 2007).
[0065] 1) Yeast Chemical Transformation Steps:
[0066] 1. Waiting to be transformed into the YPD board, cultured overnight at 37 ° C.
[0067] 2. Pick a monoclonal from the YPD plates of overnight culture, inoculated into 5 ml of fresh YPD liquid medium, 37 ° C, 250 rpm, and cultured overnight.
[0068] 3. Take 500 μl of culture to transfer to a 5 ml fresh YPD liquid medium test tube, 37 ° C, 250 rpm, and shaker for 5 h.
[0069] 4. Take out the culture, centrifuge at normal temperature, 3 minutes, discard the supernatant, and retain the bacteria.
[0070] 5. Formulated 500 μL of converted buffer: 400 μL 50% PEG4000; 50 μl of 2M acetate; 50 μl of 1 M DTT (dissolved in 10 mM sodium acetate, pH 5.2).
[0071]...
Embodiment 2
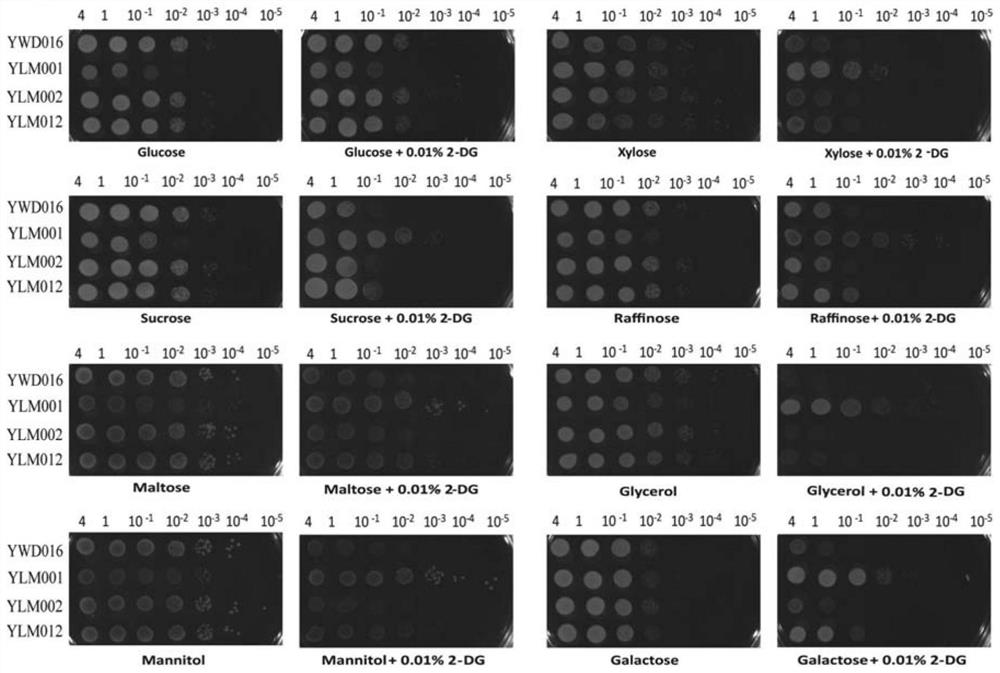
[0160] Example 2. Water-resistant yeast strain glucose inhibitory release
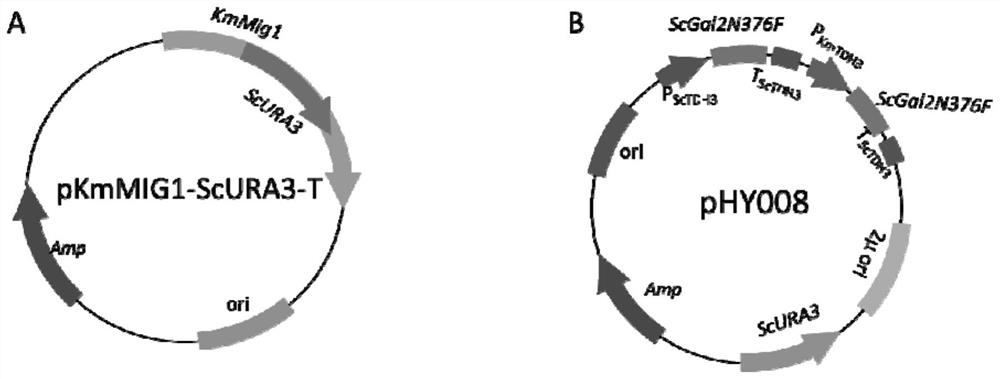
[0161] This example is used to verify that the engineered strain in the present invention is compared to whether the glucose inhibitory effect is released in the wild-type strain. The results show that the glucose inhibitory effect of YLM001 has been greatly released, which can grow in a variety of non-glucose carbon sources of 2-deoxyl glucose (2-DG), and KMGLK knockout is not in the glucose inhibitory effect. Any effect is produced; KmmiG1 is only a slight growth advantage compared to the control YWD016 compared to the control YWD016 compared to the control YWD016 compared to the control YWD016 compared to the control YWD016, which contains 2-DG. The growth state of the glycerol culture is basically consistent with the control, indicating that Kmmig1 knockout inhibition in glucose is not released inhibition of xylose and glycerol utilization; at the same time verifying the YLM005 obtained in YLM001, the ...
Embodiment 3
[0167] Example 3. Fermentation conditions of transforming strains under conditions of 42 ° C
[0168] This example is used in comparison of different engineered strains for glucose and xylose sharing effect. The results indicate that the strain YHY013 of all engineering genes is used to use glucose and xylose to produce xylitol.
[0169] 1. In the YPD medium plate, the strain was recovered: control strain: yzj119, experiment strain: YLM005, YHY006, YHY008 and YHY013, 37 ° C for 1 day.
[0170] 2. Pick a monoclonal, followed by 5 ml of liquid YPD medium. 37 ° C, 250 rpm, overnight.
[0171] 3. Formulated 30 ml of fermentation medium is dispensed into 250 ml tapered flask. Formulation: 20g / L glucose, 80 g / L xylose, 10g / L yeast extract, 20 g / L bacteriology protein, sterilization.
[0172] 4. Take an appropriate amount of overnight culture to access 30 ml of xylose fermentation medium to make them initial OD 600 It was cultured in 1,42 ° C, 250 rpm.
[0173] 5. Sampling at 0H,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com