Low frequency mutation detection method, kit and device
A technology for sequencing and sequencing adapters, used in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, chemical libraries, etc., can solve problems such as unavoidable false positives, and achieve good sealing effect, improved capture efficiency, and data utilization. high effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0109] 1. Extraction of free DNA
[0110] Collect 10ml of peripheral blood with a Streck tube, centrifuge at 1500g, 4°C for 10min, transfer the supernatant to another new 15ml centrifuge tube, centrifuge again at 15000g, 4°C for 10min, aspirate the supernatant for extraction or cryopreservation. The plasma was extracted according to the QIAamp Circulating Nucleic Acid Kit (55114) extraction reagent manual, and then the free DNA was extracted and quantified by qPCR method (ALU115).
[0111] 2. Preparation of sample library
[0112] The cell-free DNA extracted from plasma was subjected to two-step enzymatic reactions according to the instructions of KAPA Hyper Prep Kits (KK8504) for library construction.
[0113] 2.1 End Repair & Add A Tail
[0114] Table 4 End Repair & Add A Tail Reaction System
[0115]
[0116]
[0117] 2.2 Joint connection
[0118] Table 5 Adapter Ligation Reaction System
[0119]
[0120] Sequencing adapters such as figure 1shown. Afterwards...
Embodiment 2
[0149] Example 2 Evaluation of Randomness of Molecular Tag Synthesis
[0150] Theoretically, the probability of occurrence of each of the four bases A, T, G, and C on each position on the molecular label should be 25%. For example, ideally, the molecular label diversity of 8 bases is 4 8 = 65336 kinds. However, when evaluating the randomness of the molecular tags synthesized by Yingweijie bases, there are significant differences in the incorporation efficiency of the four bases. The content of base A is significantly higher than that of the other three bases. Seven or eight consecutive bases in the molecular tag Base A accounts for up to 2%.
[0151] The randomness (or diversity) of molecular tags makes each original DNA fragment of the same sample carry a different molecular tag sequence to distinguish each other. If the randomness of the molecular tag sequence is poor, the probability of obtaining the same molecular tag from different original DNA fragments increases, resu...
Embodiment 3
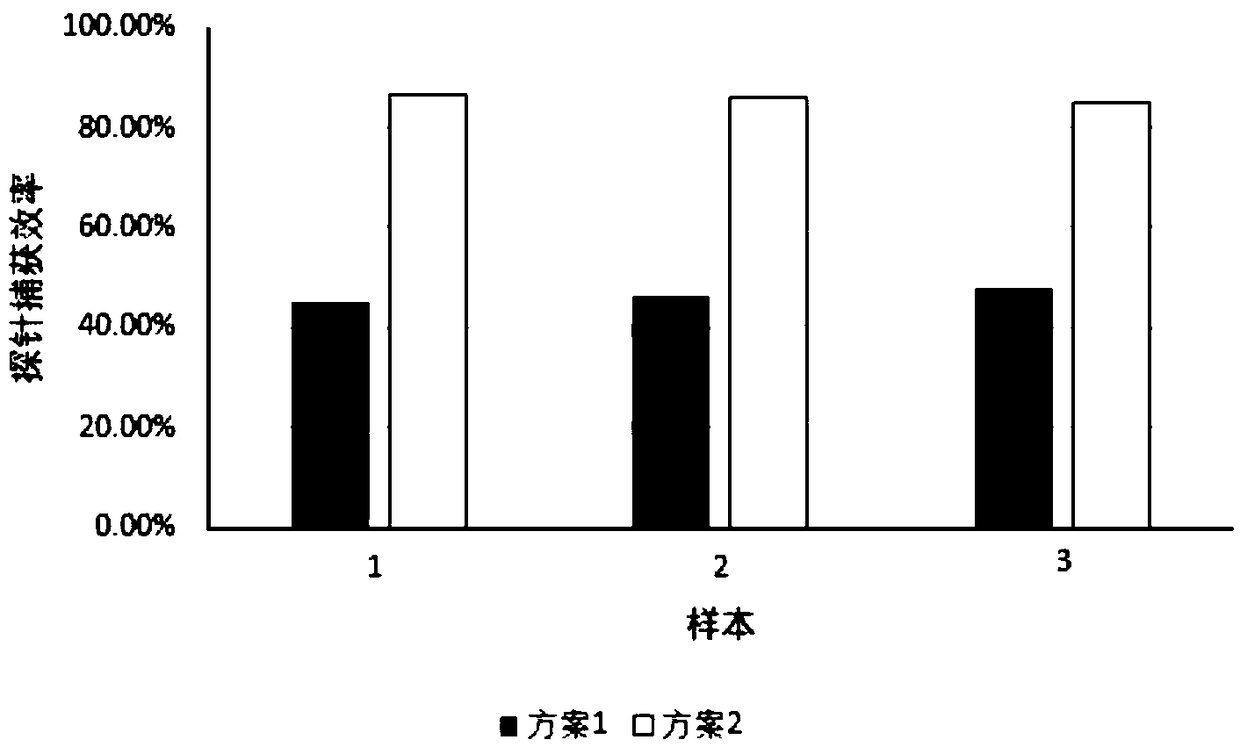
[0156] Example 3 Adapter Blocking Sequence Optimization Screening
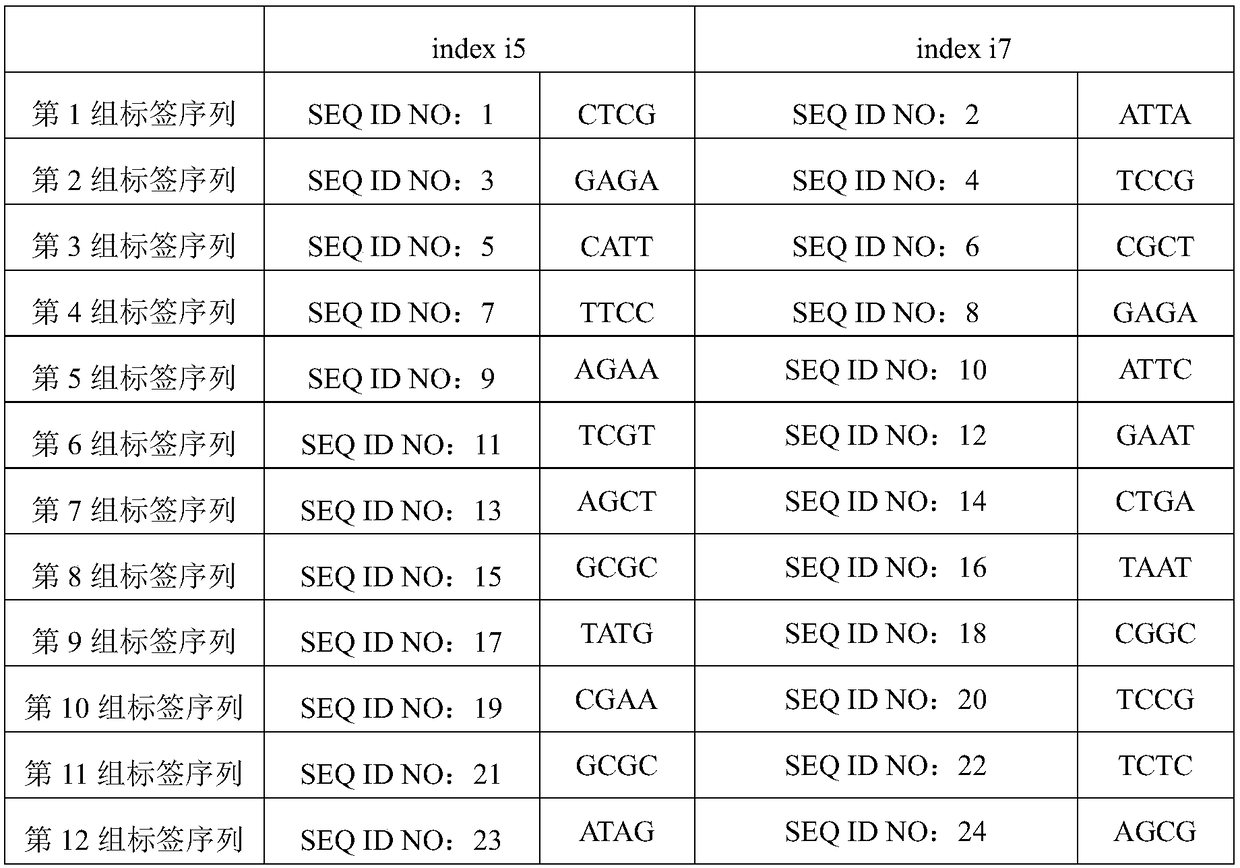
[0157] During the hybridization capture process, the addition of adapter blocking sequences can significantly improve the capture specificity and improve the data utilization rate. However, the strategy of "adding the corresponding blocking sequence according to the sample label" in the Roche capture chip is not suitable for the library in which the molecular label is inserted in the adapter sequence. Based on this, the inventor proposes two adapter sealing strategies: (1) Add the corresponding sealing sequence according to the sample label, and at the same time, the random base N is blocked by the merged base I, as shown in Table 3, in which each group of adapter sealing sequence groups One-to-one correspondence with the sequencing adapter sequences in Table 2; (2) Blocking with an adapter blocking sequence that does not distinguish between sample tags, specifically the nucleotide sequences shown in SEQ ID NO...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com