Detection method for sensitively and rapidly detecting staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin B
A technology for the detection of staphylococcus enterotoxin B, which is applied in the field of sensitive and rapid detection of Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin B, and can solve the problems of limiting the application of molecular beacons
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Example 1: Design of hairpin probe and determination of denatured conditions
[0029] In order to ensure the rationality of the sequence design, the hairpin probe was designed using NUPACK software. In the Analysis work interface, the type of nucleic acid was adjusted to DNA, and the working temperature was set to 37°C. At the same time, in the Advanced options option box, set Na + 0.4M, Mg 2+is 5mM. First, use NUPACK software to verify whether the designed H1 and H2 sequences can normally form the hairpin structure. Secondly, set Number of strand species to 2, Maxium complex size to 4, perform hybridization operation on H1 and H2 at equal concentrations, and verify whether H1 and H2 hybridize without priming strand H0. Finally, set the Number ofstrand species to 3, the Maxium complex size to 5, and other parameters unchanged, import the sequences of H0 or SEBaptamer into the software respectively, and introduce the sequences of H1 and H2 as shown in Table 1 and Table...
Embodiment 2
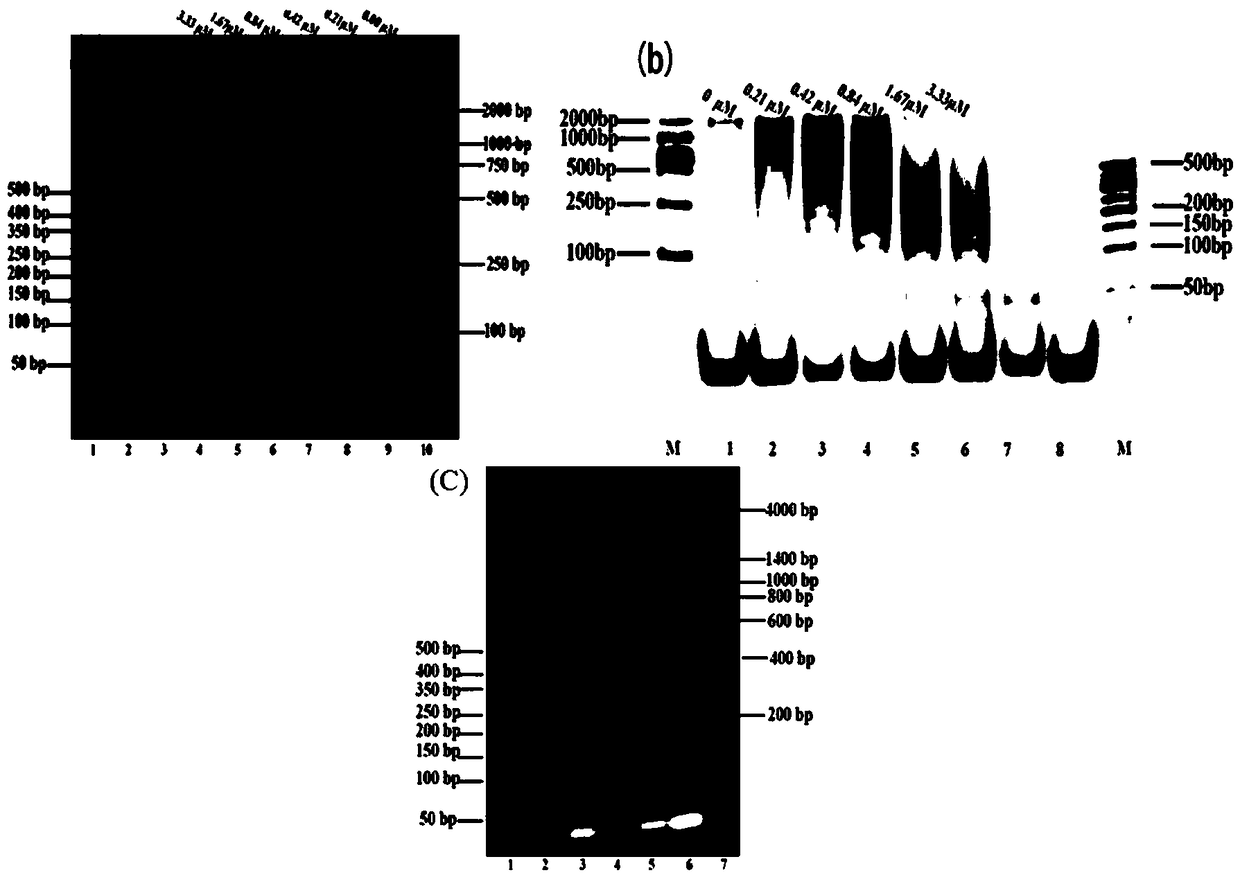
[0030] Example 2: Gel electrophoresis characterization confirms the feasibility of the SEB system detected by competitive fluorescent hybridization chain reaction
[0031] (1) Pretreatment of hairpin DNA H1 and H2 and SEB nucleic acid aptamers: Before the reaction, H1 and H2 with a concentration of 5 μM were heated and denatured at 95°C for 5 minutes, and then slowly cooled and kept at 4°C for 1 hour, 1 μM The SEB nucleic acid aptamer was heated and denatured at 95°C for 5 minutes, and then rapidly cooled in an ice-water bath.
[0032] (2) Gel electrophoresis characterization verification HCR amplification: in Tris-HCl buffer (20mM, 400mM NaCl, 5mMMgCl 2 , pH 7.2) were added 10 μL of H1 (5 μM), 10 μL of H2 (5 μM), 10 μL of priming chain (0, 0.63, 1.25, 2.5, 5, 10 μM), mixed the reaction solution and reacted in a metal bath at 37 ° C for 60 min .
[0033] (3) Gel electrophoresis characterization verification Competitive fluorescence hybridization chain reaction detection SEB:...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Embodiment 3: Measuring HCR dynamics process by fluorescence method
[0043] (1) Before the reaction, H1 and H2 at a concentration of 5 μM were heated and denatured at 95° C. for 5 minutes, and then cooled slowly and kept at 4° C. for 1 hour. See Table 1 for the sequences used.
[0044] (2) To prepare a reaction system, take 1136 μL hybridization buffer, add 80 μL H1 (5 μM) and 80 μL H2 (5 μM) and mix well to prepare a mixed reaction system.
[0045] (3) Take 20 μL of priming strand H0 with a concentration of 10 μM, and dilute to 5 μM, 2.5 μM, 1.25 μM, 0.625 μM, and 0.3125 μM respectively, each concentration being at least 10 μL.
[0046] (4) Put the reaction system in a constant temperature water bath at 37° C., and react in the dark for 2 hours.
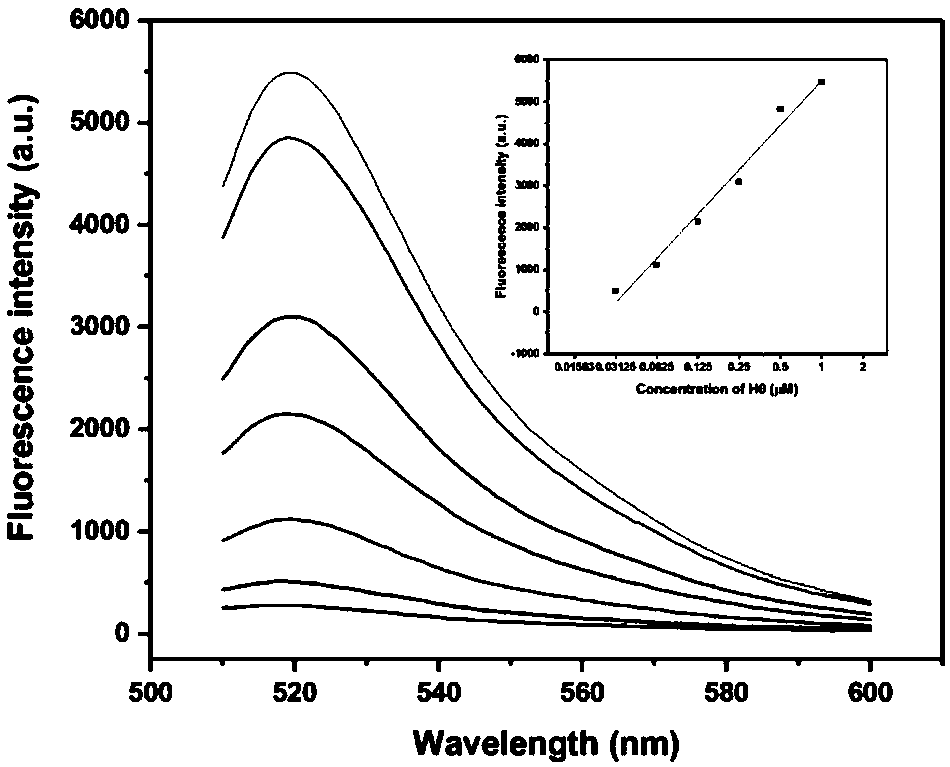
[0047] Since H1 is designed in the form of a molecular beacon, when the hairpin structure is opened, the fluorescence recovers. At this time, in order to study whether there is a linear or nonlinear dynamic law of the corre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com