A Monolithically Integrated Tunnel Junction Laser for Microwave Oscillating Source
A microwave oscillation source and monolithic integration technology, which is applied in lasers, laser components, semiconductor lasers, etc., can solve the problems of low modulation rate of microwave oscillation source, low modulation rate, and high power loss, so as to reduce phase noise and realize modulation , The effect of reducing power loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Embodiment 1 is a monolithically integrated tunnel junction laser for a microwave oscillation source with a lasing wavelength around 1.55 μm.
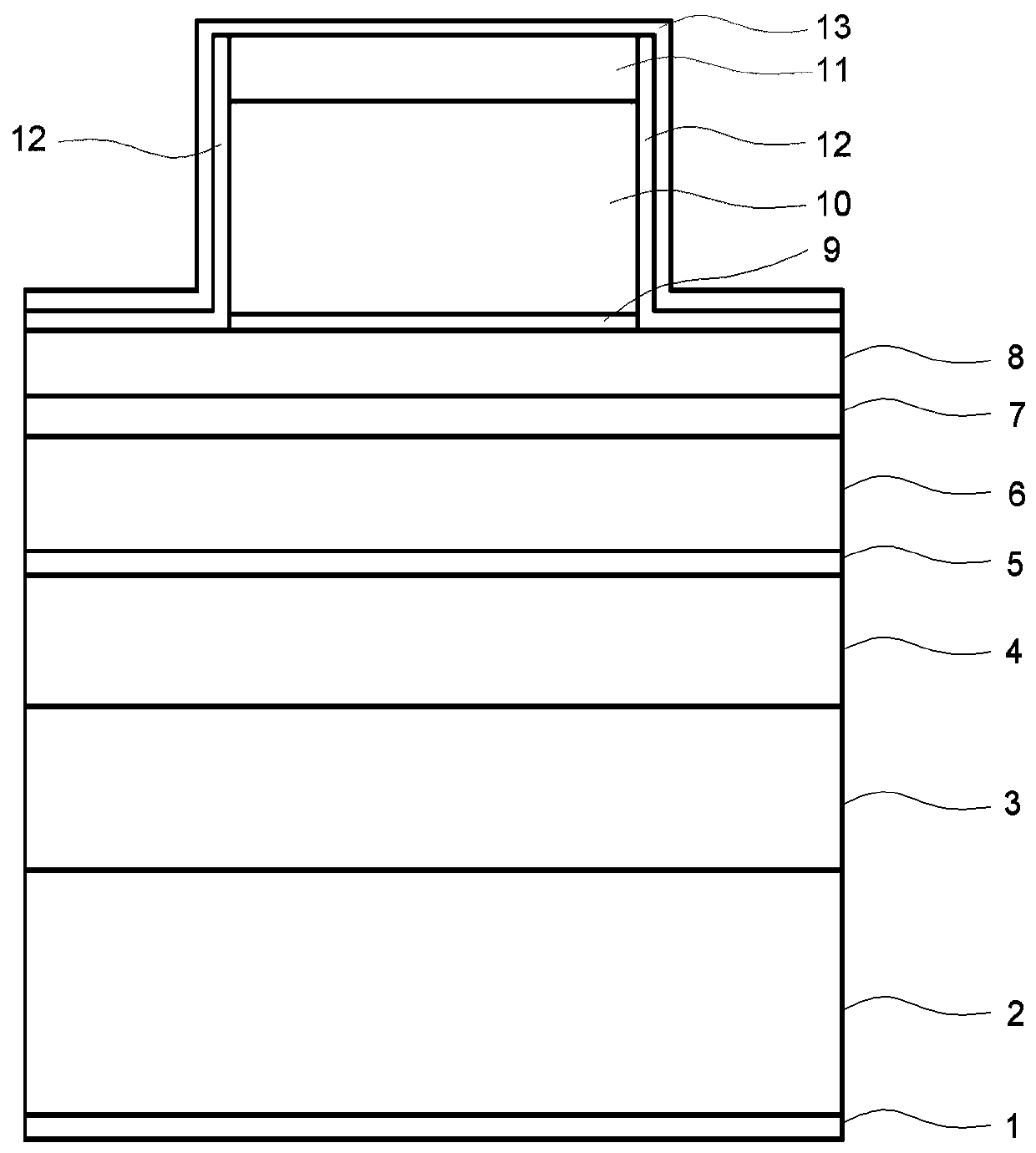
[0042] like figure 1 As shown, the monolithic integrated tunnel junction laser for microwave oscillation source in Example 1 is, from bottom to top, an N electrode 1, an N-type InP substrate 2, an N-type InP buffer layer 3, a lower confinement layer 4, a quantum Well active region 5 , upper confinement layer 6 , grating layer 7 , N-type InP layer 8 , tunnel junction 9 , P-type InP capping layer 10 , P-type contact layer 11 , insulating isolation layer 12 and P electrode 13 .
[0043] N electrode 1, N-type InP substrate 2, N-type InP buffer layer 3, lower confinement layer 4, quantum well active region 5, upper confinement layer 6, grating layer 7, N-type InP layer 8 have the same width; On the type InP layer 8 is a ridge waveguide structure formed by a tunnel junction 9, a P type InP cap layer 10 and a P type contact layer 11. ...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Embodiment 2 is a monolithically integrated tunnel junction laser for a microwave oscillation source with a lasing wavelength around 1.31 μm.
[0057] like figure 1 As shown, the monolithic integrated tunnel junction laser used for the microwave oscillation source in Example 2 is, from bottom to top, an N electrode 1, an N-type InP substrate 2, an N-type InP buffer layer 3, a lower confinement layer 4, a quantum Well active region 5 , upper confinement layer 6 , grating layer 7 , N-type InP layer 8 , tunnel junction 9 , P-type InP capping layer 10 , P-type contact layer 11 , insulating isolation layer 12 and P electrode 13 .
[0058] N electrode 1, N-type InP substrate 2, N-type InP buffer layer 3, lower confinement layer 4, quantum well active region 5, upper confinement layer 6, grating layer 7, N-type InP layer 8 have the same width; On the type InP layer 8 is a ridge waveguide structure formed by a tunnel junction 9, a P type InP cap layer 10 and a P type contact l...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com